Abstract
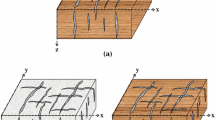
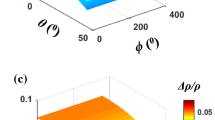
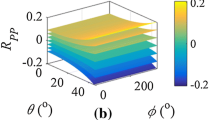
Based on the long-wavelength approximation, a set of parallel vertical fractures embedded in periodic thin interbeds can be regarded as an equivalent orthorhombic medium. Rock physics is the basis for constructing the relationship between fracture parameters and seismic response. Seismic scattering is an effective way to inverse anisotropic parameters. In this study, we propose a reliable method for predicting the Thomsen’s weak anisotropic parameters and fracture weaknesses in an orthorhombic fractured reservoir using azimuthal pre-stack seismic data. First, considering the influence of fluid substitution in mineral matrix, porosity, fractures and anisotropic rocks, we estimate the orthorhombic anisotropic stiffness coefficients by constructing an equivalent rock physics model for fractured rocks. Further, we predict the logging elastic parameters, Thomsen’s weak parameters, and fracture weaknesses to provide the initial model constraints for the seismic inversion. Then, we derive the P-wave reflection coefficient equation for the inversion of Thomsen’s weak anisotropic parameters and fracture weaknesses. Cauchy-sparse and smoothing-model constraint regularization taken into account in a Bayesian framework, we finally develop a method of amplitude variation with angles of incidence and azimuth (AVAZ) inversion for Thomsen’s weak anisotropic parameters and fracture weaknesses, and the model parameters are estimated by using the nonlinear iteratively reweighted least squares (IRLS) strategy. Both synthetic and real examples show that the method can directly estimate the orthorhombic characteristic parameters from the azimuthally pre-stack seismic data, which provides a reliable seismic inversion method for predicting Thomsen’s weak anisotropic parameters and fracture weaknesses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemie W, Sacchi M D. 2011. High-resolution three-term AVO inversion by means of a Trivariate Cauchy probability distribution. Geophysics, 76: R43–R55
Ba J. 2010. Wave propagation theory in double-porosity medium and experimental analysis on seismic responses (in Chinese). Sci China Earth Sci, 40: 1398–1409
Bachrach R. 2015. Uncertainty and nonuniqueness in linearized AVAZ for orthorhombic media. Leading Edge, 34: 1048–1056
Bachrach R, Sengupta M, Salama A, Miller P. 2009. Reconstruction of the layer anisotropic elastic parameters and high-resolution fracture characterization from P-wave data: A case study using seismic inversion and Bayesian rock physics parameter estimation. Geophys Prospect, 57: 253–262
Backus G E. 1962. Long-wave elastic anisotropy produced by horizontal layering. J Geophys Res, 67: 4427–4440
Bakulin A, Grechka V, Tsvankin I. 2000a. Estimation of fracture parameters from reflection seismic data—Part I: HTI model due to a single fracture set. Geophysics, 65: 1788–1802
Bakulin A, Grechka V, Tsvankin I. 2000b. Estimation of fracture parameters from reflection seismic data—Part II: Fractured models with orthorhombic symmetry. Geophysics, 65: 1803–1817
Bakulin A, Grechka V, Tsvankin I. 2002. Seismic inversion for the parameters of two orthogonal fracture sets in a VTI background medium. Geophysics, 67: 292–299
Batzle M L, Han D H, Hofmann R. 2006. Fluid mobility and frequencydependent seismic velocity—Direct measurements. Geophysics, 71: N1–N9
Biot M A. 1956a. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. I. Low-frequency range. J Acoust Soc Am, 28: 168–178
Biot M A. 1956b. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. II. Higher frequency range. J Acoust Soc Am, 28: 179–191
Brown R J S, Korringa J. 1975. On the dependence of the elastic properties of a porous rock on the compressibility of the pore fluid. Geophysics, 40: 608–616
Buland A, Omre H. 2003. Bayesian linearized AVO inversion. Geophysics, 68: 185–198
Chapman M. 2009. Modeling the effect of multiple sets of mesoscale fractures in porous rock on frequency-dependent anisotropy. Geophysics, 74: D97–D103
Chen H Z, Yin X Y, Gao J H, Liu B Y, Zhang G Z. 2015. Seismic inversion for underground fractures detection based on effective anisotropy and fluid substitution. Sci China Earth Sci, 58: 805–814
Chen H Z, Zhang G Z, Ji Y X, Yin X Y. 2017. Azimuthal seismic amplitude difference inversion for fracture weakness. Pure Appl Geophys, 174: 279–291
Cheng C H. 1978. Seismic velocities in porous rocks: Direct and inverse problems. Dissertation for Doctoral Degree. Cambridge: Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Cheng C H. 1993. Crack models for a transversely isotropic medium. J Geophys Res, 98: 675–684
Chichinina T, Obolentseva I, Gik L, Bobrov B, Ronquillo-Jarillo G. 2009. Attenuation anisotropy in the linear-slip model: Interpretation of physical modeling data. Geophysics, 74: WB165–WB176
Daubechies I, De Vore R, Fornasier M, Güntürk C S. 2010. Iteratively reweighted least squares minimization for sparse recovery. Comm Pure Appl Math, 63: 1–38
Downton J E, Roure B. 2015. Interpreting azimuthal Fourier coefficients for anisotropic and fracture parameters. Interpretation, 3: ST9–ST27
Dvorkin J, Nur A. 1993. Dynamic poroelasticity: A unified model with the squirt and the Biot mechanisms. Geophysics, 58: 524–533
Gassmann F. 1951. Uber die elastizitat poroser medien. Vier der Natur Gesellschaft in Zurich, 96: 1–23
Gurevich B. 2003. Elastic properties of saturated porous rocks with aligned fractures. J Appl Geophys, 54: 203–218
Hornby B E, Schwartz L M, Hudson J A. 1994. Anisotropic effectivemedium modeling of the elastic properties of shales. Geophysics, 59: 1570–1583
Hsu C J, Schoenberg M. 1993. Elastic waves through a simulated fractured medium. Geophysics, 58: 964–977
Huang L, Stewart R R, Sil S, Dyaur N. 2015. Fluid substitution effects on seismic anisotropy. J Geophys Res-Solid Earth, 120: 850–863
Hudson J A. 1981. Wave speeds and attenuation of elastic waves in material containing cracks. Geophys J Int, 64: 133–150
Liu E, Martinez A. 2012. Seismic Fracture Characterization. Amsterdam: EAGE Publication
Mallick S, Craft K L, Meister L J, Chambers R E. 1998. Determination of the principal directions of azimuthal anisotropy from P-wave seismic data. Geophysics, 63: 692–706
Mavko G, Mukerji T, Dvorkin J. 2009. The Rock Physics Handbook Tools for Seismic Analysis of Porous Media. 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge University Press
Parra J O. 1997. The transversely isotropic poroelastic wave equation including the Biot and the squirt mechanisms: Theory and application. Geophysics, 62: 309–318
Pšenčík I, Martins J L. 2001. Properties of weak contrast PP reflection/transmission coefficients for weakly anisotropic elastic media. Studia Geophys Geod, 45: 176–199
Rüger A. 1996. Reflection coefficients and azimuthal AVO analysis in anisotropic media. Dissertation for Doctoral Degree. Golden: Colorado School of Mines
Schoenberg M. 1980. Elastic wave behavior across linear slip interfaces. J Acoust Soc Am, 68: 1516–1521
Schoenberg M. 1983. Reflection of elastic waves from periodically stratified media with interfacial slip. Geophys Prospect, 31: 265–292
Schoenberg M, Helbig K. 1997. Orthorhombic media: Modeling elastic wave behavior in a vertically fractured earth. Geophysics, 62: 1954–1974
Shaw R K, Sen M K. 2004. Born integral, stationary phase and linearized reflection coefficients in weak anisotropic media. Geophys J Int, 158: 225–238
Shaw R K, Sen M K. 2006. Use of AVOA data to estimate fluid indicator in a vertically fractured medium. Geophysics, 71: C15–C24
Stolt R H, Weglein A B. 2012. Seismic Imaging and Inversion: Application of Linear Inverse Theory. New York: Cambridge University Press
Tang X M. 2011. A unified theory for elastic wave propagation through porous media containing cracks—An extension of Biot’s poroelastic wave theory. Sci China Earth Sci, 54: 1441–1452
Thomsen L. 1986. Weak elastic anisotropy. Geophysics, 51: 1954–1966
Thomsen L. 1995. Elastic anisotropy due to aligned cracks in porous rock1. Geophys Prospect, 43: 805–829
Thomsen L. 2002. Understanding seismic anisotropy in exploration and exploitation. SEG 2010 Distinguished Instructor Short Course
Tsvankin I. 1997. Anisotropic parameters and P-wave velocity for orthorhombic media. Geophysics, 62: 1292–1309
Wood A W. 1955. A Textbook of Sound. New York: McMillan Co
Wu R S, Aki K. 1985. Scattering characteristics of elastic waves by an elastic heterogeneity. Geophysics, 50: 582–595
Xu S, White R E. 1995. A new velocity model for clay-sand mixtures. Geophys Prospect, 43: 91–118
Xue J, Gu H M, Cai C G. 2015. General fracture weaknesses for quasistatic porous fractured media (in Chinese). OGP, 50: 1146–1153
Yang D H, Zhang Z J. 2000. Effects of the Biot and the squirt-flow coupling interaction on anisotropic elastic waves. Chin Sci Bull, 45: 2130–2138
Yang D H, Zhang Z J. 2002. Poroelastic wave equation including the Biot/squirt mechanism and the solid/fluid coupling anisotropy. Wave Motion, 35: 223–245
Yin X Y, Zong Z Y, Wu G C. 2014. Seismic wave scattering inversion for fluid factor of heterogeneous media. Sci China Earth Sci, 57: 542–549
Zhang G Z, Chen H Z, Wang Q, Yin X Y. 2013. Estimation of S-wave velocity and anisotropic parameters using fractured carbonate rock physics model (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 56: 1707–1715
Zong Z Y, Yin X Y, Wu G C. 2012. Fluid identification method based on compressional and shear modulus direct inversion (in Chinese). Chin J Geophys, 55: 284–292
Zong Z Y, Yin X Y, Wu G C. 2015a. Complex seismic amplitude inversion for P-wave and S-wave quality factors. Geophys J Int, 202: 564–577
Zong Z Y, Yin X Y, Wu G C, Wu Z P. 2015b. Elastic inverse scattering for fluid variation with time-lapse seismic data. Geophysics, 80: WA61–WA67
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, X., Zhang, G. & Yin, X. Azimuthally pre-stack seismic inversion for orthorhombic anisotropy driven by rock physics. Sci. China Earth Sci. 61, 425–440 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-017-9124-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-017-9124-6