Abstract
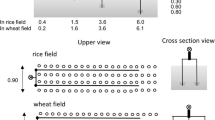
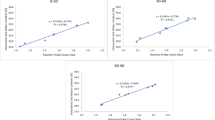
Irrigation practices greatly affect sustainable agriculture development. In this study, we investigated the effects of irrigation efficiency on water flow and chemical transport in soils, which had significant impact on the environment. Field dye staining experiments were conducted at different soils with various irrigation amount. Image analysis was conducted to study the heterogeneous flow patterns and their relationships with the irrigation efficiency. Irrigation efficiency and its environmental effects were evaluated using various indictors, including application efficiency, deep percolation ratio, storage efficiency, and uniformity. Under the same irrigation condition, soil chemical distributions were more heterogeneous than soil water distributions. The distributions were mainly affected by soil texture, initial soil water content, and irrigation amount. Storage efficiency, irrigation uniformity, and deep percolation ratio increased with irrigation amount. Since the chemical distribution uniformity was lower than the water uniformity, the amount of chemical leaching increased sharply with decrease of irrigation uniformity, which resulted in high environmental risks of groundwater pollution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banedjschafie S, Bastani S, Widmoser P, et al. Improvement of water use and N fertilizer efficiency by subsoil irrigation of winter wheat. Eur J Agronomy, 2008, 28(1): 1–7
Wallace J S. Increasing water use efficiency to meet future food production. Agric Ecosystems Environ, 2000, 82(1–3): 105–119
Burke S, Mulligan M, Thornes J B. Optimal irrigation efficiency for maximum plant productivity and minimum water loss. Agric Water Manage, 1999, 40(2–3): 377–391
Allaire-Leun S E, Wu L, Mitchell J P. Nitrate leaching and soil nitrate content as affected by irrigation uniformity in a carrot field. Agric Water Manage, 2001, 48(1): 37–50
Crescimanno G, Santis A D, Provenzano G. Soil structure and bypass flow processes in a Vertisol under sprinkler and drip irrigation. Geoderma, 2007, 138(1–2): 110–118
Webber H A, Madramootoo C A, Bourgault M, et al. Water use efficiency of common bean and green gram grown using alternate furrow and deficit irrigation. Agric Water Manage, 2006, 86(3): 259–268
Home P G, Panda R K, Kar S. Effect of method and scheduling of irrigation on water and nitrogen use efficiencies on Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus). Agric Water Manage, 2002, 55(2): 159–170
Morris C, Mooney S J. A high-resolution system for the quantification of preferential flow in undisturbed soil using observations of tracers. Geoderma, 2004, 118(1–2): 133–143
Smettem K R J, Trudgill S T. An evaluation of some fluorescent and nonfluorescent dyes in the identification of water transmission routes in soils. J Soil Sci, 1983, 34(1): 45–56
Weiler M, Naef F. Simulating surface and subsurface infiltration of macropore flow. J Hydrol, 2003, 273(1–4): 139–154
Forrer I, Parrita A, Kasteel R, et al. Quantifying dye tracers in soil profiles by image processing. Eur J Soil Sci, 2000, 51(2): 313–322
Bakker D M, Plunket G, Sherrard J. Application of efficiencies and furrow infiltration functions of irrigations in sugar cane in the Ord River irrigation area of North Western Australia and the Scope of the improvement. Agric Water Manage, 2006, 86(1–2): 162–172
Samakande I, Senzanje A, Manzungu E. Sustainable water management in smallholder irrigation schemes: Understanding the impact of field water management on maize productivity on two irrigation schemes in Zimbabwe. Phys Chem Earth, 2004, 29(15–18): 1075–1081
Al-Qinna M I, Abu-Awwad A M. Soil water storage and surface runoff as influenced by irrigation method in arid soils with surface crust. Agric Water Manage, 1998, 37(3): 189–203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the NSFC (Grant Nos. 50779098, 50579079) and the National Basic Research Program of China (“973” Project) (Grant No. 2006CB403404)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Zhang, R. & Sheng, F. Effects of irrigation efficiency on chemical transport processes. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 52, 3287–3292 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-009-0327-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-009-0327-6