Abstract
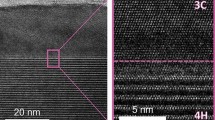
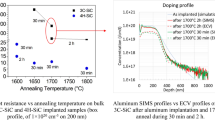
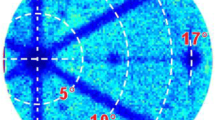
Multiple-energy aluminium (Al+) implantation into 4H-SiC (0001) epilayer and activation anneal with a graphite encapsulation layer were investigated in this paper. Measurements showed that the implanted Al+ box doping profile was formed and a high ion activation ratio of 78% was achieved by 40 min annealing at 1600°C using a horizontal chemical vapor deposition (CVD) reactor. The step bunching effect associated with the high temperature post implantation activation annealing (PIA) process was dramatically suppressed by using the graphite encapsulation layer. And a flat and smooth surface with a small average surface roughness (RMS) value of around 1.16 nm was achieved for the implanted 4H-SiC after the PIA process. It was demonstrated that this surface protection technique is a quite effective process for 4H-SiC power devices fabrication.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dhar A, Ryu S H, Agarwal A K. A study on pre-oxidation nitrogen implantation for the improvement of channel mobility in 4H-SiC MOSFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2010, 57(6): 1195–1200
Danno K, Kimoto T. Investigation of deep levels in n-type 4H-SiC epilayers irradiated with low-energy electrons. J Appl Phys, 2006, 100(11): 113728
Storasta L, Bergman J P, Janzén E, et al. Deep levels created by low energy electron irradiation in 4H-SiC. J Appl Phys, 2004, 96(9): 4909
Negoro Y, Kimoto T, Matsunami H, et al. Electrical activation of high-concentration aluminium implanted in 4H-SiC. J Appl Phys, 2004, 96(09): 4916
Saks N S, Suvorov A V, Capell D C. High temperature high-dose implantation of aluminium in 4H-SiC. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 84(25): 5195
Kawahara K, Alfieri G, Kimoto T. Detection and depth analyses of deep levels generated by ion implantation in n- and p-type 4H-SiC. J Appl Phys, 2009, 106(01): 013719
Zhao F, Ialam M, Huang C F. Study of SiO2 encapsulation for aluminium and phosphorus implant activation in 4H-SiC. Mater Lett, 2010, 64: 2593–2596
Camarda M, Severino A, Fiorenza P, et al. On the “step bunching” phenomena observed on etched and homoepitaxially grown 4H silicon carbide. Mater Sci Forum, 2011, 679-680: 358–361
Capano M A, Ryu S, Cooper J A, et al. Surface roughening in ion implanted 4H-Silicon carbide. J Electron Mater, 1999, 28(3): 214–218
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Q., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y. et al. Investigation of surface morphology and ion activation of aluminium implanted 4H-SiC. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 55, 3401–3404 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-012-4827-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-012-4827-4