Abstract
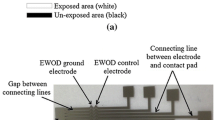
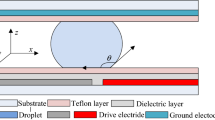
Electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD) is to directly control the wettability of liquids on the solid surface by applying the electric potential to the microelectrode array under the dielectric layer. The prototype of the EWOD droplet creator with the sandwiched structure is used: the droplet is sandwiched between the top and bottom plates; the bottom plate consists of silicon used as the substrate of the microelectrode array, nitride silicon film deposited by low pressure chemical vapor deposition as the dielectric layer and the fluorocarbon polymer film deposited by inductively coupled plasma chemical vapor deposition as the hydrophobic layer; and the top plate is the transparent electrode covered with the hydrophobic layer. To obtain the required minimum voltage, the process and the criterion of creating droplets are analyzed. At the voltage of 35 V the deionized water droplet surrounded in silicone oil is successfully created.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwartz, J. A., Vykoukal, J. V., Gascoyne, P. R. C., Droplet-based chemistry on a programmable micro-chip, Lab Chip, 2004, 4: 11–17.
Trimmer, W. S. N., Microrobots and micromechanical systems, Sensors and Actuators, 1989, 19(3): 267–287.
Adamson, A. W., Gast, A. P., Physical Chemistry of Surfaces, New York: John Wiley and Sons Inc., 1997.
Jun, T. K., Kim, C. J., Valveless pumping using traversing vapour bubbles in microchannels, Journal of Applied Physics, 1998, 83(11): 5658–5664.
Togo, H., Sato, M., Shimokawa, F., Multi-element thermo-capillary optical switch and sub-nanometer oil injection for its fabrication, Proceedings IEEE MEMS’ 99, 1998, 418–423.
Jones, T. B., On the relationship of dielectrophoresis and electrowetting, Langmuir, 2002, 18: 4437–4443.
Zeng, X. F., Yue, R. F., Wu, J. G. et al., Actuation and control of droplets by using electrowetting-on-dielectric, Chinese Physics Letter, 2004, 21(9): 1851–1854.
Pollack, M. G., Fair, R. B., Electrowetting-based actuation of liquid droplets for microfluidic application, Applied Physics Letter, 2000, 77(11): 1725–1726.
Cho, S. K., Moon, H., Kim, C. J., Creating, transporting, cutting, and merging liquid droplets by electrowetting-based actuation for digital microfluidic circuits, Journal of MicroElectroMechanical System, IEEE, 2003, 12(1): 70–80.
Lee, S. H., Lee, C. S., Kim, B. G. et al., Quantitatively controlled nanoliter liquid manipulation using hydrophobic valving and control of surface wettability, J. Micromech. Microeng., 2003, 13: 89–97.
Washizu, M., Electrostatic actuation of liquid droplets for micro-reactor applications, IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 1998, 34(4): 732–737.
Ajdari, A., Pumping liquids using asymmetric electrode arrays, Physical Review E, 2000, 61(1): 45–48.
Gallardo, B. S., Gupta, V. K., Eagerton, F. D. et al., Electrochemical principles for active control of liquids on submillimeter scales, Science, 1999, 283: 57–60.
Dupont Inc., Product Information: Teflon AF 1601S Amorphous Fluoropolymer Solutions, 234264C, February 1998.
Lippmann, M. G., Relations entre les phénomènes electriques et capillaries, Ann. Chim. Phys., 1875, 5(11): 494–549.
Peykov, V., Quinn, A., Ralston, J., Electrowetting: a model for contact-angle saturation, Colloid Polym. Sci., 2000, 278: 789–793.
Verheijen, H. J. J., Prins, M. W. J., Reversible electrowetting and trapping of charge: Model and experiments, Langmuir, 1999, 15: 6616–6620.
Vallet, M., Vallade, M., Berge, B., Limiting phenomena for the spreading of water on polymer films by electrowetting, The European Physical Journal B, 1999, 11: 583–591.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, X., Yue, R., Wu, J. et al. Droplet creator based on electrowetting-on-dielectric for lab on a chip. SCI CHINA SER E 49, 248–256 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-006-0248-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-006-0248-6