Abstract
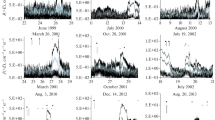
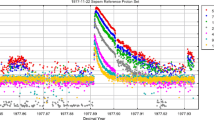
Fifty-five suprathermal particle events were selected from WIND observations between 1995 and 1999. Based on systematic analysis on the observational characteristics of these events a two-parameter (the rising time and the flux ratio of electrons to protons in each event) classification method was proposed to classify these events. The three classified classes are (1) impulsive electron events with the flux ratio of electrons to protons being bigger than 1 and rising time being shorter than 200 min, (2) impulsive proton events with the flux ratio being smaller than 1 and rising time being shorter than 200 min, and (3) gradual proton events with the flux ratio being smaller than 1 and the rising time being longer than 200 min. In the past, “impulsive solar electron events” were under intense research. However, because the selection standards of their velocity dispersions or pitch-angle distributions were inadequate, statistical surveys of selected events were different from each other and even some conclusions were not consistent with the theory, for example, the relation of type-III solar radio bursts to the “impulsive solar electron events”. The first class of impulsive electron events are associated with type-III radio bursts and with clear velocity dispersions; therefore they ought to originate from the Sun. The second class of the events, which have short continuance time and usually are not associated with type-III radio bursts and without velocity dispersion, are still far away from interplanetary shocks and most of them do not one-to-one correspond to corrotating interacting regions (CIRs); such events are possible results of local interplanetary magnetic field reconnection or electromagnetic disturbances. Finally, about 2/3 gradual proton events of the third class occur with interplanetary shocks, the delay times of which are almost equal to the rising time. Some of these events can be understood as particle accelerations by shocks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feldman W C, Asbridge J R, Bme S J, et al. Solar wind electrons. J Geophys Res, 1975, 80: 4181–4196
Van Allen J A, Krimigis S M. Impulsive emission of 40 keV electrons from the Sun. J Geophys Res, 1965, 70: 5737–5751
Anderson K A, Lin R P. Observation on the propagation of solar flare electrons in interplanetary space. Phys Rev Lett, 1966, 16: 1121–1124
Lin R P. Energetic solar electrons in the interplanetary medium. Solar Phys, 1985, 100: 537–561
Lin R P, Larson D, McFadden J, et al. Observation of an impulsive solar electron event extending down to ∼ 0.5 keV energy. Geophys Res Lett, 1996, 23: 1211
Lin, R P. Wind observations of suprathermal electrons in the interplanetary medium. Space Sci Rev, 1998, 86: 61–78
Ergun R E, Larson D, Lin R P, et al. Wind spacecraft observations of solar impulsive electron events associated with type-III radio bursts. Astrophys J, 1998, 503: 435
Krucker S, Larson D E, Lin R P, et al. On the origin of impulsive electron events observed at 1 AU. Astrophys J, 1999, 519: 864
Roelof E C, Haggerty D K. Impulsive near-relativistic solar electron events: delayed injection with respect to solar electromagnetic emission. Astrophys J, 2002, 579: 841
Simnett G M, Roelof E C, Haggerty D K. The acceleration and release of near-relativistic electrons by coronal mass ejections. Astrophys J, 2002, 579: 854
Kirsch E, Mall U. Suprathermal proton and alpha-particle bursts (E/q = 6.5–225 keV/e) observed by the WIND-, ACE-and IMP8-S/C during depressions of the interplanetary magnetic field. A&A, 2003, 400: 729
Lepreti F, Isliker H, Petraki K, et al. Quiet time particle acceleration in interplanetary space. A & A, 2005, 432: 1049–1056
Russell C T. The global geospace mission. Space Sci Rev, 1995, 71: 1–3
Posner A, Schwadron N A, McComas D J, et al. Suprathermal ions ahead of interplanetary shocks: new observations and critical instrumentation for future space weather monitoring. Space Weather, 2004, 2: S10004
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 10425312, 40574065 and 10333030), and the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 program) (Grant No. 2006CB806302), and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. KJCX2-YW-T04)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, L., Wu, D. & Wang, D. Suprathermal particle events observed by WIND spacecraft in interplanetary space during 1995–1999 and their classification. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 51, 1542–1553 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0137-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0137-2