Abstract
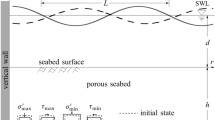
Two mechanisms for the wave-induced pore pressures in a porous seabed, i.e. oscillatory and residual excess pore pressures, have been observed in laboratory experiments and field measurements. Most previous investigations have focused on one of the mechanisms individually. In this paper, an analytical solution for the wave-induced residual pore pressure, which is not available yet, is derived, and compared with the existing experimental data. With the new solution, a parametric analysis is performed to clarify the applicable ranges of two mechanisms. Then, a simplified approximation for the prediction of wave-induced liquefaction potential is proposed for engineering practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christian J T, Taylor P K, Yen J K C, et al. Large diameter underwater pipeline for nuclear plant designed against soil liquefaction. In: The 10th Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, 1974, 597–606
Dunlap W, Bryant W R, Williams G N, et al. Storm wave effects on deltaic sediments—Results of SEAWAB I and II. Port and Ocean Engineering Under Arctic Conditions (POAC 79). Nerwegian Institute of Technology, 1979, 2: 899–920
Miyamoto T, Yoshinaga S, Soga F, et al. Seismic prospecting method applied to the detection of offshore breakwater units setting in the seabed. Coastal Engineering in Japan, 1989, 32: 103–112
Nago H, Maeno S, Matsumoto T, et al. Liquefaction and densification of loosely deposited sand bed under wave pressure variation. In: Proceedings of third (1993) International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, Singapore, 1993, 578–584
Yamamoto T, Koning H L, Sellmejjer H, et al. On the response of a poro-elastic bed to water waves. J Fluid Mech, 1978, 87: 193–206
Jeng D-S. Wave-Induced Seabed Response in Front of a Breakwater. PhD Thesis, The University of Western Australia, 1997
Seed H B, Rahman M S. Wave-induced pore pressure in relation to ocean floor stability of cohesionless soils. Marine Geotech, 1978, 3: 123–150
Sumer B M, Cheng N-S. A radom-walk model for pore pressure accumulation in marine soils. In: Proceedings 9th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference. ISOPE-99, Brest, France, 20 May–4 June, 1999, 521–526
Biot M A. General theory of three-dimensional consolidation. Journal of Applied Physics, 1941, 12(2): 155–164
Jeng D-S, Hsu J R C. Wave-induced soil response in a nearly saturated seabed of finite thickness. Geotech, 1996, 46: 427–440
Sumer B M, Fredsoe J. The Mechanics of Scour in the Marine Environment. New Jersey: World Scientific, Chapter 10, 2002. 445–520
McDough W G, Tsai Y T, Liu P L-F, et al. Wave-induced pore water pressure accumulation in marine soils. J Offshore Mech Arctic Engin, A.S.M.E., 1989, 111: 1–11
Clukey E C, Kulhawy F H, Liu P L-F. Laboratory and field investigation of wave-sediment interaction. Joseph H. Defrees Hydraulics Laboratory, Report 83-1, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, N. Y, 1983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 50509022 and 10532070) and the ‘Tenth Five-year Plan’ of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. KJCX2-SW-L03)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeng, D., Seymour, B., Gao, F. et al. Ocean waves propagating over a porous seabed: Residual and oscillatory mechanisms. SCI CHINA SER E 50, 81–89 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-007-2018-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-007-2018-5