Abstract
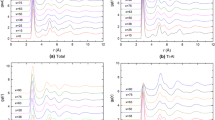
Al-Ni alloys have better glass forming ability (GFA) than other Al-based alloys. However, the relationship among the atomic arrangement, glass transition, packing density and composition hasn’t been systematically studied. In this paper the ab initio molecular dynamics simulation (AIMD) was performed on the atom packing and density of Al x Ni100−x (x=80, 83, 85, 86, 87 and 90) alloys. The pair correlation function and Voronoi tessellation indicated that there are obvious topological and chemical short-range orders in these alloys. The topological structure consists of Al-centered icosahedra like and Ni-centered tri-capped trigonal prism (TTP) like polyhedra. There is strong chemical short-range ordering between Al and Ni atoms indicated by the bond-length of Al-Ni pair shorter than the sum of the radii of Al and Ni atoms, which increases with the increasing of Ni content. It is shown that the densities of amorphous alloys don’t agree with the linear law with a peak at x=85. Based on the features of the structure and density, it is concluded that Al-Ni alloys at x=84–86 have high GFA, which can be extended to multi-component Al-based alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suzuki R O, Komatsu Y, Kobayashi K E, et al. Formation and crystallization of Al-Fe-Si amorphous alloys. J Mater Sci, 1983, 18(4): 1195–1201
Inoue A, Bizen Y, Kimura H M, et al. Development of compositional short-range ordering in an Al50Ge40Mn10 amorphous alloy upon annealing. J Mater Sci Lett, 1987, 6(7): 811–814
He Y, Poon S J, Shiflet G J. Synthesis and properties of metallic glasses that contain aluminum. Science, 1988, 241(2): 1640–1642
Zhu A W, Shiflet G J, Miracle D B. Glass forming ranges of Al-rare earth metal alloys: Thermodynamic and kinetic analysis. Scripta Mater, 2004, 50(7): 987–991
Zhu A W, Poon S J, Shiflet G J. On glass formability of Al-Gd-Ni(Fe). Scripta Mater, 2004, 50(12): 1451–1455
Senkov O N, Miracle D B. Effect of the atomic size distribution on glass forming ability of amorphous metallic alloys. Mater Res Bull, 2001, 36(12): 2183–2198
Guo F Q, Enouf S, Poon S J. Formation of ductile Al based metallic glasses without rare-earth elements. Philos Mag Lett, 2001, 81(3): 203–211
Sheng H W, Luo W K, Alamgir F M, et al. Atomic packing and short-to-mediumrange order in metallic glasses. Nature, 2006, 439(26): 419–425
Inoue A, Masumoto T. X-ray diffraction study of amorphous Al77.5Mn22.5 and Al56Si30Mn14 alloys. J Mater Sci, 1988, 23(2): 753–756
Zhang L, Wu Y S, Bian X F, et al. Short-range and medium-range order in liquid and amorphous Al90Fe5Ce5 alloys. J Non-Cryst Solids, 2000, 262(1–3): 169–176
Qin J Y, Bian X F, Sliusarenko S I, et al. Pre-peak in the structure factor of liquid Al-Fe alloy. J Phys: Conden Matter, 1998, 10(6): 1211
Inoue A. Amorphous, nanoquasicrystalline and nanocrystalline alloys in Al-based systems. Prog in Mater Sci, 1998, 43(5): 365–520
Rachek O P. X-ray diffraction study of amorphous alloys Al-Ni-Ce-Sc with using Ehrenfests formula. J Non-Cryst Solid, 2006, 352(36–37): 3781–3786
Ahn K, Louca D, Poon S J, et al. Topological and chemical ordering induced by Ni and Nd in Al87Ni7Nd6 metallic glass. Phys Rev B, 2004, 70(22): 224103
Jakse N, le Bacq O, Pasturel A. Chemical and icosahedral short-range orders in liquid and undercooled Al80Mn20 and Al80Ni20 alloys: A first-principles-based approach. J Chem Phys, 2005, 123(10): 104508
Li R Y, Qin J Y, Gu T K, et al. Structure of liquid Al80Mn20 alloy by reverse Monte Carlo simulation. J Non-Cryst Solid, 2008, 354(15–16): 1736–1739
Li H, Ding F, Wang J L, et al. Structural studies of clusters in melt of FeAl compound. J Chem Phys, 2001, 114(14): 6413
Gu T K, Qin J Y, Bian X F. Correlation between local structure of melts and glass forming ability for Al-based alloys: A first-principles study. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 91: 081907
Inoue A, Matsumoto N, Masumoto T. Al-Ni-Y-Co amorphous alloys with high mechanical strengths, wide supercooled liquid region and large glass forming capacity, Mater Trans-JIM, 1990, 31: 493–500
Sanders W S, Warner J S, Miracle D B. Stability of Al-rich glasses in the Al-La-Ni system. Intermetallics, 2006, 14: 348
Horbach J, Das S K, Griesche A, et al. Self-diffusion and interdiffusion in Al80Ni20 melts: Simulation and experiment. Phys Rev B, 2007, 75: 174304
Wang L, Wang Y Q, Peng C X, et al. Medium-range structural order in liquid Ni20Al80 alloy: Experimental and molecular dynamics studies. Phys Lett A, 2006, 350(5–6): 405–409
Miracle D B, Senkov O N. A geometric model for atomic configurations in amorphous Al alloys. J Non-Cryst Solid, 2003, 319: 174–191
Sheng H W, Cheng Y Q, Lee P L, et al. Atomic packing in multicomponent aluminum-based metallic glasses. Acta Mater, 2008, 56: 6264–6272
Li G Q, Borisenko K B, Chen Y X. Local structure variations in Al89La6Ni5 metallic glass. Acta Mater, 2009, 57(3): 804–811
Bernal J D. A geometrical approach to the structure of liquids. Nature, 1959, 183(4655): 141–147
Miracle B D. A structural model for metallic glasses. Nat Mater, 2004, 3(10): 697–702
Sheng H W, Luo W K, Alamgir F M, et al. Atomic packing and short-to-medium-range order in metallic glasses. Nature, 2006, 439: 419–425
Li Y, Guo Q, Kalb J. A, et al. Matching glass-forming ability with the density of the amorphous phase. Science, 2008, 322: 1816–1819
Car R, Parrinello M. Unified approach for molecular dynamics and density-functional theory. Phys Rev Lett, 1985, 55(22): 2471–2474
Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput Mater Sci, 1996, 6(1): 15–50
Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio totalenergy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys Rev B, 1996, 54(16): 11169–11186
Blöchl P E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B, 1994, 50(24): 17953–17979
Kresse G, Joubert D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B, 1999, 59(3): 1758–1775
Wang Y, Perdew J P. Correlation hole of the spin-polarized electron gas, with exact small-wave-vector and high-density scaling. Phys Rev B, 1991, 44(24): 13298–13307
Nose S. A unified formulation of the constant temperature molecular dynamics methods. J Chem Phys, 1984, 81(1): 511–519
Verlet L. Computer “experiments” on classical fluids. I. Thermodynamical properties of Lennard-Jones molecules. Phys Rev, 1967, 159(1): 98–103
Shimoli M. Liquid Metals. Washington: Academic Press, 1977
Mattern N, Kühn U, Hermann H, et al. Short-range order of Zr62−x TixAl10Cu20Ni8 bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater, 2002, 50: 305–314
Allen M P, Tildesley D J. Computer Simulation of Liquids. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1989
Maret M, Pomme T, Pasturel A. Structure of liquid Al80Ni20 alloy. Phys Rev B, 1990, 42(3): 1598–1604
Finney J L. Random packings and the structure of simple liquids: The geometry of random close packing. Proc R Soc Lond A, 1970, 319(1539): 479–493
Nelson D R. Order, frustration, and defects in liquids and glasses. Phys Rev B, 1983, 28: 5515–5535
Bernal J D. Geometry of the structure of monatomic liquids. Nature, 1960, 185(4707): 68–70
Zalewski W, Antonowicz J, Bacewicz R. Local atomic order in Al-based metallic glasses studied using XAFS method. J Alloy Compd, 2009, 468: 40–46
Hsieh H Y, Toby B H, He Y. Atomic structure of amorphous Al90FexCe10−x . J Mater Res, 1990, 5(12): 2807–2812
Cowley J M. An approximate theory of order in alloys. Phys Rev, 1950, 77(5): 669–675
Widom M, Lehyani A I, Moriarty J A. First-principles interatomic potentials for transition-metal aluminides. Phys Rev B, 2000, 62(6): 3648–3657
Mukherjee S, Schroers J, Zhou Z. Viscosity and specific volume of bulk metallic glass-forming alloys and their correlation with glass forming ability. Acta Mater, 2004, 52(12): 3689–3695
Yokoyama Y, Ishikawa T, Okada J T. Volume and viscosity of Zr-Cu-Al glass-forming liquid alloys. J Non-Cryst Solid, 2009, 355: 317–322
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, C., Hui, X., Chen, X. et al. Ab initio molecular dynamics simulation of the atom packing and density of Al-Ni amorphous alloys. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 53, 3175–3182 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-4173-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-4173-3