Abstract
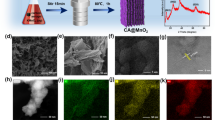
Tubular nanocomposite with interconnected MnO2 nanoflakes coated on MWCNTs (MWCNTs@MnO2) was fabricated by an aqueous solution method at 80°C. Scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction and galvanostatic charge-discharge tests were used to characterize the structures and electrochemical performances of the as-prepared nanocomposite. The capacity reaches 1233.6 mA h g−1 at a current density of 100 mA g−1 for the first discharge, and it can still maintain a capacity of 633.1 mA h g−1 after 100 charge-discharge cycles. The results show that MWCNTs with good electrical conductivity as anchors of MnO2 can provide fast electron transport channels for MnO2 in the electrochemical reactions, and the as-prepared MWCNTs@MnO2 nanocomposite is a potential anode material for lithium ion batteries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tian W, Yang H S, Fan X Y, et al. Catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over different-shaped MnO2 at low temperature. J Hazard Mater, 2011, 188: 105–109
Zhou M, Zhang X, Wei J M, et al. Morphology-controlled synthesis and novel microwave absorption properties of hollow urchinlike α-MnO2 nanostructures. J Phys Chem, 2011, 115: 1398–1402
Li Y, Xie H Q, Wang J F, et al. Preparation and electrochemical performances of α-MnO2 nanorod for supercapacitor. Mater Lett, 2011, 65: 403–405
Liu H W, Tan L. A novel method for preparing lithium manganese oxide nanorods from nanorod precursor. J Nanopart Res, 2010, 12: 301–305
Jiang H, Zhao T, Ma J, et al. Ultrafine manganese dioxide nanowire network for high-performance supercapacitors. Chem Commun, 2011, 47: 1264–1266
Wang X H, Ni S B, Zhou G, et al. Facile synthesis of ultra-long α-MnO2 nanowires and their microwave absorption properties. Mater Lett, 2010, 64: 1496–1498
Zhang H, Cao G P, Wang Z Y, et al. Growth of manganese oxide nanoflowers on vertically-aligned carbon nanotube arrays for high-rate electrochemical capacitive energy storage. Nano Lett, 2008, 8: 2664–2668
Yan Y J, Huang C D. Effect of synthetical conditions, morphology, and crystallographic structure of MnO2 on its electrochemical behavior. J Solid State Electrochem, 2010, 14: 1293–1301
He P, Luo J Y, Yang X H, et al. Preparation and electrochemical profile of Li0.33MnO2 nanorods as cathode material for secondary lithium batteries. Electrochim Acta, 2009, 54: 7345–7349
Lee H W, Muralidharan P, Ruffo R, et al. Ultrathin spinel LiMn2O4 nanowires as high power cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. Nano Lett, 2010, 10: 3852–3856
Wei W F, Cui X W, Mao X H, et al. Morphology evolution in anodically electrodeposited manganese oxide nanostructures for electrochemical supercapacitor applications effect of supersaturation ratio. Electrochim Acta, 2011, 56: 1619–1628
Liu D W, Garcia B B, Zhang Q F, et al. Mesoporous hydrous manganese dioxide nanowall arrays with large lithium ion energy storage capacities. Adv Funct Mater, 2009, 19: 1015–1023
Wu G T, Wang C B, Zhang X B, et al. Structure and lithium insertion properties of carbon nanotubes. J Electrochem Soc, 1999, 146: 1696–1701
Kim B, Im J, Lee B Y, et al. Carbon nanotube-metal nano-laminate for enhanced mechanical strength and electrical conductivity. Carbon, 2011, 49: 2549–2554
Vazquez E, Prato M. Carbon nanotubes and microwaves: Interactions, Responses, and Applications. ACS Nano, 2009, 3: 3819–3824
Masarapu C, Subramanian V, Zhu H W, et al. Long-cycle electrochemical behavior of multiwall carbon nanotubes synthesized on stainless steel in Li-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater, 2009, 19: 1008–1014
Xia H, Lai M O, Lu L. Nanoflaky MnO2/carbon nanotube nanocomposites as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem, 2010, 20: 6896–6902
Pushpendra K, Kedar S. Element directed aqueous solution synthesis of copper telluride nanoparticles, characterization, and optical properties. Crystal Growth Design, 2009, 9: 3089–3094
Reddy A L M, Shaijumon M M, Gowda S R, et al. Coaxial MnO2/carbon nanotube array electrodes for high-performance lithium batteries. Nano Lett, 2009, 9: 1002–1006
Wang X H, Li X W, Sun X L, et al. Nanostructured NiO electrode for high rate Li-ion batteries. J Mater Chem, 2011, 21: 3571–3573
Varghese B, Reddy M V, Zhu Y W, et al. Fabrication of NiO nanowall electrodes for high performance lithium ion battery. Chem Mater, 2008, 20: 3360–3367
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Li, X., Wei, Z. et al. Preparation and electrochemical performance of MWCNTs@MnO2 nanocomposite for lithium ion batteries. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 57, 1077–1080 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5468-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5468-6