Abstract
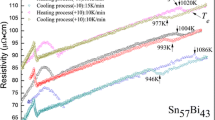
Evolution of the electrical resistivity of Sn-40wt%Bi melt with time under different overheating temperatures during isothermal experiments has been studied, and the relationship between different melt state, solidification behavior and solidified structure has also been investigated. The results show that the melt structure transition revealed by the abnormal change of resistivity would take place within a certain holding time just when the holding temperature is above a certain critical, and that the higher the temperature above the critical, the shorter the “incubation period” of the melt structure transition, and the faster the transition speed. The results of solidification experiments suggest that the melt structure transition caused by different holding time at the same temperature can lead to a higher solidification undercooling degree, finer grain size and change of microscopic pattern. Further exploration indicates that the solidification undercooling degree can come to a head when the melt is held at the specific temperature for a given time. The functionary mechanism of the phenomena above is also discussed briefly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen G, Yan Y B, Cui P, et al. Effect of melt superheating on solidified structure of a Sb-Bi alloy. Mater Sci Tech (in Chinese), 2001, 9(2): 113–116
Li P J, Nikitin V I, Kandalova E G, et al. Effect of overheating, cooling and solidification rates on Al-16wt.%Si alloy structure. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, 332: 371–374
Koh H J, Rudolph P, Schäfer N, et al. The effect of various thermal treatments on supercooling of PbTe melts. Mater Sci Eng B, 1995, 34: 199–203
Wang J, He S X, Sun B D, et al. Grain refinement of Al-Si alloy (A356) by melt thermal treatment. J Mater Process Tech, 2003, 141: 29–34
Zu F Q, Zhu Z G, Guo L J, et al. Liquid-liquid phase transition in Pb-Sn melts. Phys Rev B, 2001, 64:180–203
Zu F Q, Zhu Z G, Guo L J, et al. Observation of anomalous discontinuous liquid-structure change with temperature. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 89: 125–505
Shen R R, Zu F Q, Li Q, et al. Study on temperature dependence of resistivity in liquid In-Sn alloy. Phys Scr, 2006, 73: 184–187
Zu F Q, Li X F, Guo L J, et al. Temperature dependence of liquid structures in In-Sn20: diffraction experimental evidence. Phys Lett A, 2004, 324: 472–478
Kawakita Y, Takeda S, Inui M, et al. Structure and dynamical properties of liquid In2Te3. J Non-Crys Soli, 2002, 312–314: 366–370
Wang L, Bian X F, Liu J T. Discontinuous structural phase transition of liquid metal and alloys (1). Phys Lett A, 2004, 326: 429–435
Wang Y Q, Wu Y Q, Bian X F. Liquid-liquid structure transition in metallic melts: experimental evidence by viscosity measurement. Chin Phys Lett, 2007, 24: 2028–2031
Xi Y, Zu F Q, Liu L J, et al. Abnormal solidification of Pb-Sn alloy induced by liquid structure transition. Kovove Mater, 2005, 43: 432–439
Wang W M, Bian X F, Qin J Y, et al. The atomic-structure changes in Al-16%Si alloy above the liquidus. Metall Mater Tran A, 2000, 31A: 2163–2168
Asryan N A, Mikula A. Thermodynamic properties of Bi-Sn melts. Inorganic Mater, 2004, 40(4): 386–390
Hideyuki Yasuda, Itsuo Ohnaka, Koichi Kawasaki, et al. Direct observation of stray crystal formation in unidirectional solidification of Sn-Bi alloy by X-ray imaging. J Cry Grow, 2004, 262: 645–652
Decastro W B, Kiminami C S. Heterogeneous nucleation behavior in undercooled Sn-Bi alloys. J Mater Sci Lett, 1999, 18: 487–488
Li X F, Zu F Q, Ding H F, et al. High-temperature liquid-liquid structure transition in liquid Sn-Bi alloys: Experimental evidence by electrical resistivity method. Phy Lett A, 2006, 354: 325–329
Yu J, Zu F Q, Ding H F, et al. Design and application of instrument of electrical resistivity testing for solid-liquid metal during temperature continuous change (in Chinese). Chin J Rare Metals, 2004, 28(5): 880–884
Takamichi I, Roderick I L G. The Properties of Liquid Metals. New York: Oxford University Press Inc, 1988, 70–71
Dahlborg U, Calvo-Dahlborg M, Popel P S, et al. Structure and properties of some glass-forming liquid alloys. Eur Phys J B, 2000, 14: 639–648
Aoki H, Hotoduka K, Itami T. The hidden structure in liquid IIIB-VB alloys. J. Non-Cryst Solids, 2002, 312–314: 222–226
Okamoto H, Massalski T B. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams. ASM International, Metals Park, OH, 1990, 1: 796
Hu H Q. The Principle of Metal Solidification (in Chinese). Beijing: China Machine Press, 2000, 66–86
Zhou B. The Reversibility of the Liquid-Liquid Structure Transition and its Effect on the Solidification of Sn-Bi and Pb-Sb30% alloy (in Chinese). Master Dissertation. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2007. 20–30
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 50571033, 50371024) and the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province(Grant No.070414178)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Zu, F., Chen, J. et al. The effect of melt overheating on the melt structure transition and solidified structures of Sn-Bi40 alloy. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 51, 1402–1408 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0130-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0130-9