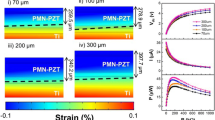
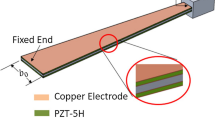
Abstract
Piezoelectric energy harvesting is widely used to scavenge vibration energy in the environment. For some vibration sources with fixed frequency, cantilevered harvester can generate the energy effectively, so the optimization theory for cantilevered harvester in such an application is needed. In this article, we present the theoretical and experimental studies of the cantilevered piezoelectric energy harvester with a fixed resonance frequency. An analytical model based on energy method is used to estimate the open-circuit voltage and generated energy. Considering that the harvester may be subjected to the static force or steady-state sinusoidal vibration excitation, static and dynamic analysis is performed for device structure to achieve efficient energy. In the analysis, the effects of geometrical dimension on the energy harvesting performance are discussed comprehensively. Eventually, a prototype is designed and fabricated using (1−x)Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3−x PbTiO3 (PMN-PT) single crystal with ultrahigh piezoelectric properties and coupling factor. Performances of the cantilever with different clamped length are evaluated under sinusoidal vibration excitation, proving the good consistency between experimental results and theoretical prediction. The established analysis can provide useful guidelines for the structure design of cantilevered piezoelectric energy harvester with a fixed resonance frequency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roundy S, Wright P K, Rabaey J. A study of low level vibrations as a power source for wireless sensor nodes. Comput Commun, 2003, 26(11): 1131–1144
Priya S. Advances in energy harvesting using low profile piezoelectric transducers. J Electroceram, 2007, 19(1): 165–182
Beeby S P, Wang L R, Zhu D B, et al. A comparison of power output from linear and nonlinear kinetic energy harvesters using real vibration data. Smart Mater Struct, 2013, 22: 0750227
Kim Y, Shim J, Park K, et al. Structure vibration analysis and active noise control of a power transformer by mobility measurement. In: International Conferences, CA and CES3 2011. Jeju Island, Korea: Springer, 2011. 322–332
Anton S R, Sodano H A. A review of power harvesting using piezoelectric materials (2003–2006). Smart Mater Struct, 2007, 16(3): R1–R21
Tang L H, Yang Y W, Soh C K. Toward broadband vibration-based energy harvesting. J Intel Mat Syst Str, 2010, 21(18): 1867–1897
Zhu D B, Tudor M J, Beeby S P. Strategies for increasing the operating frequency range of vibration energy harvesters: a review. Meas Sci Technol, 2010, 21: 022001
Beeby S P, Tudor M J, White N M. Energy harvesting vibration sources for microsystems applications. Meas Sci Technol, 2006, 17(12): R175–R195
Friswell M I, Ali S F, Bilgen O, et al. Non-linear piezoelectric vibration energy harvesting from a vertical cantilever beam with tip mass. J Intel Mat Syst Str, 2012, 23(13): 1505–1521
Mak K H, McWilliam S, Popov A A, et al. Performance of a cantilever piezoelectric energy harvester impacting a bump stop. J Sound Vib, 2011, 330(25): 6184–6202
Ren B, Or S W, Zhang Y Y, et al. Piezoelectric energy harvesting using shear mode 0.71Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.29PbTiO3 single crystal cantilever. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96: 083502
Xu J W, Shao W W, Kong F R, et al. Right-angle piezoelectric cantilever with improved energy harvesting efficiency. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96: 152904
Myers R, Vickers M, Kim H, et al. Small scale windmill. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90: 054106
Williams C B, Yates R B. Analysis of a micro-electric generator for microsystems. Sensors Actuat A-Phys, 1996, 52(1–3): 8–11
Roundy S, Wright P K. A piezoelectric vibration based generator for wireless electronics. Smart Mater Struct, 2004, 13(5): 1131–1142
duToit N E, Wardle B L, Kim S G. Design considerations for MEMS-scale piezoelectric mechanical vibration energy harvesters. Integr Ferroelectr, 2005, 71: 121–160
Erturk A, Inman D J. A distributed parameter electromechanical model for cantilevered piezoelectric energy harvesters. J Vib Acoust, 2008, 130: 041002
Erturk A, Inman D J. Issues in mathematical modeling of piezoelectric energy harvesters. Smart Mater Struct, 2008, 17: 065016
Smits J G, Dalke S I, Cooney T K. The constituent equations of piezoelectric bimorphs. Sensors Actuat A-Phys, 1991, 28(1): 41–61
Wang Q M, Cross L E. Constitutive equations of symmetrical triple layer piezoelectric benders. IEEE T Ultrason Ferr, 1999, 46(6): 1343–1351
Sun C L, Qin L F, Li F, et al. Piezoelectric energy harvesting using single crystal Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3−x PbTiO3 (PMN-PT) device. J Intel Mat Syst Str, 2009, 20(5): 559–568
Erturk A, Inman D J. Mechanical considerations for modeling of vibration-based energy harvesters. Proceedings of the ASME 2007 IDETC 21st Biennial Conference on Mechanical Vibration and Noise. Las Vegas, USA: ASME Press, 2007. 769–778
Shen D N, Choe S Y, Kim D J. Analysis of piezoelectric materials for energy harvesting devices under high-g vibrations. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2007, 46(10A): 6755–6760
Wang Z L, Song J H. Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science, 2006, 312(5771): 242–246
Service R F. Shape-changing crystals get shiftier. Science, 1997, 275(5308): 1878
Hagood N W, Chung W H, Von Flotow A. Modelling of piezoelectric actuator dynamics for active structural control. J Intel Mat Syst Str, 1990, 1 (3): 327–354
Mo C, Kim S, Clark A W. Theoretical analysis of energy harvesting performance for unimorph piezoelectric benders with interdigitated electrodes. Smart Mater Struct, 2009, 18: 0550175
Song H J, Choi Y, Wereley N M, et al. Energy harvesting devices using macro-fiber composite materials. J Intel Mat Syst Str, 2010, 21(6): 647–658
Rao S S. Mechenical Vibrations. Beijing: Pearson Education Printice Hall, 2010. 475
Luo H S, Xu G S, Wang P C, et al. Growth and characterization of relaxor ferroelectric PMNT single crystals. Ferroelectrics, 1999, 231(1): 97–102
Wang F F, Luo L H, Zhou D, et al. Complete set of elastic, dielectric, and piezoelectric constants of orthorhombic 0.71Pb (Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-0.29PbTiO3 single crystal. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90: 212903
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Z., Xu, C., Ren, B. et al. Optimization of cantilevered piezoelectric energy harvester with a fixed resonance frequency. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 57, 1093–1100 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5556-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5556-7