Abstract
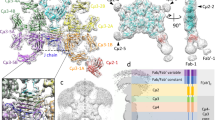
Human alpha-2-macroglobulin is a well-known inhibitor of a broad spectrum of proteases and plays important roles in immunity, inflammation, and infections. Here, we report the cryo-EM structures of human alpha-2-macroglobulin in its native state, induced state transformed by its authentic substrate, human trypsin, and serial intermediate states between the native and fully induced states. These structures exhibit distinct conformations, which reveal the dynamic transformation of alpha-2-macro-globulin that acts as a protease inhibitor. The results shed light on the molecular mechanism of alpha-2-macroglobulin in entrapping substrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimura, Y., and Funabiki, H. (2021). Structural mechanics of the alpha-2-macroglobulin transformation. J Mol Biol 434, 167413.
Asplin, I.R., Wu, S.M., Mathew, S., Bhattacharjee, G., and Pizzo, S.V. (2001). Differential regulation of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family by α2-macroglobulin: evidence for selective modulation of FGF-2-induced angiogenesis. Blood 97, 3450–3457.
Barrett, A.J., Brown, M.A., and Sayers, C.A. (1979). The electrophoretically “slow” and “fast” forms of the α2-macroglobulin molecule. Biochem J 181, 401–418.
Blacker, D., Wilcox, M.A., Laird, N.M., Rodes, L., Horvath, S.M., Go, R. C.P., Perry, R., Watson Jr. B., Bassett, S.S., McInnis, M.G., et al. (1998). Alpha-2 macroglobulin is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet 19, 357–360.
Borth, W., and Luger, T.A. (1989). Identification of α2-macroglobulin as a cytokine binding plasma protein. J Biol Chem 264, 5818–5825.
Bu, G., Williams, S., Strickland, D.K., and Schwartz, A.L. (1992). Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor is an hepatic receptor for tissue-type plasminogen activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89, 7427–7431.
Cáceres, L.C., Bonacci, G.R., Sánchez, M.C., and Chiabrando, G.A. (2010). Activated α2 macroglobulin induces matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression by low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 through MAPK-ERK1/2 and NF-κB activation in macrophage-derived cell lines. J Cell Biochem 111, 607–617.
Cater, J.H., Wilson, M.R., and Wyatt, A.R. (2019). Alpha-2-macroglobulin, a hypochlorite-regulated chaperone and immune system modulator. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019, 1–9.
Chuang, W.H., Liu, P.C., Hung, C.Y., and Lee, K.K. (2014). Purification, characterization and molecular cloning of alpha-2-macroglobulin in cobia, Rachycentron canadum. Fish Shellfish Immunol 41, 346–355.
Dodds, A.W., Ren, X.D., Willis, A.C., and Law, S.K.A. (1996). The reaction mechanism of the internal thioester in the human complement component C4. Nature 379, 177–179.
Dolmer, K., Huang, W., and Gettins, P.G.W. (2000). NMR solution structure of complement-like repeat CR3 from the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem 275, 3264–3269.
Dursun, E., Gezen-Ak, D., Hanağasi, H., Bilgiç, B., Lohmann, E., Ertan, S., Atasoy, İ.L., Alaylioğlu, M., Araz, Ö.S., Önal, B., et al. (2015). The interleukin 1 alpha, interleukin 1 beta, interleukin 6 and alpha-2-macroglobulin serum levels in patients with early or late onset Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment or Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroimmunol 283, 50–57.
Emsley, P., Lohkamp, B., Scott, W.G., and Cowtan, K. (2010). Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystlogr D Biol Crystlogr 66, 486–501.
Fredslund, F., Jenner, L., Husted, L.B., Nyborg, J., Andersen, G.R., and Sottrup-Jensen, L. (2006). The structure of bovine complement component 3 reveals the basis for thioester function. J Mol Biol 361, 115–127.
Fyfe, C.D., Grinter, R., Josts, I., Mosbahi, K., Roszak, A.W., Cogdell, R.J., Wall, D.M., Burchmore, R.J.S., Byron, O., and Walker, D. (2015). Structure of protease-cleaved Escherichia coli α-2-macroglobulin reveals a putative mechanism of conformational activation for protease entrapment. Acta Crystlogr D Biol Crystlogr 71, 1478–1486.
Galliano, M.F., Toulza, E., Gallinaro, H., Jonca, N., Ishida-Yamamoto, A., Serre, G., and Guerrin, M. (2006). A novel protease inhibitor of the α2-macroglobulin family expressed in the human epidermis. J Biol Chem 281, 5780–5789.
Garcia-Ferrer, I., Arêde, P., Gómez-Blanco, J., Luque, D., Duquerroy, S., Castón, J.R., Goulas, T., and Gomis-Rüth, F.X. (2015). Structural and functional insights into Escherichia coli α2-macroglobulin endopeptidase snap-trap inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 8290–8295.
Gettins, P.G.W., Beechem, J.M., and Crews, B.C. (1993). α2-Macroglobulin bait region integrity. FEBS Lett 325, 267–270.
Gettins, P.G.W., Crews, B., Beth, A.H., and Hideg, K. (1995). Bait region-thiol ester mapping in human α2-macroglobulin. FEBS Lett 367, 137–140.
Harthun, N.L., Weaver, A.M., Brinckerhoff, L.H., Deacon, D.H., Gonias, S. L., and Slingluff Jr., C.L. (1998). Activated α2-macroglobulin reverses the immunosuppressive activity in human breast cancer cell-conditioned medium by selectively neutralizing transforming growth factor-β in the presence of interleukin-2. J Immunother 21, 85–94.
Harwood, S.L., Lyngsø, J., Zarantonello, A., Kjøge, K., Nielsen, P.K., Andersen, G.R., Pedersen, J.S., and Enghild, J.J. (2021). Structural investigations of human A2M identify a hollow native conformation that underlies its distinctive protease-trapping mechanism. Mol Cell Proteomics 20, 100090.
He, H., McCartney, D.J., Wei, Q., Esadeg, S., Zhang, J., Foster, R.A., Hayes, M.A., Tayade, C., Van Leuven, F., and Croy, B.A. (2005). Characterization of a murine alpha 2 macroglobulin gene expressed in reproductive and cardiovascular tissue1. Biol Reprod 72, 266–275.
Hibbetts, K., Hines, B., and Williams, D. (1999). An overview of proteinase inhibitors. J Vet Internal Med 13, 302–308.
Holtet, T.L., Nielsen, K.L., Etzerodt, M., Moestrup, S.K., Gliemann, J., Sottrup-Jensen, L., and Thøgersen, H.C. (1994). Receptor-binding domain of human α2-macroglobulin expression, folding and biochemical characterization of a high-affinity recombinant derivative. FEBS Lett 344, 242–246.
Janssen, B.J.C., Huizinga, E.G., Raaijmakers, H.C.A., Roos, A., Daha, M. R., Nilsson-Ekdahl, K., Nilsson, B., and Gros, P. (2005). Structures of complement component C3 provide insights into the function and evolution of immunity. Nature 437, 505–511.
Kidmose, R.T., Laursen, N.S., Dobó, J., Kjaer, T.R., Sirotkina, S., Yatime, L., Sottrup-Jensen, L., Thiel, S., Gál, P., and Andersen, G.R. (2012). Structural basis for activation of the complement system by component C4 cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, 15425–15430.
Kimanius, D., Forsberg, B.O., Scheres, S.H., and Lindahl, E. (2016). Accelerated cryo-EM structure determination with parallelisation using GPUs in RELION-2. eLife 5, e18722.
Kolodziej, S.J., Wagenknecht, T., Strickland, D.K., and Stoops, J.K. (2002). The three-dimensional structure of the human α2-macroglobulin dimer reveals its structural organization in the tetrameric native and chymotrypsin α2-macroglobulin complexes. J Biol Chem 277, 28031–28037.
LaMarre, J., Wollenberg, G.K., Gonias, S.L., and Hayes, M.A. (1991). Cytokine binding and clearance properties of proteinase-activated alpha 2-macroglobulins. Lab Invest 65, 3–14.
Le, B.V., Williams, M., Logarajah, S., and Baxter, R.H.G. (2012). Molecular basis for genetic resistance of Anopheles gambiae to Plasmodium: structural analysis of TEP1 susceptible and resistant alleles. PLoS Pathog 8, e1002958.
Liebschner, D., Afonine, P.V., Baker, M.L., Bunkóczi, G., Chen, V.B., Croll, T.I., Hintze, B., Hung, L.W., Jain, S., McCoy, A.J., et al. (2019). Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: recent developments in Phenix. Acta Crystlogr D Struct Biol 75, 861–877.
Liu, Q., Ling, T.Y., Shieh, H.S., Johnson, F.E., Huang, J.S., and Huang, S.S. (2001). Identification of the high affinity binding site in transforming growth factor-β involved in complex formation with α2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem 276, 46212–46218.
Luque, D., Goulas, T., Mata, C.P., Mendes, S.R., Gomis-Rüth, F.X., and Castón, J.R. (2022). Cryo-EM structures show the mechanistic basis of pan-peptidase inhibition by human α2-macroglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 119, e2200102119.
Marrero, A., Duquerroy, S., Trapani, S., Goulas, T., Guevara, T., Andersen, G.R., Navaza, J., Sottrup-Jensen, L., and Gomis-Rüth, F.X. (2012). The crystal structure of human α2-macroglobulin reveals a unique molecular cage. Angew Chem Int Ed 51, 3340–3344.
Meyer, C., Hinrichs, W., and Hahn, U. (2012). Human α2-macroglobulin-another variation on the venus flytrap. Angew Chem Int Ed 51, 5045–5047.
Misra, U.K., and Pizzo, S.V. (2015). Activated α2-macroglobulin binding to human prostate cancer cells triggers insulin-like responses. J Biol Chem 290, 9571–9587.
Nielsen, K.L., Holtet, T.L., Etzerodt, M., Moestrup, S.K., Gliemann, J., Sottrup-Jensen, L., and Thogersen, H.C. (1996). Identification of residues in α-macroglobulins important for binding to the α2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem 271, 12909–12912.
Okubo, H., Ishibashi, H., Shibata, K., Tsuda-Kawamura, K., and Yanase, T. (1984). Distribution of α2-macroglobulin in normal, inflammatory, and tumor tissues in rats. Inflammation 8, 171–179.
Panyutich, A., and Ganz, T. (1991). Activated α2-macroglobulin is a principal defensin-binding protein. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 5, 101–106.
Peslova, G., Petrak, J., Kuzelova, K., Hrdy, I., Halada, P., Kuchel, P.W., Soe-Lin, S., Ponka, P., Sutak, R., Becker, E., et al. (2009). Hepcidin, the hormone of iron metabolism, is bound specifically to α-2-macroglobulin in blood. Blood 113, 6225–6236.
Pettersen, E.F., Goddard, T.D., Huang, C.C., Couch, G.S., Greenblatt, D. M., Meng, E.C., and Ferrin, T.E. (2004). UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25, 1605–1612.
Pettersen, E.F., Goddard, T.D., Huang, C.C., Meng, E.C., Couch, G.S., Croll, T.I., Morris, J.H., and Ferrin, T.E. (2021). UCSF ChimeraX: structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci 30, 70–82.
Pochon, F., Tourbez, M., Favaudon, V., and Delain, E. (1987). Covalent and non-covalent interaction of chymotrypsin with α2-macroglobulin. FEBS Lett 217, 101–105.
Punjani, A., Rubinstein, J.L., Fleet, D.J., and Brubaker, M.A. (2017). cryoSPARC: algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination. Nat Methods 14, 290–296.
Rehman, A.A., Ahsan, H., and Khan, F.H. (2013). Alpha-2-macroglobulin: a physiological guardian. J Cell Physiol 228, 1665–1675.
Sottrup-Jensen, L., Gliemann, J., and Van Leuven, F. (1986). Domain structure of human α2-macroglobulin. FEBS Lett 205, 20–24.
Sottrup-Jensen, L., Petersen, T.E., and Magnusson, S. (1980). A thiol-ester in α2-macroglobulin cleaved during proteinase complex formation. FEBS Lett 121, 275–279.
Sottrup-Jensen, L., Petersen, T.E., and Magnusson, S. (1981). Trypsin-induced activation of the thiol esters in α2-macroglobulin generates a short-lived intermediate (“nascent” α2-M) that can react rapidly to incorporate not only methylamine or putrescine but also proteins lacking proteinase activity. FEBS Lett 128, 123–126.
Sottrup-Jensen, L., Sand, O., Kristensen, L., and Fey, G.H. (1989). The α-macroglobulin bait region. J Biol Chem 264, 15781–15789.
Van Leuven, F., Cassiman, J.J., and Van den Berghe, H. (1981a). Functional modifications of α2-macroglobulin by primary amines. I. Characterization of α2 M after derivatization by methylamine and by factor XIII. J Biol Chem 256, 9016–9022.
Van Leuven, F., Cassiman, J.J., and Van den Berghe, H. (1981b). Functional modifications of α2-macroglobulin by primary amines. II. Inhibition of covalent binding of trypsin to α2 M by methylamine and other primary amines. J Biol Chem 256, 9023–9027.
Van Leuven, F., Cassiman, J.J., and Van den Berghe, H. (1982). Functional modifications of α2-macroglobulin by primary amines. Kinetics of inactivation of α2-macroglobulin by methylamine, and formation of anomalous complexes with trypsin. Biochem J 201, 119–128.
Van Leuven, F., Marynen, P., Sottrup-Jensen, L., Cassiman, J.J., and Van den Berghe, H. (1986). The receptor-binding domain of human α2-macroglobulin. Isolation after limited proteolysis with a bacterial proteinase. J Biol Chem 261, 11369–11373.
Vandooren, J., and Itoh, Y. (2021). Alpha-2-macroglobulin in inflammation, immunity and infections. Front Immunol 12, 803244.
Wong, S.G., and Dessen, A. (2014). Structure of a bacterial α2-macroglobulin reveals mimicry of eukaryotic innate immunity. Nat Commun 5, 4917.
Wyatt, A.R., Constantinescu, P., Ecroyd, H., Dobson, C.M., Wilson, M.R., Kumita, J.R., and Yerbury, J.J. (2013). Protease-activated alpha-2-macroglobulin can inhibit amyloid formation via two distinct mechanisms. FEBS Lett 587, 398–403.
Wyatt, A.R., Kumita, J.R., Farrawell, N.E., Dobson, C.M., and Wilson, M. R. (2015). Alpha-2-macroglobulin is acutely sensitive to freezing and lyophilization: implications for structural and functional studies. PLoS ONE 10, e0130036.
Yang, B., Wu, Y.J., Zhu, M., Fan, S.B., Lin, J., Zhang, K., Li, S., Chi, H., Li, Y.X., Chen, H.F., et al. (2012). Identification of cross-linked peptides from complex samples. Nat Methods 9, 904–906.
Zhang, K. (2016). Gctf: real-time CTF determination and correction. J Struct Biol 193, 1–12.
Zheng, S.Q., Palovcak, E., Armache, J.P., Verba, K.A., Cheng, Y., and Agard, D.A. (2017). MotionCor2: anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy. Nat Methods 14, 331–332.
Zhong, E.D., Bepler, T., Berger, B., and Davis, J.H. (2021). CryoDRGN: reconstruction of heterogeneous cryo-EM structures using neural networks. Nat Methods 18, 176–185.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31971154, 31730023, 31521002), the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology (2017YFA0504700, 2021YFA1300100), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) (XDB37010100), and the National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules of China (2019KF07). We thank Jianhui Li, Zhenwei Yang, Yuanyuan Chen, and Xiaoxia Yu at the Core Facility for Protein Research (Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for assistance with CD and ITC experiments; Gang Ji, Xiaojun Huang, Boling Zhu, Xujing Li at the Center for Biological Imaging (CBI), Core Facility for Protein Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences for assistance with EM data collection; and Jifeng Wang, Zhensheng Xie, Xiang Ding, Mengmeng Zhang (Proteomics, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for assistance with the Q-Exactive mass spectrometer analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Wang, Y., Yu, C. et al. Cryo-EM structures reveal the dynamic transformation of human alpha-2-macroglobulin working as a protease inhibitor. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 2491–2504 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2139-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2139-2