Abstract
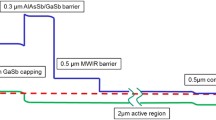
High performance 1.3 μm InGaAsN superluminescent diodes (SLDs) were fabricated with Schottky contact. The structure was grown by metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). Output power of 3 mW was obtained in continuous wave (CW) mode at room temperature. The full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the emission spectrum was 30 nm. The devices operated up to 100°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bohm K, Marten P, Petermann K, et al. Low-drift fibre gyro using a superluminescent diode. Electron Lett, 1981, 17: 352–353
Huang D, Swanson E A, Lin C P, et al. Optical coherence tomography. Science, 1991, 254: 1178–1181
Takada K, Yokohama I, Chida K, et al. New measurement system for fault location in optical waveguide devices based on an interferometric technique. Appl Opt, 1987, 26: 1603–1606
Sampson D D, Holloway W T. 100 mW spectrally uniform broadband ASE source for spectrum-sliced WDM systems. Electron Lett, 1994, 30(19): 1611–1612
Semenov T, Batovrin V K, Garmash I A, et al. (GaAl)As SQW superluminescent diodes with extremely low coherence length. Electron Lett, 1995, 31(4): 314–315
Takayama T, Imafuji O, Kouchi Y, et al. 100-mW high-power angled-stripe superluminescent diodes with a new real refractive-index-guides self-aligned structure. IEEE J Quant Electron, 1996, 32(11): 1981–1987
Lin C F, Lee B L. Extremely broadband AlGaAs/GaAs superluminescent diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 1997, 71(12): 1598–1600
Middlemast I, Sarma J, Yunus S. High power tapered superluminescent diodes using novel etched deflectors. Electron Lett, 1997, 33: 903–904
Gen-ei K, Tanioka A, Suhara H, et al. High coupled power 1.3 μm edge-emitting light-emitting diode with a rear window and an integrated absorber. Appl Phys Lett, 1988, 53(13): 1138–1140
Norman S, Kwong K, Bar-Chaim N. High-power 1.3 μm superluminescent diode. Appl Phys Lett, 1989, 54(4): 298–300
Nagai H, Noguchi Y, Sudo S. High-power, high-efficiency 1.3 μm superluminescent diode with a buried bent absorbing guide structure. Appl Phys Lett, 1989, 54(18): 1719–1721
Mikami O, Yasaka H, Noguchi Y. Broader spectral width InGaAsP stacked active layer superluminescent diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 1990, 56(11): 987–989
Kashima Y, Matoba A, Takano H. Performance and reliability of InGaAsP superluminescent diode. IEEE J Lightwave Technol, 1992, 10(11): 1644–1649
Holtmann C, Besse P A, Melchior H. High power superluminescent diodes for 1.3 μm wavelengths. Electron Lett, 1996, 32: 1705–1706
Wu B R, Fuh C, Laih L W, et al. Extremely broadband InGaAsP/InP superluminescent diodes. Electron Lett, 2000, 36: 2093–2095
Chen T R, Zhuang Y H, Xu Y J, et al. 1.5 μm InGaAsP/InP buried crescent superluminescent diode on a p-InP substrate. Appl Phys Lett, 1990, 56(25): 2502–2503
Noguchi Y, Yasaka H, Mikami O, et al. High-power, borad-band In-GaAsp superluminescent diode emitting at 1.5 μm. J Appl Phys, 1990, 67(5): 2665–2667
Song J H, Cho S H, Han I K, et al. High-power broad-band superluminescent diode with low spectral modulation at 1.5 μm wavelength. IEEE Photonic Tech L, 2000, 12(7): 783–785
Yamatoya T, Sekiguchi S, Koyama F, et al. High-power CW operation of GaInAsP/InP superluminescent light-emitting diode with tapered active region, Jpn. J Appl Phys, 2001, 40(7A): 678–680
Kaniewska M, Ratajczak J. Anomalies in characteristics of broad-contact ridge waveguide SCH-SQW lasers based on AlGaAs/InGaAs grown by MBE. Phys Status Solidi A, 2003, 195(1): 44–49
Li W, Turpeinen J, Manen P, et al. Effects of rapid thermal annealing on strain-compensated GaInNAs/GaAsP quantum well structures and lasers. Appl Phys Lett, 2001, 78(1): 91–93
Tansu N, Mawst L J. Low-reshold strain-compensated InGaAs(N) (λ= 1.19–1.31 μm) quantum-well lasers. IEEE Photonic Tech L, 2002, 14(4): 444–446
Qu Y, Yuan S, Liu C Y, et al. High-power InAlGaAs/GaAs and AlGaAs/GaAs semiconductor laser arrays emitting at 808 nm. IEEE Photonic Tech L, 2004, 16(2): 389–291
Yuan S, Kim Y, Jagadish C, et al. Anodic-oxide-induced interdiffusion in GaAs/AlGaAs quantum wells. J Appl Phys, 1998, 83(3): 1305–1311
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 60677008), and the Foundation of National Key Lab on High Power Semiconductor Laser (Grant No. 9140C3102060703)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Y., Li, H., Zhang, J.X. et al. High performance 1.3 μm InGaAsN superluminescent diodes. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 52, 2396–2399 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0233-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0233-3