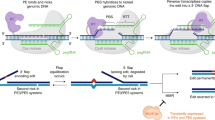
Abstract
Prime editing (PE) is a recent gene editing technology that can mediate insertions or deletions and all twelve types of base-to-base conversions. However, its low efficiency hampers the application in creating novel breeds and biomedical models, especially in pigs and other important farm animals. Here, we demonstrate that the pig genome is editable using the PE system, but the editing efficiency was quite low as expected. Therefore, we aimed to enhance PE efficiency by modulating both exogenous PE tools and endogenous pathways in porcine embryonic fibroblasts (PEFs). First, we modified the pegRNA by extending the duplex length and mutating the fourth thymine in a continuous sequence of thymine bases to cytosine, which significantly enhanced PE efficiency by improving the expression of pegRNA and targeted cleavage. Then, we targeted SAMHD1, a deoxynucleoside triphosphate triphosphohydrolase (dNTPase) that impedes the reverse transcription process in retroviruses, and found that treatment with its inhibitor, cephalosporin C zinc salt (CPC), increased PE efficiency up to 29-fold (4-fold on average), presumably by improving the reverse transcription process of Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase (M-MLV RT) in the PE system. Moreover, PE efficiency was obviously improved by treatment with a panel of histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACis). Among the four HDACis tested, panobinostat was the most efficient, with an efficiency up to 122-fold (7-fold on average), partly due to the considerable HDACi-mediated increase in transgene expression. In addition, the synergistic use of the three strategies further enhanced PE efficiency in PEFs. Our study provides novel approaches for optimization of the PE system and broadens the application scope of PE in agriculture and biomedicine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anzalone, A.V., Randolph, P.B., Davis, J.R., Sousa, A.A., Koblan, L.W., Levy, J.M., Chen, P.J., Wilson, C., Newby, G.A., Raguram, A., et al. (2019). Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature 576, 149–157.
Chen, B., Gilbert, L.A., Cimini, B.A., Schnitzbauer, J., Zhang, W., Li, G. W., Park, J., Blackburn, E.H., Weissman, J.S., Qi, L.S., et al. (2013). Dynamic imaging of genomic loci in living human cells by an optimized CRISPR/Cas system. Cell 155, 1479–1491.
Chen, P.J., Hussmann, J.A., Yan, J., Knipping, F., Ravisankar, P., Chen, P. F., Chen, C., Nelson, J.W., Newby, G.A., Sahin, M., et al. (2021). Enhanced prime editing systems by manipulating cellular determinants of editing outcomes. Cell 184, 5635–5652.e29.
Dang, Y., Jia, G., Choi, J., Ma, H., Anaya, E., Ye, C., Shankar, P., and Wu, H. (2015). Optimizing sgRNA structure to improve CRISPR-Cas9 knockout efficiency. Genome Biol 16, 280.
Gerdts, V., Wilson, H.L., Meurens, F., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk, S., Wilson, D., Walker, S., Wheler, C., Townsend, H., and Potter, A.A. (2015). Large animal models for vaccine development and testing. ILAR J 56, 53–62.
Goldsmith, M.E., Kitazono, M., Fok, P., Aikou, T., Bates, S., and Fojo, T. (2003). The histone deacetylase inhibitor FK228 preferentially enhances adenovirus transgene expression in malignant cells. Clin Cancer Res 9, 5394–5401.
Goldstone, D.C., Ennis-Adeniran, V., Hedden, J.J., Groom, H.C.T., Rice, G. I., Christodoulou, E., Walker, P.A., Kelly, G., Haire, L.F., Yap, M.W., et al. (2011). HIV-1 restriction factor SAMHD1 is a deoxynucleoside triphosphate triphosphohydrolase. Nature 480, 379–382.
Gutierrez, K., Dicks, N., Glanzner, W.G., Agellon, L.B., and Bordignon, V. (2015). Efficacy of the porcine species in biomedical research. Front Genet 6, 293.
Hwang, G.H., Jeong, Y.K., Habib, O., Hong, S.A., Lim, K., Kim, J.S., and Bae, S. (2021). PE-Designer and PE-Analyzer: web-based design and analysis tools for CRISPR prime editing. Nucleic Acids Res 49, W499–W504.
Isaac, R.S., Jiang, F., Doudna, J.A., Lim, W.A., Narlikar, G.J., and Almeida, R. (2016). Nucleosome breathing and remodeling constrain CRISPR-Cas9 function. Elife 5, e13450.
Jensen, K.T., Flee, L., Petersen, T.S., Huang, J., Xu, F., Bolund, L., Luo, Y., and Lin, L. (2017). Chromatin accessibility and guide sequence secondary structure affect CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing efficiency. FEBS Lett 591, 1892–1901.
Kitazono, M., Goldsmith, M.E., Aikou, T., Bates, S., and Fojo, T. (2001). Enhanced adenovirus transgene expression in malignant cells treated with the histone deacetylase inhibitor FR901228. Cancer Res 61, 6328–6330.
Landrum, M.J., Lee, J.M., Benson, M., Brown, G., Chao, C., Chitipiralla, S., Gu, B., Hart, J., Hoffman, D., Hoover, J., et al. (2016). ClinVar: public archive of interpretations of clinically relevant variants. Nucleic Acids Res 44, D862–D868.
Li, H., Li, J., Chen, J., Yan, L., and Xia, L. (2020). Precise modifications of both exogenous and endogenous genes in rice by prime editing. Mol Plant 13, 671–674.
Li, X., Zhou, L., Gao, B.Q., Li, G., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Wei, J., Han, W., Wang, Z., Li, J., et al. (2022). Highly efficient prime editing by introducing same-sense mutations in pegRNA or stabilizing its structure. Nat Commun 13, 1669.
Lin, Q., Jin, S., Zong, Y., Yu, H., Zhu, Z., Liu, G., Kou, L., Wang, Y., Qiu, J.L., Li, J., et al. (2021). High-efficiency prime editing with optimized, paired pegRNAs in plants. Nat Biotechnol 39, 923–927.
Lin, Q., Zong, Y., Xue, C., Wang, S., Jin, S., Zhu, Z., Wang, Y., Anzalone, A.V., Raguram, A., Doman, J.L., et al. (2020). Prime genome editing in rice and wheat. Nat Biotechnol 38, 582–585.
Liu, G., Yin, K., Zhang, Q., Gao, C., and Qiu, J.L. (2019). Modulating chromatin accessibility by transactivation and targeting proximal dsgRNAs enhances Cas9 editing efficiency in vivo. Genome Biol 20, 145.
Liu, N., Zhou, L., Lin, G., Hu, Y., Jiao, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, J., Yang, S., and Yao, S. (2022). HDAC inhibitors improve CRISPR-Cas9 mediated prime editing and base editing. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 29, 36–46.
Liu, P., Liang, S.Q., Zheng, C., Mintzer, E., Zhao, Y.G., Ponnienselvan, K., Mir, A., Sontheimer, E.J., Gao, G., Flotte, T.R., et al. (2021a). Improved prime editors enable pathogenic allele correction and cancer modelling in adult mice. Nat Commun 12, 2121.
Liu, Y., Li, X., He, S., Huang, S., Li, C., Chen, Y., Liu, Z., Huang, X., and Wang, X. (2020). Efficient generation of mouse models with the prime editing system. Cell Discov 6, 27.
Liu, Y., Yang, G., Huang, S., Li, X., Wang, X., Li, G., Chi, T., Chen, Y., Huang, X., and Wang, X. (2021b). Enhancing prime editing by Csy4-mediated processing of pegRNA. Cell Res 31, 1134–1136.
Lunney, J.K. (2007). Advances in swine biomedical model genomics. Int J Biol Sci 3, 179–184.
Nelson, J.W., Randolph, P.B., Shen, S.P., Everette, K.A., Chen, P.J., Anzalone, A.V., An, M., Newby, G.A., Chen, J.C., Hsu, A., et al. (2022). Engineered pegRNAs improve prime editing efficiency. Nat Biotechnol 40, 402–410.
Petri, K., Zhang, W., Ma, J., Schmidts, A., Lee, H., Horng, J.E., Kim, D.Y., Kurt, I.C., Clement, K., Hsu, J.Y., et al. (2022). CRISPR prime editing with ribonucleoprotein complexes in zebrafish and primary human cells. Nat Biotechnol 40, 189–193.
Qian, Y., Zhao, D., Sui, T., Chen, M., Liu, Z., Liu, H., Zhang, T., Chen, S., Lai, L., and Li, Z. (2021). Efficient and precise generation of Tay-Sachs disease model in rabbit by prime editing system. Cell Discov 7, 50.
Schene, I.F., Joore, I.P., Oka, R., Mokry, M., van Vugt, A.H.M., van Boxtel, R., van der Doef, H.P.J., van der Laan, L.J.W., Verstegen, M.M.A., van Hasselt, P.M., et al. (2020). Prime editing for functional repair in patient-derived disease models. Nat Commun 11, 5352.
Seamon, K.J., and Stivers, J.T. (2015). A high-throughput enzyme-coupled assay for SAMHD1 dNTPase. SLAS Discov 20, 801–809.
Song, M., Lim, J.M., Min, S., Oh, J.S., Kim, D.Y., Woo, J.S., Nishimasu, H., Cho, S.R., Yoon, S., and Kim, H.H. (2021). Generation of a more efficient prime editor 2 by addition of the Rad51 DNA-binding domain. Nat Commun 12, 5617.
Summerfield, A., Meurens, F., and Ricklin, M.E. (2015). The immunology of the porcine skin and its value as a model for human skin. Mol Immunol 66, 14–21.
Tang, X., Sretenovic, S., Ren, Q., Jia, X., Li, M., Fan, T., Yin, D., Xiang, S., Guo, Y., Liu, L., et al. (2020). Plant prime editors enable precise gene editing in rice cells. Mol Plant 13, 667–670.
Zhang, J.P., Yang, Z.X., Zhang, F., Fu, Y.W., Dai, X.Y., Wen, W., Zhang, B., Choi, H., Chen, W., Brown, M., et al. (2021). HDAC inhibitors improve CRISPR-mediated HDR editing efficiency in iPSCs. Sci China Life Sci 64, 1449–1462.
Zhang, Y., Hong, Q., Cao, C., Yang, L., Li, Y., Hai, T., Zhang, H., Zhou, Q., Sui, R., and Zhao, J. (2019). A novel porcine model reproduces human oculocutaneous albinism type II. Cell Discov 5, 48.
Zhang, Y., Xue, Y., Cao, C., Huang, J., Hong, Q., Hai, T., Jia, Q., Wang, X., Qin, G., Yao, J., et al. (2017). Thyroid hormone regulates hematopoiesis via the TR-KLF9 axis. Blood 130, 2161–2170.
Zong, Y., Liu, Y., Xue, C., Li, B., Li, X., Wang, Y., Li, J., Liu, G., Huang, X., Cao, X., et al. (2022). An engineered prime editor with enhanced editing efficiency in plants. Nat Biotechnol 40, 1394–1402.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFA0509503, 2022YFF0710703, 2021YFA0805902), the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (31925036, 32025034), the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by the China Association for Science and Technology (2019QNRC001), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31801031), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA16030304) and Lingnan Modern Agriculture Project (NT2021005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Y., Zhang, Y., Tian, S. et al. An optimized prime editing system for efficient modification of the pig genome. Sci. China Life Sci. 66, 2851–2861 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2334-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2334-y