Abstract
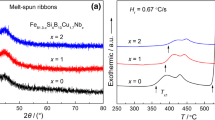
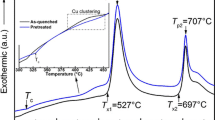
The correlation between microstructure and magnetic properties of Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si15.5B7 alloy annealed at 360°C–620°C has been investigated. The best static and dynamic soft magnetic properties have been obtained after annealing at 500°C and 550°C for 1 h, respectively. The dependence of annealing temperature on coercivity has shown three magnetic hardenings for the studied alloys annealed at 460°C, 530°C and 620°C, respectively. And the plot of core loss as a function of annealing temperature manifests a peak at 530°C, and this peak increases with increasing magnetic induction at low frequencies. This effect can probably be attributed to the precipitation of a new phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshizawa Y, Oguma S, Yamauchi K. New Fe-based soft magnetic alloys composed of ultrafine grain structure. J Appl Phys, 1988, 64(10): 6044–6046
Herzer G. Grain structure and magnetism of nanocrystalline ferromagnets. IEEE Trans Magn, 1989, 25(5): 3327–3329
Marin P, Vazquez M, Hernando A. Magnetic hardening during the amorphous to nanocrystalline transformation in FeSiBCuNb alloys: Theoretical considerations. J Magn Magn Mater, 1999, 196–197: 221–223
Kulik T, Zuberek R, Hernando A. Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si16.5B6. J Magn Magn Mater, 1995, 140–144: 433–434
Kollar P, Kafkova L, Fuzer J, et al. The influence of boron content on the magnetic properties of annealed Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si22.5−xBx (5≤x≤13) alloys. J Magn Magn Mater, 1995, 140–144: 333–334
Marin P, Gomez-Polo C, Hernando A. Magnetism of two-phase magnetic systems composed of nanograins embedded in an amorphous matrix. Mater Sci Eng, 2007, A 449–451: 71–78
Hono K, Li J L, Ueki Y, et al. Atom probe study of the crystallization process of an Fe73.5Si13.5B9Nb3Cu1 amorphous alloy. Appl Surf Sci, 1993, 67(4): 398–406
Phan M H, Peng H X, Wisnom M R, et al. Effect of annealing on the microstructure and magnetic properties of Fe-based nanocomposite materials. Compos Part A, 2006, 37: 191–196
Navarro I, Pulido E, Crespo P, et al. Effect of the hard magnetic inclusion on the macroscopic anisotropy of nanocrystalline magnetic materials. J Appl Phys, 1993, 73: 6525
Zhi Q Z, Dong B S, Chen W Z, et al. Elevated temperature initial permeability study of Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 alloy. Mater Sci Eng, 2007, A 448: 249–252
Twarowski K, Kuzminski M, Slawska-Waniewska A, et al. Magnetostriction and its temperature dependence in FeCuNbSiB nanocrystalline alloy. J Magn Magn Magn, 1995, 150: 85–92
Kulik T, Hernando A, Vazquez M. Correlation between structure and the magnetic properties of amorphous and nanocrystalline Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si22.5−xBx alloys. J Magn Magn Mater, 1994, 133: 310–313
Wittwer C, Riehemann W, Heye W. Dynamic losses in nanocrystalline finemet for various annealing temperatures. J Magn Magn Mater, 1994, 133: 287–290
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, B., Zhi, Q., Li, D. et al. Abnormality of magnetic behavior and core loss of nanocrystalline Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si15.5B7 alloy. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 53, 343–347 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-0049-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-0049-9