Abstract
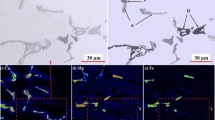
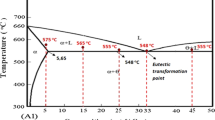
The effects of major alloy element contents of Zn, Mg, Cu in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys on the formation and evolution of intermetallic phases during casting, homogenization and solution treatment have been investigated through using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. Experimental results showed that a relatively higher Zn content with lower Mg and Cu contents was beneficial to the formation of MgZn2 phase instead of the Al2CuMg phase, which resulted in the unicity of the intermetallics in the Al matrix, and that the MgZn2 phase was easier for diffusion and dissolution during homogenization and solution than the Al2CuMg phase. Additionally, the results of the first-principles calculations gave support for explaining the experimental phenomena. A larger absolute value of formation enthalpy and a smaller value of binding energy of the MgZn2 phase, as compared with the Al2CuMg phase, give it priority to precipitate during casting and make it easier to re-dissolve during homogenization and solution treatment. What’s more, higher elastic constants with severe anisotropy of Young’s modulus make undissolved blocks of Al2CuMg phase act as crack initiation, which degrade the performance of the materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jia Z H, Hu G Q, Forbord B, et al. Effect of homogenization and alloying elements on recrystallization resistance of Al-Zr-Mn alloys. Mater Sci Eng A, 2007, 444: 284–290
Eivani A R, Ahmed H, Zhou J, et al. An experimental and theoretical investigation of the formation of Zr-containing dispersoids in Al-4.5Zn-1Mg aluminum alloy. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 527: 2418–2430
Robson J D. Optimizing the homogenization of zirconium containing commercial aluminium alloys using a novel process model. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, 338: 219–229
Du Z W, Zhou T T, Chen C Q, et al. Quantitative analysis of precipitation in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Li alloy. Mater Charact, 2005, 55: 75–82
Du Y, Zhang L J, Cui S L, et al. Atomic mobilities and diffusivities in Al alloys. Sci China Tech Sci, 2012, 55: 306–328
Deng Y, Yin Z M, Cong F G. Intermetallic phase evolution of 7050 aluminum alloy during homogenization. Intermetallics, 2012, 26: 114–121
Fan X G, Jiang D M, Meng Q C, et al. The microstructural evolution of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy during homogenization. Mater Lett, 2006, 60: 1475–1479
He L Z, Li X H, Zhu P, et al. Effects of high magnetic field on the evolutions of constituent phases in 7085 aluminum alloy during homogenization. Mater Charact, 2012, 71: 19–23
Gandin C A, Jacot A. Modeling of precipitate-free zone formed upon homogenization in a multi-component alloy. Acta Mater, 2007, 55: 2539–2553
Shuey R T, Barlat F, Karbin M E, et al. Experimental and analytical investigations on plane strain toughness for 7085 aluminum alloy. Metall Mater Trans A, 2009, 40A: 365–376
Boselli J, Chakrabarti D J, Shuey R T. Aerospace applications: Metallurgical insights into the improved performance of aluminum alloy 7085 thick products. Al Alloys, 2008, 1: 202–208
Bobzin K, Bagcivan N, Parkot D, et al. Calculation of effective properties of textile reinforced aluminum alloy by a two-step homogenization procedure. Comput Mater Sci, 2010, 47: 801–806
Gao F H, Li N K, Tian N, et al. Overheating temperature of 7B04 high strength aluminum alloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2008, 18: 321–326
Dons A L. The Alstruc homogenization model for industrial aluminum alloys. J Light Metal, 2001, 1: 133–149
Zhang J, Huang Y N, Mao C, et al. Structure, elastic and electronic properties of θ (Al2Cu) and S (Al2CuMg) strengthening precipitates in Al-Cu-Mg series alloys. Solid State Commun, 2012, 152: 2100–2104
Zhang C L, Han P D, Zhang Z X, et al. Transformation of the theta-phase in Mg-Li-Al alloys: a density functional theory study. J Mol Mode, 2012, 18: 1123–1127
Zhang J J, Chen Z, Wang Y X, et al. Gibbs free energy calculation of Al-Cu-Li alloy with the effect of electric field from electron level. J Alloy Compd, 2008, 457: 526–531
Zhang C L, Han P D, Yan X, et al. First-principles study of typical precipitates in creep resistant magnesium Alloys. J Phys D-Appl Phys, 2009, 42: 125403–125407
Zhang C L, Han P D, Li J M, et al. First-principles study of the mechanical properties of NiAl microalloyed by M(Y, Zr, Nb, Mo, Tc, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Cd). J Phys D-Appl Phys, 2008, 41: 095410–095414
Hu X L, Liu X, Xu Z, et al. First-principles investigation of the effects of B impurities on the mechanical properties of NiAl intermetallics. Sci China Phys Mech Astron, 2011, 54: 809–814
Mehrer H, editor. Diffusion in Solid Metals and Alloys, Vol.26. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1990
Wang T, Yin Z M, Sun Q. Effect of homogenization treatment on microstructure and hot workability of high strength 7B04 aluminium alloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2007, 17: 335–339
Liu S D, You J H, Zhang X M, et al. Influence of cooling rate after homogenization on the flow behavior of aluminum alloy 7050 under hot compression. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 527: 1200–1205
Medvedeva M I, Gornostyrev Y N, Novikov D L, et al. Ternary site preference energies size misfits and solid soluteion hardening in NiAl and FeAl. Acta Mater, 1998, 46(10): 3433–3442
Sahu B R. Electronic structure and bonding of ultralight LiMg. Mater Sci Eng B, 1997, 49(1): 74–78
Wandahl G, Christensen A N. Occurrence of extinction correlated with crystal growth mode for crystals of Pd3Ce and MgZn2. Acta Chem Scand, 1989, 43: 296–297
Komura Y, Tokunaga K. Structural studies of stacking variants in Mg-base Friauf-Laves phases. Acta Crystallogr B, 1980, B36: 1548–1554
Friauf J B. The crystal structure of magnesium di-zincide. Phys Rev, 1927, 29(1): 34–40
Ohba T, Kitano Y, Komura Y. The charge-density study of the Laves phases, MgZn2 and MgCu2. Acta Cryst, 1984, C40: 1–5
Li C H, Hoe J L, Wu P. Empirical correlation between melting temperature and cohesive energy of binary Laves phases. J Phys Chem Solids, 2003, 64: 201–212
Heying B, Hoffmann R D, Pöttgen R. Structure refinement of the S-phase precipitate MgCuAl2. Z Naturforsch, 2005, 60b: 491–494
Zhang H, Shang S L, Saal J E, et al. Enthalpies of formation of magnesium compounds from first-principles calculations. Intermetallics, 2009, 17(11): 878–885
Heying B, Hoffmann R D, Pöttgen R. Structure refinement of the S-phase precipitate MgCuAl2. Z Naturforsch, 2005, 60b: 491–494
Ostoja-Starzewski M, Wang C. Linear elasticity of planar Delaunay networks. Part Π: Voigt and Reuss bounds, and modification for cetroids. Acta Mech, 1990, 84: 47–61
Bouhemadou A. Calculated structural, electronic and elastic properties of M2GeC(M =Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb,Mo, Hf, Ta andW). Appl Phys A, 2009, 96: 959–967
Pugh S F. Relations between the elastic moduli and the plastic properties of polycrystalline pure metals. Philos Mag, 1954, 45: 823–843
Ravindran P, Fast L, Korzhavyi P A, et al. Density functional theory for calculation of elastic properties of orthorhombic crystals: Application to TiSi2. J Appl Phys, 1998, 84: 4891–4904
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Chen, Z., Zeng, S. et al. Intermetallic phase formation and evolution during homogenization and solution in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 56, 2827–2838 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-013-5356-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-013-5356-5