Abstract
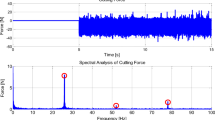
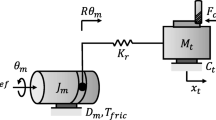
This paper addresses double-loop robust tracking controller design of the miniaturized linear motor drive precision stage with mass and damping ratio uncertainties. As an inner-loop, a disturbance observer (DOB) is employed to suppress exogenous low frequency disturbances such as friction and cutting force. To further eliminate the residual disturbance and to guarantee the robust tracking to the reference input, a µ-synthesis outer-loop controller is designed. For eliminating the steady state error, a technique is proposed to design the µ-synthesis outer-loop controller with an integrator. A guideline to select the bandwidth of the Q-filter in the DOB is provided. Simulations using a model of a prototype micro-milling machine indicate that the proposed outer-loop synthesis scheme is superior to the H ∞ suboptimal control in disturbance rejection performance and steady state tracking performance. Furthermore, it is shown experimentally that the proposed double-loop robust tracking controller improves the tracking performance of the stage by 29.6% over PID control with a DOB inner-loop.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chae J, Park S S, Freiheit T. Investigation of micro-cutting operations. Int J Mach Tool Manu, 2006, 46: 313–332
Corbett J, McKeon P A, Peggs G N, et al. Nanotechnology: International developments and emerging products. CIRP Ann-Manuf Techn, 2000, 49: 523–546
Madou M J. Fundamentals of Microfabrication. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1997
Weck M, Fischer S, Vos M. Fabrication of micro components using ultra precision machine tools. Nanotechnology, 1997, 8: 145–148
Lang W. Reflexions on the future of microsystems. Sensor Actuat, 1999, 72: 1–15
Alter D M, Tsao T C. Stability of turning processes with actively controlled linear motorfeed drives. J Eng Ind Trans ASME, 1994, 116: 298–307
Alter D M, Tsao T C. Control of linear motors for machine tool feed drives: Design and implementation of H-infinity optimal feedback control. J Dyn Syst-T ASME, 1996, 118: 649–656
Van den Braembussche P, Swevers J, Van Brussel H. Design and experimental validation of robust controllers for machine tool drives with linear motor. Mechatronics, 2001, 11: 545–562
Yen P L. A two-loop robust controller for compensation of the variant friction force in an over-constrained parallel kinematic machine. Int J Mach Tool Manu, 2008, 48: 1354–1365
Azadi Yazdi E, Nagamune R. Multiple robust H-infinity controller design using the nonsmooth optimization method. Int J Robust Nonlin, 2010, 20(11): 1197–1312
Doyle J, Francis B, Tannenbaum A. Feedback Control Theory. New York: McMillam, 1992
Zhou K M, Doyle J C, Glover K. Robust and Optimal Control, Upper Saddle River. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 1996
Gu D W, Petkov P Hr, Konstantinov M M. Robust Control Design with MATLAB. Lodon: Springer Press, 2005
Gahinet P, Apkarian P. A linear matrix inequality approach to H ∞-control. Int J Robust Nonlin, 1994, 4(4): 421–448
Iwasaki T, Skelton R E. All controllers for the general H ∞-control problem: LMI existence conditions and state space formulas. Automatica, 1994, 30(8): 1307–1317
Erkorkmaz K, Altintas Y. High speed CNC system design. Part II: Modeling and identification of feed drives. Int J Mach Tool Manu, 2001, 41: 1487–1509
Umeno T, Hori Y. Robust speed control of dc servomotors using modern 2 degrees-of-freedom controller-design. IEEE T Ind Electron, 1991, 38: 363–368
Lee H S, Tomizuka M. Robust motion controller design for high-accuracy positioning systems. IEEE T Ind Electron, 1996, 43: 48–55
Endo S, Kobayashi H, Kempf C J, et al. Robust digital tracking controller design for high-speed positioning systems. Control Eng Pract, 1996, 4(4): 527–536
Schrijver E, Van Dijk J. Disturbance observers for rigid mechanical systems: Equivalence, stablity, and design. J Dyn Syst-T ASME, 2002, 124: 539–548
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, S., Nagamune, R. & Fan, D. Double-loop robust tracking control for micro machine tools. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 54, 3054–3063 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-011-4561-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-011-4561-3