Abstract
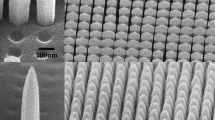
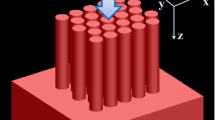
Based on the structure and dimensions of a vertical ZnO nanorod array (V-ZNA) sample, an ideal 2-D photonic crystal model was established. The optical properties of the V-ZNAs were analyzed with finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method, and the influences of the geometry parameters, including the circumcircle diameters of the top and bottom surfaces (D t and D b) and the height (H) of the nanorods, and the pitch between each column (L), were discussed. High transmittance and low reflectance in the waveband of 400–800 nm were proved, and the highest transmittance can be obtained with D t<50 nm, H=200 nm, and D b/L=0.85, which was verified by Effective Index Method (EIM). The result indicates that V-ZNAs can be used as excellent light coupling element and antireflection material for solar energy applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Willander M, Nur O, Zhao Q X, et al. Zinc oxide nanorod based photonic devices: Recent progress in growthnology. Nanotechnology, 2009, 20: 332001
Lee G H. Synthesis of pencil-shaped zno nanowires using sunlight. Mater Lett, 2012, 73: 53–55
Hong K Q, Song R, Liu L Q, et al. Synthesis and cathode luminescence properties of ZnO multipod nanoneedles. Mater Lett, 2012, 67: 202–204
Fragala M E, Aleeva Y, Malandrino G. Effects of metal-organic chemical vapour deposition grown seed layer on the fabrication of well aligned zno nanorods by chemical bath deposition. Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519: 7694–7701
Gargas D J, Moore M C, Ni A, et al. Whispering gallery mode lasing from zinc oxide hexagonal nanodisks. Acs Nano, 2010, 4: 3270–3276
Zhang D, Wang C, Liu Y, et al. High c-axis preferred orientation zno thin films prepared by oxidation of metallic zinc. Opt Laser Tech, 2012, 44: 1136–1140
Xi Y, Wu W Z, Fang H, et al. Integrated ZnO nanotube arrays as efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. J Alloy Compd, 2012, 529: 163–168
Yuan Z L, Yu J S, Wang N N, et al. Well-aligned ZnO nanorod arrays from diameter-controlled growth and their application in inverted polymer solar cell. J Mater Sci-Mater, 2011, 22: 1730–1735
Jing X F, Shao P D, Jin Y X, et al. Near-field distribution of broadband antireflective nanostructure arrays. Optik, 2012, 123: 527–533
Yun D Q, Xia X Y, Zhang S, et al. ZnO nanorod arrays with different densities in hybrid photovoltaic devices: fabrication and the density effect on performance. Chem Phys Lett, 2011, 516: 92–95
Jha S, Wang C D, Luan C Y, et al. Near-ultraviolet light-emitting devices using vertical ZnO nanorod arrays. J Electron Mater, 2012, 41: 853–856
Lim Y T, Son J Y, Rhee J S. Vertical ZnO nanorod array as an effective hydrogen gas sensor. Ceram Int, 2013, 39: 887–890
Singh D, Narasimulu A A, Garcia-Gancedo L, et al. Vertically aligned smooth ZnO nanorod films for planar device applications. J Mater Chem C, 2013, 1: 2525–2528
Zhang X, Lu Z, Meng F, et al. Effects of oxygen partial pressure and substrate temperature on the structure and optical properties of MgxZn1−x O thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering. Appl Surf Sci, 2011, 257: 6554–6559
Solis-Pomar F, Martinez E, Melendrez M F, et al. Growth of vertically aligned zno nanorods using textured ZnO films. Nanosc Res Lett, 2011, 6: 524
Shin B K, Lee T I, Xiong J, et al. Bottom-up grown ZnO nanorods for an antireflective moth-eye structure on cuingase2 solar cells. Sol Energ Mat Sol C, 2011, 95: 2650–2654
Chen J, Ye H, Ae L, et al. Tapered aluminum-doped vertical zinc oxide nanorod arrays as light coupling layer for solar energy applications. Sol Energ Mat Sol C, 2011, 95: 1437–1440
Mamat M H, Ishak N I, Khusaimi Z, et al. Thickness-dependent characteristics of aluminium-doped zinc oxide nanorod-array-based, ultraviolet photoconductive sensors. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2012, 51: 06FF03
Hsu C H, Chen D H. Synthesis and conductivity enhancement of Al-doped ZnO nanorod array thin films. Nanotechnology, 2010, 21: 285603
Ruankham P, Macaraig L, Sagawa T, et al. Surface modification of ZnO nanorods with small organic molecular dyes for polymer-inorganic hybrid solar cells. J Phys Chem C, 2011, 115: 23809–23816
Lee S W, Cho H D, Panin G, et al. Vertical ZnO nanorod/Si contact light-emitting diode. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 98: 093110
Wang H H, Dong S J, Zhou X P, et al. Effect of synthesis conditions on microstructures and photoluminescence properties of Ga doped ZnO nanorod arrays. Physica E, 2011, 44: 307–312
Chen S W, Wu J M. Nucleation mechanisms and their Influences on characteristics of ZnO nanorod arrays prepared by a hydrothermal method. Acta Mater, 2011, 59: 841–847
Shinagawa T, Watase S, Izaki M. Size-controllable growth of vertical ZnO nanorod arrays by a Pd-catalyzed chemical solution process. Cryst Growth Des, 2011, 11: 5533–5539
Holmgaard T, Bozhevolnyi S I. Theoretical analysis of dielectric-loaded surface plasmon-polariton waveguides. Phys Rev B, 2007, 75: 245405
Kuester E F, Holloway C L. A low-frequency model for wedge or pyramid absorber arrays. 1. Theory. IEEE T Electromagn C, 1994, 36: 300–306
Holloway C L, Kuester E F. A Low-frequency model for wedge or pyramid absorber arrays. 2. Computed and measured results. IEEE T Electromagn C, 1994, 36: 307–313
Ilican S, Caglar M, Caglar Y. Sn doping effects on the electro-optical properties of sol-gel derived transparent ZnO films. Appl Surf Sci, 2010, 256: 7204–7210
Chao Y C, Chen C Y, Lin C A, et al. Light scattering by nanostructured anti-reflection coatings. Energy Environ Sci, 2011, 4: 3436–3441
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shu, Y., Ye, H. & Chen, J. FDTD analysis of the optical properties of vertical ZnO nanorod array. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 57, 1147–1153 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5525-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5525-1