Abstract
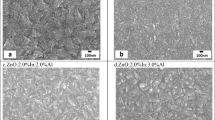
The effect of the annealing temperature T a on the optical, electrical and structural properties of the In2S3 films obtained by the spray pyrolysis method at 350°C substrate temperature was studied. All the In2S3 films annealed in the range from 100 to 400°C are polycrystalline with (220) preferential orientation. The resistivity decreases as T a increases until it reaches a value of 25 Ohm-cm for T a=400°C. The grain size also increases when T a increases as observed in data calculated from X-ray measurements. XRD data indicates that samples show microstructural perfection improvement as a function of annealing temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seyam M A M. Optical and electrical properties of indium monosulfide (InS) thin films. Vacuum, 2001, 63: 441–447
Hara K, Sayama K, Arakawa H. Semiconductor-sensitized solar cells based on nanocrystalline In2S3/In2O3 thin film electrodes. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 2001, 62: 441–447
Shay J L, Tell B. Energy band structure of I–III–VI2 semiconductors. Surf Sci, 1973, 37: 748–762
George J, Joseph K S, Prodeep B, et al. Reactively evaporated films of indium sulphide. Phys Status Solidi, Appl Res, 1988, 106: 123
Barreau N, Bernède J C, Marsillac S, et al. New Cd-free buffer layer deposited by PVD: In2S3 containing Na compounds. Thin Solid Films, 2003, 431: 326–329
Bube R H, McCarroll W H. Photoconductivity in indium sulfide powders and crystals. J Phys Chem Solids. 1959, 10(4): 333–335
Yukawa T, Kuwabara K, Koumoto K. Electrodeposition of CuInS2 from aqueous solution (II) electrodeposition of CuInS2 film. Thin Solid Films, 1996, 286: 151–153
Belgacem S, Amlouk M, Bennaceur R. The effect of Cu/In ratio on the structure of thin films of CuInS2 made by airless spraying (in French.). Rev Phys Appl, 1990, 25(12): 1213–1223
Kazuki I M, Nakamura T A, Arai E. Photochemical deposition of Se and CdSe films from aqueous solutions. Thin Solid Films, 2001, 384: 157–159
John T T, Bini S, Kashiwaba Y, et al. Characterization of spray pyrolysed indium sulfide thin films. Semicond Sci Technol, 2003, 18: 491
Kumaresan R, Ichimura M, Sato N, et al. Application of novel photochemical deposition technique for the deposition of indium sulfide. Mater Sci Eng B Solid-State Mater Adv Technol, 2002, 96: 37–42
Kamoun N, Bennaceur R, Amlouk M, et al. L. Optical properties of InS layers deposited using an airless spray technique. Phys Status Solidi (a), 1998, 169(1): 97–104
Bouguila N, Bouzouita H, Lacaze E, et al. Effet de la température de fabrication sur les propriétés structurales et morphologiques des couches épaisses de In2S3 “spray”. J Phys III France, 1997, 7(8): 1647–1660
Naghavi N, Henriquez R, Laptev V, et al. Growth studies and characterisation of In2S3 thin films deposited by atomic layer deposition (ALD). Appl Surf Sci, 2004, 222: 65–73
Asikainen T, Ritala M, Leskelä M. Growth of In2S3 thin films by atomic layer epitaxy. Appl Surf Sci, 1994, 82/83: 122–125
George J, Joseph K S, Pradeep B, et al. Reactively evaporated films of indium sulphide. Phys Status Solidi (a), 1988, 106(1): 123–131
El Shazly A A, Abd Elhady D, Metwally H S, et al. Electrical properties of β-In2S3 thin films. J Phys: Condensed Matter, 1998, 10(26): 5943
Guillén C, García T, Herrero J, et al. Tailoring growth conditions for modulated flux deposition of In2S3 thin films. Thin Solid Films, 2004, 451/452: 112–115
Diehl R, Nitsche R. Vapour growth of three In2S3 modifications by iodine transport. J Cryst Growth, 1975, 28: 306–310
Bessergenev V G, Ivanova E N, Kovalevskaya Yu A, etal. Electrical properties of conductive In2S3 and In2O3S films prepared from the In(S2COC3H7-iso)3 volatile precursor. Inorganic Mater, 1996, 32(6): 592
Hai-Ning C, Xi S Q, The fabrication of dipped CdS and sputtered ITO thin films for photovoltaic solar cells. Thin Film Solids, 1996, 288: 325–329
Morgan D V, Aliyu Y H, Bunce R. W, Salehi A. Annealing effects on opto-electronic properties of sputtered and thermally evaporated indium-tin-oxide films. Thin Solid Films, 2004, 84: 126–130
Bhatti M T, Rana A M, Khan A F. Characterization of rf-sputtered indium tin oxide thin films. Mater Chem Phys, 2004, 84: 126–130
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bedir, M., Öztas, M. Effect of air annealing on the optical electrical and structural properties of In2S3 films. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 51, 487–493 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0074-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0074-0