Abstract
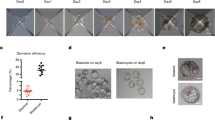
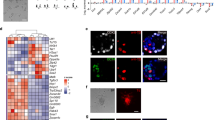
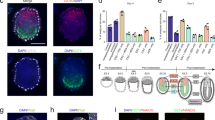
Mammalian embryogenesis begins with a totipotent zygote. Blastocyst-like structures can be captured by aggregated cells with extended pluripotent properties in a three-dimensional (3D) culture system. However, the efficiency of generating blastoids is low, and it remains unclear whether other reported totipotent-like stem cells retain a similar capacity. In this study, we demonstrated that spliceosomal repression-induced totipotent blastomere-like cells (TBLCs) form blastocyst-like structures within around 80% of all microwells. In addition, we generated blastoids initiating from a single TBLC. TBLC-blastoids express specific markers of constituent cell lineages of a blastocyst and resemble blastocyst in cell-lineage allocation. Moreover, single-cell RNA sequencing revealed that TBLC-blastoids share a similar transcriptional profile to natural embryos, albeit composed of fewer primitive endoderm-like cells. Furthermore, TBLC-blastoids can develop beyond the implantation stage in vitro and induce decidualization in vivo. In summary, our findings provided an alternative cell type to efficiently generate blastoids for the study of early mouse embryogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All raw sequencing data can be accessed at the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) (accession number: GSE197779). The raw count of scRNA-sequencing data of E3.5–E7.5 embryos (in-house data) can be found in the Supplementary File.
References
Bedzhov, I., Leung, C.Y., Bialecka, M., and Zernicka-Goetz, M. (2014). In vitro culture of mouse blastocysts beyond the implantation stages. Nat Protoc 9, 2732–2739.
Bradley, A., Evans, M., Kaufman, M.H., and Robertson, E. (1984). Formation of germ-line chimaeras from embryo-derived teratocarcinoma cell lines. Nature 309, 255–256.
Dobin, A., Davis, C.A., Schlesinger, F., Drenkow, J., Zaleski, C., Jha, S., Batut, P., Chaisson, M., and Gingeras, T.R. (2013). STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 29, 15–21.
Evans, M.J., and Kaufman, M.H. (1981). Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature 292, 154–156.
Frias-Aldeguer, J., Kip, M., Vivié, J., Li, L., Alemany, A., Korving, J., Darmis, F., van Oudenaarden, A., Geijsen, N., and Rivron, N.C. (2020). Embryonic signals perpetuate polar-like trophoblast stem cells and pattern the blastocyst axis. bioRxiv, 510362.
Goossens, K., Van Soom, A., Van Poucke, M., Vandaele, L., Vandesompele, J., Van Zeveren, A., and Peelman, L.J. (2007). Identification and expression analysis of genes associated with bovine blastocyst formation. BMC Dev Biol 7, 64.
Hao, Y., Hao, S., Andersen-Nissen, E., Mauck Iii, W.M., Zheng, S., Butler, A., Lee, M.J., Wilk, A.J., Darby, C., Zager, M., et al. (2021). Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell 184, 3573–3587.e29.
Harrison, S.E., Sozen, B., Christodoulou, N., Kyprianou, C., and Zernicka-Goetz, M. (2017). Assembly of embryonic and extraembryonic stem cells to mimic embryogenesis in vitro. Science 356.
Hesse, M., Franz, T., Tamai, Y., Taketo, M.M., and Magin, T.M. (2000). Targeted deletion of keratins 18 and 19 leads to trophoblast fragility and early embryonic lethality. EMBO J 19, 5060–5070.
Huang, B., Hu, J., Peng, X., Huang, Q., Peng, L., Deng, E., Barakat, T.S., Chen, J., Pei, D., Fan, X., et al. (2022). Modulation of HDAC activity directly reprogramme embryonic stem cell to trophoblast stem cell. SSRN J, doi: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4017898.
Kruithof-de Julio, M., Alvarez, M.J., Galli, A., Chu, J., Price, S.M., Califano, A., and Shen, M.M. (2011). Regulation of extra-embryonic endoderm stem cell differentiation by Nodal and Cripto signaling. Development 138, 3885–3895.
Kunath, T., Arnaud, D., Uy, G.D., Okamoto, I., Chureau, C., Yamanaka, Y., Heard, E., Gardner, R.L., Avner, P., and Rossant, J. (2005). Imprinted X-inactivation in extra-embryonic endoderm cell lines from mouse blastocysts. Development 132, 1649–1661.
Kunath, T., Strumpf, D., and Rossant, J. (2004). Early trophoblast determination and stem cell maintenance in the mouse—a review. Placenta 25, S32–S38
Li, R., Zhong, C., Yu, Y., Liu, H., Sakurai, M., Yu, L., Min, Z., Shi, L., Wei, Y., Takahashi, Y., et al. (2019). Generation of blastocyst-like structures from mouse embryonic and adult cell cultures. Cell 179, 687–702.e18.
Love, M.I., Huber, W., and Anders, S. (2014). Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15, 550.
Macfarlan, T.S., Gifford, W.D., Driscoll, S., Lettieri, K., Rowe, H.M., Bonanomi, D., Firth, A., Singer, O., Trono, D., and Pfaff, S.L. (2012). Embryonic stem cell potency fluctuates with endogenous retrovirus activity. Nature 487, 57–63.
McGrath, J., and Solter, D. (1984). Completion of mouse embryogenesis requires both the maternal and paternal genomes. Cell 37, 179–183.
Niakan, K.K., Schrode, N., Cho, L.T.Y., and Hadjantonakis, A.K. (2013). Derivation of extraembryonic endoderm stem (XEN) cells from mouse embryos and embryonic stem cells. Nat Protoc 8, 1028–1041.
Ohinata, Y., Endo, T.A., Sugishita, H., Watanabe, T., Iizuka, Y., Kawamoto, Y., Saraya, A., Kumon, M., Koseki, Y., Kondo, T., et al. (2022). Establishment of mouse stem cells that can recapitulate the developmental potential of primitive endoderm. Science 375, 574–578.
Posfai, E., Schell, J.P., Janiszewski, A., Rovic, I., Murray, A., Bradshaw, B., Yamakawa, T., Pardon, T., El Bakkali, M., Talon, I., et al. (2021). Evaluating totipotency using criteria of increasing stringency. Nat Cell Biol 23, 49–60.
Rivron, N.C., Frias-Aldeguer, J., Vrij, E.J., Boisset, J.C., Korving, J., Vivié, J., Truckenmüller, R.K., van Oudenaarden, A., van Blitterswijk, C.A., and Geijsen, N. (2018). Blastocyst-like structures generated solely from stem cells. Nature 557, 106–111.
Rossant, J. (2008). Stem cells and early lineage development. Cell 132, 527–531.
Rossant, J., and Tam, P.P.L. (2009). Blastocyst lineage formation, early embryonic asymmetries and axis patterning in the mouse. Development 136, 701–713.
Saiz, N., and Plusa, B. (2013). Early cell fate decisions in the mouse embryo. Reproduction 145, R65–R80.
Schwarz, N., Windoffer, R., Magin, T.M., and Leube, R.E. (2015). Dissection of keratin network formation, turnover and reorganization in living murine embryos. Sci Rep 5, 9007.
Shen, H., Yang, M., Li, S., Zhang, J., Peng, B., Wang, C., Chang, Z., Ong, J., and Du, P. (2021). Mouse totipotent stem cells captured and maintained through spliceosomal repression. Cell 184, 2843–2859.e20.
Sozen, B., Amadei, G., Cox, A., Wang, R., Na, E., Czukiewska, S., Chappell, L., Voet, T., Michel, G., Jing, N., et al. (2018). Self-assembly of embryonic and two extra-embryonic stem cell types into gastrulating embryo-like structures. Nat Cell Biol 20, 979–989.
Sozen, B., Cox, A.L., De Jonghe, J., Bao, M., Hollfelder, F., Glover, D.M., and Zernicka-Goetz, M. (2019). Self-organization of mouse stem cells into an extended potential blastoid. Dev Cell 51, 698–712.e8.
Tanaka, S., Kunath, T., Hadjantonakis, A.K., Nagy, A., and Rossant, J. (1998). Promotion of trophoblast stem cell proliferation by fgf4. Science 282, 2072–2075.
Tarkowski, A.K. (1961). Mouse chimæras developed from fused eggs. Nature 190, 857–860.
Wu, T., Hu, E., Xu, S., Chen, M., Guo, P., Dai, Z., Feng, T., Zhou, L., Tang, W., Zhan, L., et al. (2021). clusterProfiler 4.0: a universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2, 100141.
Xu, Y., Zhao, J., Ren, Y., Wang, X., Lyu, Y., Xie, B., Sun, Y., Yuan, X., Liu, H., Yang, W., et al. (2022). Derivation of totipotent-like stem cells with blastocyst-like structure forming potential. Cell Res 32, 513–529.
Yang, J., Ryan, D.J., Wang, W., Tsang, J.C.H., Lan, G., Masaki, H., Gao, X., Antunes, L., Yu, Y., Zhu, Z., et al. (2017a). Establishment of mouse expanded potential stem cells. Nature 550, 393–397.
Yang, Y., Liu, B., Xu, J., Wang, J., Wu, J., Shi, C., Xu, Y., Dong, J., Wang, C., Lai, W., et al. (2017b). Derivation of pluripotent stem cells with in vivo embryonic and extraembryonic potency. Cell 169, 243–257.e25.
Zenker, J., White, M.D., Gasnier, M., Alvarez, Y.D., Lim, H.Y.G., Bissiere, S., Biro, M, and Plachta, N. (2018). Expanding actin rings zipper the mouse embryo for blastocyst formation. Cell 173, 776–791.e17.
Zhang, Y., Parmigiani, G., and Johnson, W.E. (2020). ComBat-seq: batch effect adjustment for RNA-seq count data. NAR Genom Bioinf 2.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Peng Du (Peking University) for their TC1-EGFP ESCs and TC1-EGFP TBLCs, thank Dr. Jiekai Chen and Dr. Duanqing Pei for their single-cell RNA-seq data of blastocysts, and thank Dr. Xudong Fu (Zhejiang University) for his helpful comments on this manuscript. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Materials availability
All unique/stable reagents generated in this study are available from the Lead Contact with a completed Materials Transfer Agreement.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Zhai, X., Huang, B. et al. Highly efficient generation of blastocyst-like structures from spliceosomes-repressed mouse totipotent blastomere-like cells. Sci. China Life Sci. 66, 423–435 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2209-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2209-3