Abstract
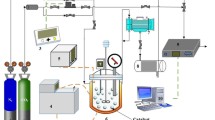
Study on desorption and regeneration of simulated decarbonization solution using ammonia method for CO2 capture was carried out in order to understand the feature of regeneration of decarbonization solution. The mechanisms about solution desorption after decarbonization were introduced briefly. Under the atmospheric pressure and in the presence of nitrogen carrier gas, several effects related to desorption of simulated decarbonization solution were analyzed, such as temperature, solution concentration, pH, loading capacity, etc. The results showed that the CO2 desorption percentage increased with the increases of temperature, solution concentration and loading capacity, but CO2 desorption percentage increased with the increasing of pH and then decreased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
IPCC. IPCC Fourth Assessment Report (AR4). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007
Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, et al. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007
Schimel D S, House J I, Hibbard K A, et al. Recent patterns and mechanisms of carbon exchange by terrestrial ecosystems. Nature, 2001, 414: 169–172
Energy Information Administration. Office of Integrated Analysis and Forecasting, U.S. Department of Energy. International Energy Outlook 2006. Washington D.C: DOE/EIA, 2006
Liu L B, Huang B, Du S W. Process and key equipment for capture CO2 3000–5000 t/a in coal-fired power station (in Chinese). Electrical Equipment, 2008, 9(5): 21–24
Pehnt M, Henkel J. Life cycle assessment of carbon dioxide capture and storage from lignite power plants. Inter J Greenhouse Gas Control, 2009, (3): 49–66
Zeng L, Luo S W, Li F X, et al. Chemical looping technology and its applications in fossil fuel conversion and CO2 capture. Sci China Chem, 2012, 42(3): 260–281
Shen L H, Zheng M, Xiao J, et al. Chemical looping combustion of coal in interconnected fluidized beds. Sci China Ser E-Tech Sci, 2007, 50(2): 230–240
Wu Y, Wang Y F, Zeng Q H, et al. Experimental study on capturing CO2 greenhouse gas by mixture of ammonia and soil (in Chinese). Frontiers Chem Eng China, 2009, 3(4): 1673–7369
Ciferno Jared P, Dipietro P, Tarka T. An economic Scoping Study for CO2 Capture using Aqueous Ammonia. Washington D.C.: US Department of Energy (DOE), 2005
Pazuki G R, Pahlevanzadeh H, Mohseni Ahooei A. Solubility of CO2 in aqueous ammonia solution at low temperature. Comput Coupling Phase Diagrams Thermochem, 2006, 30: 27–32
Reiner D, Liang X. Opportunities and hurdles in applying CCS technologies in China with a focus on industrial stakeholders. Energy Procedia, 2009, 1: 4827–4834
McLamon C, Dunean J L. Testing of ammonia based CO2 capture with multi-pollutant control technology. In: 9th International Conference on Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies, Washington DC, 2009. 102–103
Qin F, Wang S J, Hartono A, et al. Kinetics of CO2 absorption in aqueous ammonia solution. Inter J Greenhouse Gas Control, 2010, 4(5): 729–738
Derks P W J, Versteeg G F. Kinetics of absorption of carbon dioxide in aqueous ammonia solutions. Energy Procedia, 2009, 1: 1139–1146
NPCC. Study on CO2 Sequestration by Spray Concentrated Aqueous NH3 and Production of Modified NH4HCO3 Fertilizer-a Proposal for US-China Joint Research. State Engineering Technology Research Center of Combustion of Power Plants (NPCC), China
Diao Y F, Zheng X Y, Chen C H. Study on removal mechanism of CO2 greenhouse gas by ammonia scrubbing (in Chinese). Acta Sci Circumstantiae, 2003, 23(6): 753–757
Liu F, Wang S J, Zhang X, et al. Study on ammonium bicarbonate decomposition after CO2 sequestration by ammonia method (in Chinese). Acta Sci Circumstantiae, 2009, 9(29): 1887–1890
Zhang Y Z, Ai N, Ji J B. Dissociation of ammonium acid carbonate after CO2 sequestration by aqueous ammonia method (in Chinese). Guangzhou Chem Indust, 2011, 39(8): 56–58
Resnik Kevin P, Yeh James T, Pennline Henry W. Aqua ammonia process for simultaneous removal of CO2, SO2 and NOX. Env Tech Manag, 2004, 4: 89–103
Resnik Kevin P, Garber W, Hreha Deborah C, et al. A parametric scan for regenerative ammonia-based scrubbing for the capture of CO2. In: Proeeedings of 23rd Annual International Pittsburgh Coal Conference. Pittsburgh, 2006
Yeh James T, Resnik Kevin P, Rygle K, et al. Semi-batch absorption and regeneration studies for CO2 capture by aqueous ammonia. Fuel Process Tech, 2005, 86: 1533–1546
Yeh James T, Pennline Henry W. Absorption and regeneration studies for CO2 capture by aqueous ammonia. In: Third Annual Conference on Carbon Capture & Sequestration. Alexandria, VA, 2004
Ma S C, Sun Y X, Zhao Y, et al. Experimental and mechanism research on CO2 capture from simulating flue gas using ammonia solution (in Chinese). Acta Chim Sinica, 2011, 69(12): 1469–1474
Liu S M. Application on the balance of carbonic acid in the alkalinity mensuration of the water analysis (in Chinese). J Huainan Vocat Tech College, 2002, 2(2): 75–77
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, S., Wang, M., Han, T. et al. Research on desorption and regeneration of simulated decarbonization solution in the process of CO2 capture using ammonia method. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 55, 3411–3418 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-012-4991-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-012-4991-6