Abstract
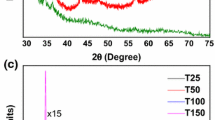
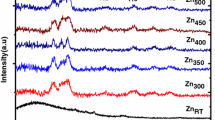
ZnO thin films were deposited on fused silica via pulsed laser deposition (PLD) at substrate temperatures from 300°C to 800°C and ambient oxygen pressures ranging from 10−2 mTorr to 240 mTorr. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Raman spectra indicated that wurtzite ZnO was obtained in all cases. The highly c-oriented ZnO films were obtained for oxygen pressures above 11 mTorr. The room-temperature photoluminescence (PL) spectra demonstrated that all the films exhibited strong near-band-edge (NBE) emission, while deep-level (DL) emission was also observed in films deposited at oxygen pressures below 80 mTorr. From analysis of the XRD, Raman and photoluminescence PL data, an optimal condition was identified for the deposition of highly crystallized ZnO films.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki T, Hatanaka Y, Look D C. ZnO diode fabricated by excimer-laser doping. Appl Phys Lett, 2000, 76: 3257
Tsukazaki A, Ohtomo A, Onuma T, et al. Repeated temperature modulation epitaxy for p-type doping and light-emitting diode based on ZnO. Nature Materials, 2005, 4: 42
Ryu Y, Lee T S, Jorge A L, et al. Next generation of oxide photonic devices: ZnO-based ultraviolet light emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 88: 241108
Wang Z L, Song J. Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science, 2006, 312: 243
Carcia P F, McLean R S, Reily M H, et al. Transparent ZnO thin-film transistor fabricated by rf magnetron sputtering. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 82: 1117
Jeong W J, Kim S K, Park G C. Preparation and characteristic of ZnO thin film with high and low resistivity for an application of solar cell. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 506/507: 180
Shiosaki T, Ohnishi S, Hirokawa Y, et al. As-grown CVD ZnO optical waveguides on sapphire. Appl Phys Lett, 1978, 33: 406
Agarwal D C, Chauhan R S, Amit K, et al. Synthesis and characterization of ZnO thin film grown by electron beam evaporation. J Appl Phys, 2006, 99: 123105
Li B S, Liu Y C, Chu Z S, et al. High quality ZnO thin films grown by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. J Appl Phys, 2002, 91: 501
Smith F T J. Metalorganic chemical vapor deposition of oriented ZnO films over large areas. Appl Phys Lett, 1983, 43: 1108
Lu Y M, Hwang W S, Liu W Y, et al. Effect of RF power on optical and electrical properties of ZnO thin film by magnetron sputtering. Mater Chem Phys, 2001, 72: 269
Bagnall D M, Chen Y F, Zhu Z, et al. High temperature excitonic stimulated emission from ZnO epitaxial layers. Appl Phys Lett, 1998, 73: 1038
He Y N, Zhang J W, Yang X D, et al. Study on pulsed laser ablation and deposition of ZnO thin film by L-MBE. Sci China Ser E-Tech Sci, 2007, 50: 290
Tang Z K, Wong G K L, Yu P, et al. Room-temperature ultraviolet laser emission from self-assembled ZnO microcrystallite thin films. Appl Phys Lett, 1998, 72: 3270
Choopun S, Vispute R D, Noch W, et al. Oxygen pressure-tuned epitaxy and optoelectronic properties of laser-deposited ZnO films on sapphire. Appl Phys Lett, 1999, 75: 3947
Misra P, Kukreja L M. Buffer-assisted low temperature growth of high crystalline quality ZnO films using Pulsed Laser Deposition. Thin Solid Films, 2005, 485: 42
Vispute R D, Talyansky V, Trajanovic Z, et al. High quality crystalline ZnO buffer layers on sapphire (001) by pulsed laser deposition for III-V nitrides. Appl Phys Lett, 1997, 70: 2735
Hayamizu S, Tabata H, Tanaka H, et al. Preparation of crystallized zinc oxide films on amorphous glass substrates by pulsed laser deposition. J Appl Phys, 1996, 80: 787
Shan F K, Liu G X, Lee W J, et al. Transparent conductive ZnO thin films on glass substrates deposited by pulsed laser deposition. J Cryst Growth, 2005, 277: 284
Jin C M, Ashutosh T, Roger J N. Ultraviolet-illumination-enhanced photoluminescence effect in zinc oxide thin films. J Appl Phys, 2005, 98: 083707
Miyake A, Kominami H, Tatsuoka H, et al. Luminescent properties of ZnO thin films grown epitaxially on Si substrate. J Cryst Growth, 2000, 214/215: 294
Ryu Y R, Zhu S, Budai J D. Optical and structural properties of ZnO films deposited on GaAs by pulsed laser deposition. J Appl Phys, 2000, 88: 201
Vispute R D, Talyansky V, Choopun S, et al. Heteroepitaxy of ZnO on GaN and its implications for fabrication of hybrid optoelectronic devices. Appl Phys Lett, 1998, 73: 348
Ohtomo A, Tamura K, Saikusa K, et al. Single crystalline ZnO films grown on lattice-matched ScAIMgO4(0001) substrates. Appl Phys Lett, 1999, 75: 2635
White G K. Thermal expansion of reference materials: Copper, silica and silicon. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 1973, 6: 2070
Yim W M, Paff R J. Thermal expansion of AlN, sapphire, and silicon. J Appl Phys, 1974, 45: 1456
Albertsson J, Abrahams S C, Kvick A. Atomic displacement, anharmonic thermal vibration, expansivity and pyroelectric coefficient thermal dependences in ZnO. Acta Cryst B, 1989, 45: 34
Ryu Y R, Zhu S, Han S W, et al. Application of pulsed-laser deposition technique for cleaning a GaAs surface and for epitaxial ZnSe film growth. J Vac Sci Technol A, 1998, 16: 3058
Jeong S H, Kim B S, Lee B T. Photoluminescence dependence of ZnO films grown on Si(100) by radio-frequency magnetron sputtering on the growth ambient. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 82: 2625
Yan J F, Lu Y M, Liu Y C, et al. Improvement of the crystalline quality of the ZnO epitaxial layer on a low-temperature grown ZnO buffer layer. J Cryst Growth, 2004, 266: 505
Kim I S, Kim K H, Kimm S S, et al. Magnetron sputtering growth and characterization of single crystal ZnO thin films on Si using GaN interlayer. J Cryst Growth, 2007, 299: 295
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L., Xu, C., Liu, Y. et al. Effects of temperature and pressure on the structural and optical properties of ZnO films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 53, 317–321 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-0047-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-0047-y