Abstract
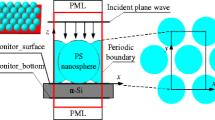
The temperature of a solar cell will increase when it is exposed to the sunlight, which results in variations of optical parameters and thermal expansion coefficient of the cell, thus affecting its spectral absorption feature. This paper is aimed to investigate the effects of temperature on the absorption property of solar cells with micro-structured surfaces. By taking hemispherical, cylindrical and spherical surfaces as models, numerical computation is conducted to obtain spectral distribution of absorptance of such surfaces with different structural parameters by means of the finite difference time domain (FDTD) method. Furthermore, the effects of material properties and structural period on the absorption property are also investigated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang H M, Yin Y H. Research status and development trend of solar cells. Water Resour Power, 2008, 26(6): 193–197
Cheng Z X, Wang X L. The summarization of solar cells. Inform Record Datum, 2007, 8(2): 41–47
Xu M, Xia D L, Sheng Y, et al. Thin-film solar cells. Mater Rev, 2006, 20(9): 109–111
Ikeda K, Miyazaki H T, Kasaya T, et al. Controlled thermal emission of polarized infrared waves from arrayed plasmon nanocavities. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92: 021117
Carsten R, Falk L. Photon management by metallic nanodiscs in thin film solar cells. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94: 213102
Chiu C H, Yu P C. Broadband and omnidirectional antireflection employing disordered GaN nanopillars. Opt Express, 2008, 16(12): 8748–8754
Irina P, Schaich W L. Narrow-band, tunable infrared emission from arrays of microstrip patches. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92: 021117
Mapel J K, Singh M, Baldo M A. Plasmonic excitation of organic double hetero-structure solar cells. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90: 121102
Ferry V E, Sweatlock L A, Pacifici D, et al. Plasmonic nanostructure design for efficient light coupling into solar cells. Nano Lett, 2008, 12(8): 4391–4397
Rand B P, Peumans P, Forrest S R. Long-range absorption enhancement in organic tandem thin-film solar cells containing silver nanoclusters. J Appl Phys, 2004, 96(12): 7519–7526
Hägglund C, Zäch M, Göran P, et al. Electromagnetic coupling of light into a silicon solar cell by nanodisk plasmons. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92: 053110
Nakayama K, Tanabe K, Atwater H A. Plasmonic nanoparticle enhanced light absorption in GaAs solar cells. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 93: 121904
Derkacs D, Lim S H, Matheu P, et al. Improved performance of amorphous silicon solar cells via scattering from surface plasmon polaritons in nearby metallic nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89: 093103
Catchpole K R, Polman A. Design principles for particle plasmon enhanced solar cells. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 93: 191113
Pillai S, Catchpole K R, Trupke T, et al. Surface plasmon enhanced silicon solar cells. J Appl Phys, 2007, 101: 093105
Springer J, Poruba A, Mullerova L, et al. Absorption loss at nanorough silver back reflector of thin-film silicon solar cells. J Appl Phys, 2004, 95 (3): 1427–1429
Ge D B, Yan Y B. Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method for Electromagnetic Waves (in Chinese). Xi’an: Xidian University Press, 2005
Taflove A, Hagness S. Computational Eelectrodynamics: The Finite- Difference Time-Domain Method. 2nd ed. Norwood: Artech House Publishers, 2000
Tang J F, Gu P F. Thin-film Optics and Technology (in Chinese). Beijing: China Machine Press, 1989
Jellison G E, Modine F A. Optical functions of silicon between 1.7 and 4.7 eV at elevated temperature. Phys Rev B, 1983, 27(12): 7466–7472
Anuj K S, Banshi D G. Influence of temperature on the sensitivity and signal-to-noise ratio of a fiber-optic surface-plasmon resonance sensor. Appl Opt, 2006, 45(1): 151–161
Yasumasa O, Tokumaru Y. Precise determination of lattice parameter and thermal expansion coefficient of silicon between 300 and 1500 K. J Appl Phys, 1984, 56(2): 314–320
Liu C, Zheng R L. The expansion coefficient and elastic modulus of FCC Crystal. J Southwest China Norm Univ (Nat Sci), 2006, 31(5): 83–87
Heinz R. Surface Plasmons. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1988
Stefan A M. Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications. New York: Springer-Verlag, 2007
Hitoshi S. Numerical study on spectral properties of tungsten one-dimensional surface-relief gratings for spectrally selective devices. J Opt Soc Am A, 2005, 22(9): 1805–1813
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Xuan, Y., Han, Y. et al. Investigation on the temperature-dependence of absorption properties of solar cells with micro-structured surfaces. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 53, 2304–2310 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-009-3237-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-009-3237-8