Abstract
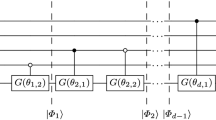
The miniaturization of transistors led to advances in computers mainly to speed up their computation. Such miniaturization has approached its fundamental limits. However, many practices require better computational resources than the capabilities of existing computers. Fortunately, the development of quantum computing brings light to solve this problem. We briefly review the history of quantum computing and highlight some of its advanced achievements. Based on current studies, the Quantum Computing Advantage (QCA) seems indisputable. The challenge is how to actualize the practical quantum advantage (PQA). It is clear that machine learning can help with this task. The method used for high accuracy surface modelling (HASM) incorporates reinforced machine learning. It can be transformed into a large sparse linear system and combined with the Harrow-Hassidim-Lloyd (HHL) quantum algorithm to support quantum machine learning. HASM has been successfully used with classical computers to conduct spatial interpolation, upscaling, downscaling, data fusion and model-data assimilation of eco-environmental surfaces. Furthermore, a training experiment on a supercomputer indicates that our HASM-HHL quantum computing approach has a similar accuracy to classical HASM and can realize exponential acceleration over the classical algorithms. A universal platform for hybrid classical-quantum computing would be an obvious next step along with further work to improve the approach because of the many known limitations of the HHL algorithm. In addition, HASM quantum machine learning might be improved by: (1) considerably reducing the number of gates required for operating HASM-HHL; (2) evaluating cost and benchmark problems of quantum machine learning; (3) comparing the performance of the quantum and classical algorithms to clarify their advantages and disadvantages in terms of accuracy and computational speed; and (4) the algorithms would be added to a cloud platform to support applications and gather active feedback from users of the algorithms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaronson S. 2015. Read the fine print. Nat Phys, 11: 291–293
Abigail L, Downs J A. 2021. Machine learning in geography—Past, present, and future. Geography Compass, 15, https://doi.org/10.1111/gec3.12563
Alaminos D, Salas M B, Fernández-Gámez M A. 2022. Quantum machine learning algorithms: Read the fine print. Comput Econ, 59: 803–829
Alkhasawneh M S, Ngah U K, Tay LT, Isa N AM. 2014. Determination of importance for comprehensive topographic factors on landslide hazard mapping using artificial neural network. Environ Earth Sci, 72: 787–799
Arute F, Arya K, Babbush R, Bacon D, Bardin J C, Barends R, Biswas R, Boixo S, Brandao F G S L, Buell D A, Burkett B, Chen Y, Chen Z, Chiaro B, Collins R, Courtney W, Dunsworth A, Farhi E, Foxen B, Fowler A, Gidney C, Giustina M, Graff R, Guerin K, Habegger S, Harrigan M P, Hartmann M J, Ho A, Hoffmann M, Huang T, Humble T S, Isakov S V, Jeffrey E, Jiang Z, Kafri D, Kechedzhi K, Kelly J, Klimov P V, Knysh S, Korotkov A, Kostritsa F, Landhuis D, Lindmark M, Lucero E, Lyakh D, Mandrà S, McClean J R, McEwen M, Megrant A, Mi X, Michielsen K, Mohseni M, Mutus J, Naaman O, Neeley M, Neill C, Niu M Y, Ostby E, Petukhov A, Platt J C, Quintana C, Rieffel E G, Roushan P, Rubin N C, Sank D, Satzinger K J, Smelyanskiy V, Sung K J, Trevithick M D, Vainsencher A, Villalonga B, White T, Yao Z J, Yeh P, Zalcman A, Neven H, Martinis J M. 2019. Quantum supremacy using a programmable superconducting processor. Nature, 574: 505–510
Bacon D. 2006. Operator quantum error-correcting subsystems for self-correcting quantum memories. Phys Rev A, 73: 012340
Benioff P. 1980. The computer as a physical system: A microscopic quantum mechanical Hamiltonian model of computers as represented by Turing machines. J Stat Phys, 22: 563–591
Bennett C H, Bernstein E, Brassard G, Vazirani U. 1997. Strengths and weaknesses of quantum computing. SIAM J Comput, 26: 1510–1523
Bennewitz E R, Hopfmueller F, Kulchytskyy B, Carrasquilla J, Ronagh P. 2022. Neural error mitigation of near-term quantum simulations. Nat Mach Intell, 4: 618–624
Biamonte J, Wittek P, Pancotti N, Rebentrost P, Wiebe N, Lloyd S. 2017. Quantum machine learning. Nature, 549: 195–202
Bravo-Prieto C, LaRose R, Cerezo M, Subasi Y, Cincio L,Coles P J. 2019. Variational quantum linear solver. DOI: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1909.05820
Brill K F, Uccellini L W, Manobianco J, Kocin P J, Homan J H. 1991 The use of successive dynamic initialization by nudging to simulate cyclogenesis during GALE IOP 1. Meteorl Atmos Phys, 45: 15–40
Bush A B G, Bishop M P, Huo D, Chi Z H, Tiwari U. 2020. Issues in climate analysis and modeling for understanding mountain erosion dynamics. Treatise Geomorphol, 1: 121–140, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818234-5.00022-5
Butt N, Epps K, Overman H, Iwamura T, Fragoso J M V. 2015. Assessing carbon stocks using indigenous peoples’ field measurements in Amazonian Guyana. For Ecol Manage, 338: 191–199
Caro M C, Huang H Y, Cerezo M, Sharma K, Sornborger A, Cincio L, Coles P J. 2022. Generalization in quantum machine learning from few training data. Nat Commun, 13: 4919
Cavender-Bares J, Schneider F D, Santos M J, Armstrong A, Carnaval A, Dahlin K M, Fatoyinbo L, Hurtt G C, Schimel D, Townsend P A, Ustin S L, Wang Z, Wilson A M. 2022. Integrating remote sensing with ecology and evolution to advance biodiversity conservation. Nat Ecol Evol, 6: 506–519
Chalumuri A, Kune R, Manoj B S. 2020. Training an artificial neural network using qubits as artificial neurons: A quantum computing approach. Procedia Comput Sci, 171: 568–575
Chambers J Q, Asner G P, Morton D C, Anderson L O, Saatchi S S, Espirito-Santo F D B, Palace M, Souza Jr C. 2007. Regional ecosystem structure and function: Ecological insights from remote sensing of tropical forests. Trends Ecol Evol, 22: 414–423
Chiesi M, Fibbi L, Genesio L, Gioli B, Magno R, Maselli F, Moriondo M, Vaccari F P. 2011. Integration of ground and satellite data to model Mediterranean forest processes. Int J Appl Earth Observation GeoInf, 13: 504–515
Cohen L Z, Kim I H, Bartlett S D, Brown B J. 2022. Low-overhead fault-tolerant quantum computing using long-range connectivity. Sci Adv, 8: eabn1717
Daley A J, Bloch I, Kokail C, Flannigan S, Pearson N, Troyer M, Zoller P. 2022. Practical quantum advantage in quantum simulation. Nature, 607: 667–676
Davis M. 1958. Computability and Unsolvability. New York: Dover Publications
Deshpande A, Mehta A, Vincent T, Quesada N, Hinsche M, Ioannou M, Madsen L, Lavoie J, Qi H, Eisert J, Hangleiter D, Fefferman B, Dhand I. 2022. Quantum computational advantage via high-dimensional Gaussian boson sampling. Sci Adv, 8: eabi7894
Deutsch D. 1985. Quantum theory, the Church-Turing principle and the universal quantum computer. Proc R Soc Lond A, 400: 97–117
Djaferis T E, Schick I C. 2000. System theory: Modeling, analysis, and control. Boston: Kluwer
Dobermann A, Ping J L. 2004. Geostatistical integration of yield monitor data and remote sensing improves yield maps. Agron J, 96: 285–297
Emili E, Popp C, Wunderle S, Zebisch M, Petitta M. 2011. Mapping particulate matter in alpine regions with satellite and ground-based measurements: An exploratory study for data assimilation. Atmos Environ, 45: 4344–4353
Farhi E, Gutmann S. 1998. Quantum computation and decision trees. Phys Rev A, 58: 915–928
Fawzi A, Balog M, Huang A, Hubert T, Romera-Paredes B, Barekatain M, Novikov A, R. Ruiz F J, Schrittwieser J, Swirszcz G, Silver D, Hassabis D, Kohli P. 2022. Discovering faster matrix multiplication algorithms with reinforcement learning. Nature, 610: 47–53
Feynman R P. 1982. Simulating physics with computers. Int J Theor Phys, 21: 467–488
Fritz S, McCallum I, Schill C, Perger C, See L, Schepaschenko D, van der Velde M, Kraxner F, Obersteiner M. 2012. Geo-Wiki: An online platform for improving global land cover. Environ Model Software, 31: 110–123
Grover L K. 1997. Quantum mechanics helps in searching for a needle in a haystack. Phys Rev Lett, 79: 325–328
Haber W. 2021. Eco-environmental surface modelling requires integration of both extrinsic and intrinsic informations. Sci China Earth Sci, 64: 185–186
Harrow A W, Hassidim A, Lloyd S. 2009. Quantum algorithm for linear systems of equations. Phys Rev Lett, 103: 150502
Hilbert D, von N J, Nordheim L. 1928. Ueber die Grundlagen der Quantenmechanik. Math Ann, 98: 1–30
Hull D J. 2003. Optimal Control Theory for Applications. New York: Springer
IPBES. 2016. The Methodological Assessment Report on Scenarios and Models of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Secretariat of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Bonn. 209–215
Kempe J. 2003. Quantum random walks: An introductory overview. Contemp Phys, 44: 307–327
Khrennikov A. 2021. Roots of quantum computing supremacy: Super-position, entanglement, or complementarity? Eur Phys J Spec Top, 230: 1053–1057
Li L, Wu K, Zhou D W. 2014. Extraction algorithm of mining subsidence information on water area based on support vector machine. Environ Earth Sci, 72: 3991–4000
Liu Z P, Shao M A, Wang Y Q. 2013. Large-scale spatial interpolation of soil pH across the Loess Plateau, China. Environ Earth Sci, 69: 2731–2741
Mandayam P, Ng H K. 2012. Towards a unified framework for approximate quantum error correction. Phys Rev A, 86: 012335
Medvidović M, Carleo G. 2021. Classical variational simulation of the quantum approximate optimization algorithm. Npj Quantum Information 7, 101, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41534-021-00440-z
Mooij H. 2005. The road to quantum computing. Science, 307: 1210–1211
Morrell Jr H J, Wong H Y. 2021. Step-by-step HHL algorithm walkthrough to enhance the understanding of critical quantum computing concepts. DOI: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2108.09004
Mueller N, Tarasov A, Venugopalan R. 2021 Computing real time correlation functions on a hybrid classical/quantum computer. Nucl Phys A, 1005: 121889
Nielsen M A, Chuang I L. 2010. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. New York: Cambridge University Press
Nimbe P, Weyori B A, Adekoya A F. 2021. Models in quantum computing: A systematic review. Quantum Inf Process, 20: 80
Pereira H M, Ferrier S, Walters M, Geller G N, Jongman R H G, Scholes R J, Bruford M W, Brummitt N, Butchart S H M, Cardoso A C, Coops N C, Dulloo E, Faith D P, Freyhof J, Gregory R D, Heip C, Höft R, Hurtt G, Jetz W, Karp D S, McGeoch M A, Obura D, Onoda Y, Pettorelli N, Reyers B, Sayre R, Scharlemann J P W, Stuart S N, Turak E, Walpole M, Wegmann M. 2013. Essential biodiversity variables. Science, 339: 277–278
Pereira L M, and other 32 coauthors. 2020. Developing multiscale and integrative nature-people scenarios using the nature futures framework. People Nature, 2: 1172–1195
Perelshtein M R, Pakhomchik A I, Melnikov A A, Novikov A A, Glatz A, Paraoanu G S, Vinokur V M, Lesovik G B. 2022. Solving large-scale linear systems of equations by a quantum Hybrid Algorithm. Annalen der Physik, 534: 2200082
Phillips J D. 2002. Global and local factors in earth surface systems. Ecol Model, 149: 257–272
Ponsar S, Luyten P, Dulière V. 2016. Data assimilation with the ensemble Kalman filter in a numerical model of the North Sea. Ocean Dyn, 66: 955–971
Rebentrost P, Bromley T R, Weedbrook C, Lloyd S. 2018. Quantum Hopfield neural network. Phys Rev A, 98: 042308
Rebentrost P, Mohseni M, Lloyd S. 2014. Quantum support vector machine for big data classification. Phys Rev Lett, 113: 130503
Rønnow T F, Wang Z, Job J, Boixo S, Isakov S V, Wecker D, Martinis J M, Lidar D A, Troyer M. 2014. Defining and detecting quantum speedup. Science, 345: 420–424
Shao C. 2018. Reconsider HHL algorithm and its related quantum machine learning algorithms. DOI: https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1803.01486.
Shi W, Liu J, Du Z, Stein A, Yue T. 2011. Surface modelling of soil properties based on land use information. Geoderma 162: 347–357
Shi W, Liu J, Du Z, Song Y, Chen C, Yue T. 2009. Surface modelling of soil pH. Geoderma, 150: 113–119
Shor P W. 1994. Algorithms for quantum computation: Discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science. New York. 124–134
Silver D, Hubert T, Schrittwieser J, Antonoglou I, Lai M, Guez A, Lanctot M, Sifre L, Kumaran D, Graepel T, Lillicrap T, Simonyan K, Hassabis D. 2018. A general reinforcement learning algorithm that masters chess, shogi, and Go through self-play. Science, 362: 1140–1144
Somasundaram D. 2005. Differential Geometry. Harrow: Alpha Science International Ltd
Srivastava P K, Han D, Rico-Ramirez M A, Bray M, Islam T, Gupta M, Dai Q. 2014. Estimation of land surface temperature from atmospherically corrected LANDSAT TM image using 6S and NCEP global reanalysis product. Environ Earth Sci, 72: 5183–5196
Turing A M. 1937. On computable numbers, with an application to the Entscheidungs-problem. Proc London Mathemat Soc, 42: 230–265
Waldrop M M. 2016. More than Moore. Nature, 530: 145–147
Wiebe N, Braun D, Lloyd S. 2012. Quantum algorithm for data fitting. Phys Rev Lett, 109: 050505
Yang W, Zheng Z, Zheng C, Lu K, Ding D, Zhu J. 2018. Temporal variations in a phytoplankton community in a subtropical reservoir: An interplay of extrinsic and intrinsic community effects. Sci Total Environ, 612: 720–727
Yue T X, Chen C F, Li B L. 2010a. An adaptive method of high accuracy surface modeling and its application to simulating elevation surfaces. Trans GIS, 14: 615–630
Yue T X, Chen C F, Li B L. 2012. A high-accuracy method for filling voids and its verification. Int J Remote Sens, 33: 2815–2830
Yue T X, Du Z P, Liu J Y. 2004. High accuracy surface modelling and its error analysis (in Chinese). Prog Phys Sci, 14: 300–306
Yue T X, Du Z P, Lu M, Fan Z M, Wang C L, Tian Y Z, Xu B. 2015c. Surface modeling of ecosystem responses to climatic change in Poyang Lake Basin of China. Ecol Model, 306: 16–23
Yue T X, Du Z P, Song D J, Gong Y. 2007. A new method of surface modeling and its application to DEM construction. Geomorphology, 91: 161–172
Yue T X, Liu Y, Du Z P, Wilson J, Zhao D Y, Wang Y, Zhao N, Shi W J, Fan Z M, Zhao X M, Zhang Q, Huang H S, Wu Q Y, Zhou W, Jiao Y M, Xu Z, Li S B, Yang Y, Fu B J. 2022. Quantum machine learning of eco-environmental surfaces. Sci Bull, 67: 1031–1033
Yue T X, Liu Y, Zhao M W, Du Z P, Zhao N. 2016a. A fundamental theorem of Earth’s surface modelling. Environ Earth Sci, 75: 751
Yue T X, Song D J, Du Z P, Wang W. 2010b. High-accuracy surface modelling and its application to DEM generation. Int J Remote Sens, 31: 2205–2226
Yue T X, Wang S H. 2010. Adjustment computation of HASM: A high-accuracy and high-speed method. Int J Geogr Inf Sci, 24: 1725–1743
Yue T X, Song Y J. 2008. The YUE-HASM method. In: Li D, Ge Y, Foody G M, eds. Accuracy in geomatics. Edgbaston, UK: World Academic Union. 148–153
Yue T X, Wang Y F, Du Z P, Zhao M W, Li Zhang L, Zhao N, Lu M, Larocque G R, Wilson J P. 2016c. Analysing the uncertainty of estimating forest carbon stocks in China. Biogeosciences, 13: 3991–4004
Yue T X, Zhang L L, Zhao N, Zhao M W, Chen C F, Du Z P, Song D J, Fan Z M, Shi W J, Wang S H, Yan C Q, Li Q Q, Sun X F, Yang H, Wilson J, Xu B. 2015a. A review of recent developments in HASM. Environ Earth Sci, 74: 6541–6549
Yue T X, Zhao M W, Zhang X Y. 2015b. A high-accuracy method for filling voids on remotely sensed XCO2 surfaces and its verification. J Cleaner Production, 103: 819–827
Yue T X, Zhao N, Fan Z M, Li J, Chen C F, Lu Y M, Wang C L, Xu B, Wilson J. 2016b. CMIP5 downscaling and its uncertainty in China. Glob Planet Change, 146: 30–37
Yue T X, Zhao N, Fan Z M, Li J, Chen C F, Lu Y M, Wang C L, Gao J, Xu B, Jiao Y M, Wilson J P. 2019. Methods for simulating climate scenarios with improved spatiotemporal specificity and less uncertainty. Glob Planet Change, 181: 102973
Yue T X, Zhao N, Liu Y, Wang Y F, Zhang B, Du Z P, Fan Z M, Shi W J, Chen C F, Zhao M W, Song D J, Wang S H, Song Y J, Yan C Q, Li Q Q, Sun X F, Zhang L L, Tian Y Z, Wang W, Wang Y A, Ma S N, Huang H S, Lu Y M, Wang Q, Wang C L, Wang Y Z, Lu M, Zhou W, Liu Y, Yin X Z, Wang Z, Bao Z Y, Zhao M M, Zhao Y P, Jiao Y M, Naseer U, Fan B, Li S B, Yang Y, Wilson J P. 2020. A fundamental theorem for eco-environmental surface modelling and its applications. Sci China Earth Sci, 63: 1092–1112
Yue T X, Zhao N, Ramsey R D, Wang C L, Fan Z M, Chen C F, Lu Y M, Li B L. 2013a. Climate change trend in China, with improved accuracy. Climatic Change, 120: 137–151
Yue T X, Zhao N, Yang H, Song Y J, Du Z P, Fan Z M, Song D J. 2013b. A multi-grid method of high accuracy surface modeling and its validation. Trans GIS, 17: 943–952
Yue T X. 2011. Surface Modelling: High Accuracy and High Speed Methods. New York: CRC Press
Zhong H S, Wang H, Deng Y H, Chen M C, Peng L C, Luo Y H, Qin J, Wu D, Ding X, Hu Y, Hu P, Yang X Y, Zhang W J, Li H, Li Y, Jiang X, Gan L, Yang G, You L, Wang Z, Li L, Liu N L, Lu C Y, Pan J W. 2020. Quantum computational advantage using photons. Science, 370: 1460–1463
Zhu Q, Cao S, Chen F, Chen M C, Chen X, Chung T H, Deng H, Du Y, Fan D, Gong M, Guo C, Guo C, Guo S, Han L, Hong L, Huang H L, Huo Y H, Li L, Li N, Li S, Li Y, Liang F, Lin C, Lin J, Qian H, Qiao D, Rong H, Su H, Sun L, Wang L, Wang S, Wu D, Wu Y, Xu Y, Yan K, Yang W, Yang Y, Ye Y, Yin J, Ying C, Yu J, Zha C, Zhang C, Zhang H, Zhang K, Zhang Y, Zhao H, Zhao Y, Zhou L, Lu C Y, Peng C Z, Zhu X, Pan J W. 2022. Quantum computational advantage via 60-qubit 24-cycle random circuit sampling. Sci Bull, 67: 240–245
Zidan M, Eleuch H, Abdel-Aty M. 2021. Non-classical computing problems: Toward novel type of quantum computing problems. Results Phys, 21: 103536
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor John Wilson for his useful recommendations. This work was supported by the Open Research Program of the International Research Center of Big Data for Sustainable Development Goals (Grant No. CBAS2022ORP02), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41930647, 72221002), and the Key Project of Innovation LREIS (Grant No. KPI005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, T., Wu, C., Liu, Y. et al. HASM quantum machine learning. Sci. China Earth Sci. 66, 1937–1945 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-022-1144-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-022-1144-7