Abstract
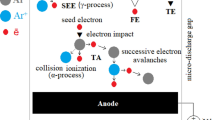
In view of the low thrust power ratio caused by the high resistance of pulsed plasma thruster using water propellant, the paper argues that the easily ionized elements Na and K with low ionic potentials are added in the water propellant to improve its performance. The measurement of the discharging current and plasma emission spectrographic analysis prove the improvement. The experiments show that the elements Na and K have certain effect on the improvement of the performance of pulsed plasma thruster: In comparison with water propellant, the NaCl and KCl water propellant has a lower total resistance and a higher ratio of thruster power and specific impulse, and the NaCl water propellant has a slightly stronger effect on pulsed plasma thruster than the KCl. The plasma emission spectrographic analysis is in consistent with the experiment of measuring the discharging current: The elements Na and K can intensify the plasma emission spectrographic signal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christopher D R, Mark E C, Mattick A T. Pulsed plasma thruster system for microsatellites. J Spac Rock, 2005, 42(1): 161–170
Uezu J J, Iio J P. Study on pulsed plasma thruster configuration to expand impulse bit range. In: 29th International Electric Propulsion Conference, 2005. 234
Spanjers G G, Lotspeich J S. Propellant losses because of particulate emission in a pulsed plasma thruster. J Propul P, 1998, 14(4): 554–559
Markusic T E, Kurt A P, Choueiri E Y, et al. Ablative z-pinch pulsed plasma thruster. J Propul P, 2005, 21(3): 392–405
Hiroyuki K, Kakami A, Furuta Y, et al. Liquid propellant pulsed plasma thruster. In: 28th International Electric Propulsion Conference, 2003. 87
Carsten A S. Investigation of thrust mechanisms in a water fed pulsed plasma thruster. Dissertation of Doctoral Degree. USA: The Ohio State University, 2003. 68–70
Hiroyuki K, Yohei F. A pulsed plasma thruster using water as the propellant. AIAA-2004-3460, 2004
Jahn R G. Physics of Electric Propulsion. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1968. 12–13
Hou D L, Zhao W S, Kang X M. Performance analysis of pulsed plasma thruster. J Propul Tech, 2008, 29(3): 377–380
Liu L L, Deng J X. Design and development of SiC(W, Ti)C gradient ceramic nozzle. Sci China Tech Sci, 2008, 51(1): 77–84
Nob H, Le C K. Closed cycle mhd generator using He/Xe working plasma. AIAA-2002-2144, 2002
Alan M P, Nick P. Salt effects on ion formation in desorption mass spectrometry: an investigation into the role of alkali chlorides on peak suppression in time-of-flight-secondary ion mass spectrometry. Analyt Chem, 2009, 81(3): 1040–1048
Yan J H, Dai S L. Emission spectroscopy diagnosis of the radicals generated in gas-liquid phases gliding arc discharge. Spectr Sp A, 2008, 28(8): 1851–1855
Song W D. Active electrospray ionization for efficient electric thrusters. AIAA-2004-3942, 2004
Wang C C, Subrata R. Microscale plasma actuators for improved thrust density. J Appl Phys, 2009, 17(7): 013310–013317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, P., Hou, L. & Zhang, W. The effect of easily ionized elements Na and K on the performance of pulsed plasma thruster using water propellant. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 53, 2878–2882 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-4086-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-4086-1