Abstract
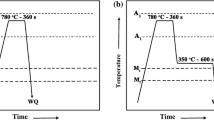
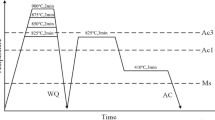
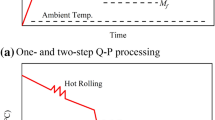
In this work, DIFT technology and Q&P process were combined in order to introduce ultrafine-grained ferrite into the matrix of martensite and retained austenite to develop a new kind of advanced high strength steel, and two kinds of steels were investigated by this novel combined process. The newly designed process resulted in a sophisticated microstructure of a large amount of ferrite(about 5 μm in diameter), martensite and a considerable amount of retained austenite for TRIP 780 steel. The ultimate tensile strength can reach about 1200 MPa with elongation above 16% for TRIP 780, that is much higher than the one solely treated by Q&P process. Tensile tests showed that both steels with the novel combined process achieved a good combination of strength and ductility, indicating that the new process is promising for the new generation of advanced high strength steels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edmonds D V, He K, Rizzo F C, et al. 1st International Conference on Super High Strength Steels. Rome, 2005. 1–20
Speer J G, Streicher A M, Matlock D K, et al. In: Damm E B, Merwin M, eds. Austenite Formation and Decomposition. PA: TMS/ISS, Warrendale, 2003. 505–522
Speer J G, Matlock D K, Cooman B C de, et al. Carbon partitioning into austenite after martensite transformation. Acta Mater, 2003, 51:2611–2622
Santofimia M J, Nguyen-Minh T, Zhao L, et al. New low carbon Q&P steels containing film-like intercritical ferrite. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 527(23): 6429–6439
Edmonds D V, He K, Rizzo F C, et al. Quenching and partitioning martensite-A novel steel heat treatment. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 438–440: 25–34
Priestner R. Strain induced Γ→α transformation in the roll gap in carbon and microalloyed steel. In: DeArdo A J, Ratz G A, Way P J, eds. Proceedings of An International Conference on The Thermomechanical Processing of Microalloyed Austenite. Littleton: Metallurgical Society AIME, 1981. 455
Matsumura Y, Yada H. Evolution of ultrafine-grained ferrite in hot successive deformation. Trans ISIJ, 1987, 27: 492–498
Dong H, Sun X J, Liu Q Y, et al. Deformation induced ferrite transformation: Phenomena and theory (in Chinese). Iron Steel, 2003, 38(10): 56–67
Young C H, Bhadeshia H K D H. Strength of mixtures of bainite and martensite. Mater Sci Technol, 1994, 10: 209–214
Lan Y J, Li D Z, Li Y Y. Modeling austenite decomposition into ferrite at different cooling rate in low-carbon steel with cellular automaton method. Acta Mater, 2004, 52(6): 1721–1729
Zheng C W, Xiao N M, Hao L H, et al. Numerical simulation of dynamic strain-induced austenite-ferrite transformation in a low carbon steel. Acta Mater, 2009, 57(10): 2956–2968
Min J Y, Lin J P, Li J Y. Effect of deformation temperature on the microstructure of boron steel 22MnB5. Adv Sci Lett, 2011, 4(3): 938–942
Moor E D, Speer J G, Matlock D K, et al. Effect of carbon and manganese on the quenching and partitioning response of CMnSi steels. ISIJ Int, 2011, 51: 137–144
Yang Z M, Wang R Z. Formation of ultra-fine grain structure of plain low carbon steel through deformation induced ferrite transformation. ISIJ Int, 2003, 43(5): 761–766
Basabe V V, Jonas J J, Mahjoubi H. Dynamic transformation of a low carbon steel at temperatures above the Ae3. ISIJ Int, 2011, 51: 612–618
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, M., Wu, R., Liu, H. et al. An ultrahigh strength steel produced through deformation-induced ferrite transformation and Q&P process. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 55, 1827–1832 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-012-4880-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-012-4880-z