Abstract
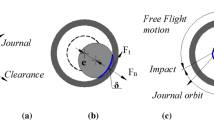
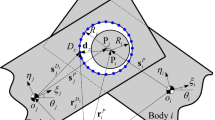
A stationary clearance link algorithm (SCLA) for calculating the reaction-force of revolute clearance joints in crank slider mechanisms is proposed in this paper. The SCLA is more efficient than other algorithms of the same accuracy. Furthermore, based on the Winkler foundation model, an unsymmetrical Winkler foundation model and a double elastic layer Winkler model are proposed. By integrating a dynamic model and the unsymmetrical Winkler foundation model with Archard wear model, an improved integrated wear prediction model is also generated. A series of experiments have been performed to compare with the predicted analysis data, and the results showed a good agreement. As a real industry application, with the double elastic layer Winkler model, the integrated wear prediction model was successfully used to predict the wear depth of the joint bearing (bimetallic bearing) for the cantilever crane of a concrete pump truck of Sany Heavy Industry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Y C, Yu Y Q. A survey of mechanism and Robot with clearances. Mech Sci Tech, 2004, 23(4): 454–457
Xie Y B. Three axioms in tribology. Tribology, 2001, 21(3): 161–165
Flores P, Ambrosio J. Revolute joints with clearance in multibody systems. Comput Struct, 2004, 82: 1359–1369
Imed K, Lotfi R. Dynamic analysis of a flexible slider-crank mechanism with clearance. European J Mecha A/Solids, 2008, 27: 882–898
Sfantos G K, Aliabadi M H. Wear simulation using an incremental sliding Boundary Element Method. Wear, 2006, 260(9–10): 1119–1128
Su Y W, Chen W, Xie Y B. Intergrated Analysis Between Tribology and Dynamics in Multibody System with Clearance Revolute Joints and Its Application. Dissertation of Doctoral Degree. Xi’an: Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2010
Wen S Z, Huang P. Principles of Tribology. 3rd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2008
Li Z, Li L, Bai S X. A new method of predicting the occurrence of contact loss between pairing elements in planar linkages with clearances. Mech Machine Theory, 1992, 27(3): 295–301
Zhang J F, Xu Q Y, Zhang L. The algorithm for the clearance joint reaction force of slider-crank mechanism and its application. Chinese J Appl Mech, 2001, 18(4): 93–97
Podra P, Andersson S. Wear simulation with the Winkler surface model. Wear, 1997, 207: 79–85
Wen S Z. Existing state and development of tribology research in China. Chinese J Mech Eng, 2004, 40(11): 1–6
Podra P, Andersson S. Simulation sliding wear with finite element method. Tribology Inter, 1999, (32): 71–81
Podra P, Andersson S. Finite element analysis wear simulation of a conical spinning contact considering surface topology. Wear, 1999, 224: 13–21
Bandeira A A, Wriggers P, Pimenta P. Numerical derivation of contact mechanics interface laws using a finite element approach for large 3D deformation. Int J Meth Engng, 2004, 59: 173–195
Flodin A, Andersson S. Simulation of mild wear in spur gears. Wear, 1997, 207: 16–23
An K N, Himenso S, Tsumura H, et al. Pressure distribution on articular surfaces-application to joint stability evaluation. J Biomech, 1990, 23(10): 1013–1020
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Chen, W. & Zhu, A. An improved practical model for wear prediction of revolute clearance joints in crank slider mechanisms. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 56, 2953–2963 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-013-5401-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-013-5401-4