Abstract
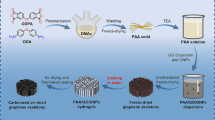
Strong chemical interactions between the oxygen-containing functional groups on graphene oxide (GO) sheets and the ions of divalent metals were exploited for the softening of hard water. GO membranes were prepared and evaluated for their ability to absorb Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions. These GO membranes can effectively absorb Ca2+ ions from hard water; a 1 mg GO membrane can remove as much as 0.05 mg Ca2+ ions. These GO membranes can be regenerated and used repeatedly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zolfigol M A, Madrakian T, Ghaemi E, et al. Synthesis of morpholinated and 8-hydroxyquinolinated silica gel and their application to water softening. Green Chem, 2002, 4: 611–614
Nanda D, Tung K L, Hsiung C C, et al. Effect of solution chemistry on water softening using charged nanofiltration membranes. Desalination, 2008, 234: 344–353
Rahimpour A, Jahanshahi M, Mortazavian N, et al. Preparation and characterization of asymmetric polyethersulfone and thin-film composite polyamide nanofiltration membranes for water softening. Appl Sur Sci, 2010, 256: 1657–1663
Geim A K, Novoselov K S. The rise of graphene. Nat Mater, 2007, 6: 183–191
Meyer J C, Geim A K, Katsnelson M I, et al. The structure of suspended graphene sheets. Nature, 2007, 446: 60–63
Liang J, Xu Y, Sui D, et al. Flexible, magnetic, and electrically conductive graphene/fe3o4 paper and its application for magnetic controlled switches, flexible. J Phys Chem C, 2010, 114: 17465–17471
Huang L, Huang Y, Liang J, et al. Graphene-based conducting inks for direct inkjet printing of flexible conductive patterns and their applications in electric circuits and chemical sensors. Nano Res, 2011, 4: 675–684
Hirata M, Gotou T, Horiuchi S, et al. Thin-film particles of graphite oxide 1: High-yield synthesis and flexibility of the particles. Carbon, 2004, 42: 2929–2937
Gao W, Majumder M, Alemany L B, et al. Engineered graphite oxide materials for application in water purification. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2011, 3: 1821–1826
Park S J, Lee K S, Bozoklu G, et al. Graphene oxide papers modified by divalent ions-enhancing mechanical properties via chemical cross-linking. ACS Nano, 2008, 2: 572–578
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, J., Huang, Y., Zhang, F. et al. The use of graphene oxide membranes for the softening of hard water. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 57, 284–287 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5467-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5467-7