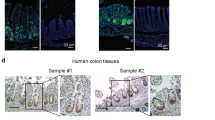
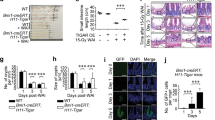
Abstract
Leucine-rich repeat containing G protein-coupled receptor 5 (Lgr5), a marker of intestinal stem cells (ISCs), is considered to play key roles in tissue homoeostasis and regeneration after acute radiation injury. However, the activation of Lgr5 by integrated signaling pathways upon radiation remains poorly understood. Here, we show that irradiation of mice with whole-body depletion or conditional ablation of REGγ in Lgr5+ stem cell impairs proliferation of intestinal crypts, delaying regeneration of intestine epithelial cells. Mechanistically, REGγ enhances transcriptional activation of Lgr5 via the potentiation of both Wnt and Hippo signal pathways. TEAD4 alone or cooperates with TCF4, a transcription factor mediating Wnt signaling, to enhance the expression of Lgr5. Silencing TEAD4 drastically attenuated β-catenin/TCF4 dependent expression of Lgr5. Together, our study reveals how REGγ controls Lgr5 expression and expansion of Lgr5+ stem cells in the regeneration of intestinal epithelial cells. Thus, REGγ proteasome appears to be a potential therapeutic target for radiation-induced gastrointestinal disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Ayyaz, A., Kumar, S., Sangiorgi, B., Ghoshal, B., Gosio, J., Ouladan, S., Fink, M., Barutcu, S., Trcka, D., Shen, J., et al. (2019). Single-cell transcriptomes of the regenerating intestine reveal a revival stem cell. Nature 569, 121–125.
Azzolin, L., Panciera, T., Soligo, S., Enzo, E., Bicciato, S., Dupont, S., Bresolin, S., Frasson, C., Basso, G., Guzzardo, V., et al. (2014). YAP/TAZ incorporation in the β-catenin destruction complex orchestrates the Wnt response. Cell 158, 157–170.
Cai, J., Zhang, N., Zheng, Y., de Wilde, R.F., Maitra, A., and Pan, D. (2010). The Hippo signaling pathway restricts the oncogenic potential of an intestinal regeneration program. Genes Dev 24, 2383–2388.
Carmon, K.S., Gong, X., Lin, Q., Thomas, A., and Liu, Q. (2011). R-spondins function as ligands of the orphan receptors LGR4 and LGR5 to regulate Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 11452–11457.
Carmon, K.S., Lin, Q., Gong, X., Thomas, A., and Liu, Q. (2012). LGR5 interacts and cointernalizes with Wnt receptors to modulate Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Biol 32, 2054–2064.
Chaves-Pérez, A., Yilmaz, M., Perna, C., de la Rosa, S., and Djouder, N. (2019). URI is required to maintain intestinal architecture during ionizing radiation. Science 364, 849.
de Lau, W., Barker, N., Low, T.Y., Koo, B.K., Li, V.S.W., Teunissen, H., Kujala, P., Haegebarth, A., Peters, P.J., van de Wetering, M., et al. (2011). Lgr5 homologues associate with Wnt receptors and mediate R-spondin signalling. Nature 476, 293–297.
de Lau, W., Peng, W.C., Gros, P., and Clevers, H. (2014). The R-spondin/Lgr5/Rnf43 module: regulator of Wnt signal strength. Genes Dev 28, 305–316.
Deng, F., Peng, L., Li, Z., Tan, G., Liang, E., Chen, S., Zhao, X., and Zhi, F. (2018). YAP triggers the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and promotes enterocyte self-renewal, regeneration and tumorigenesis after DSS-induced injury. Cell Death Dis 9, 153.
Dong, S., Jia, C., Zhang, S., Fan, G., Li, Y., Shan, P., Sun, L., Xiao, W., Li, L., Zheng, Y., et al. (2013). The REGγ proteasome regulates hepatic lipid metabolism through inhibition of autophagy. Cell Metab 18, 380–391.
Gao, X., Wang, Q., Yuan, L., Jiao, C., Yu, Y., Wang, X., Xu, P., Ma, Y., Wu, Y., Wu, Z., et al. (2021). REGγ regulates hair cycle by activating Lgr5 positive hair follicle stem cells. J Dermatol Sci 102, 101–108.
Gao, X., Wang, Q., Wang, Y., Liu, J., Liu, S., Liu, J., Zhou, X., Zhou, L., Chen, H., Pan, L., et al. (2020). The REGγ inhibitor NIP30 increases sensitivity to chemotherapy in p53-deficient tumor cells. Nat Commun 11, 3904.
Gregorieff, A., Liu, Y., Inanlou, M.R., Khomchuk, Y., and Wrana, J.L. (2015). Yap-dependent reprogramming of Lgr5 stem cells drives intestinal regeneration and cancer. Nature 526, 715–718.
Horiguchi, H., Endo, M., Kawane, K., Kadomatsu, T., Terada, K., Morinaga, J., Araki, K., Miyata, K., and Oike, Y. (2017). ANGPTL2 expression in the intestinal stem cell niche controls epithelial regeneration and homeostasis. EMBO J 36, 409–424.
Jiao, S., Li, C., Hao, Q., Miao, H., Zhang, L., Li, L., and Zhou, Z. (2017). VGLL4 targets a TCF4-TEAD4 complex to coregulate Wnt and Hippo signalling in colorectal cancer. Nat Commun 8, 14058.
Kim, K.A., Kakitani, M., Zhao, J., Oshima, T., Tang, T., Binnerts, M., Liu, Y., Boyle, B., Park, E., Emtage, P., et al. (2005). Mitogenic influence of human R-spondin1 on the intestinal epithelium. Science 309, 1256–1259.
Leung, C., Tan, S.H., and Barker, N. (2018). Recent advances in Lgr5+ stem cell research. Trends Cell Biol 28, 380–391.
Li, L., Dang, Y., Zhang, J., Yan, W., Zhai, W., Chen, H., Li, K., Tong, L., Gao, X., Amjad, A., et al. (2015). REGγ is critical for skin carcinogenesis by modulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Nat Commun 6, 6875.
Lindemans, C.A., Calafiore, M., Mertelsmann, A.M., O’Connor, M.H., Dudakov, J.A., Jenq, R.R., Velardi, E., Young, L.F., Smith, O.M., Lawrence, G., et al. (2015). Interleukin-22 promotes intestinal-stem-cell-mediated epithelial regeneration. Nature 528, 560–564.
Lv, Y., Meng, B., Dong, H., Jing, T., Wu, N., Yang, Y., Huang, L., Moses, R.E., O’Malley, B.W., Mei, B., et al. (2016). Upregulation of GSK3β contributes to brain disorders in elderly REGγ-knockout mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 41, 1340–1349.
Metcalfe, C., Kljavin, N.M., Ybarra, R., and de Sauvage, F.J. (2014). Lgr5+ stem cells are indispensable for radiation-induced intestinal regeneration. Cell Stem Cell 14, 149–159.
Novellasdemunt, L., Kucharska, A., Jamieson, C., Prange-Barczynska, M., Baulies, A., Antas, P., van der Vaart, J., Gehart, H., Maurice, M.M., and Li, V.S. (2020). NEDD4 and NEDD4L regulate Wnt signalling and intestinal stem cell priming by degrading LGR5 receptor. EMBO J 39, e102771.
Planas-Paz, L., Orsini, V., Boulter, L., Calabrese, D., Pikiolek, M., Nigsch, F., Xie, Y., Roma, G., Donovan, A., Marti, P., et al. (2016). The RSPO-LGR4/5-ZNRF3/RNF43 module controls liver zonation and size. Nat Cell Biol 18, 467–479.
Qi, Z., Li, Y., Zhao, B., Xu, C., Liu, Y., Li, H., Zhang, B., Wang, X., Yang, X., Xie, W., et al. (2017). BMP restricts stemness of intestinal Lgr5+ stem cells by directly suppressing their signature genes. Nat Commun 8, 13824.
Sato, T., and Clevers, H. (2013). Primary mouse small intestinal epithelial cell cultures. In: Randell, S., and Fulcher, M. eds. Epithelial Cell Culture Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology (Methods and Protocols). Totowa: Humana Press. 319–328.
Schuijers, J., and Clevers, H. (2012). Adult mammalian stem cells: the role of Wnt, Lgr5 and R-spondins. EMBO J 31, 2685–2696.
Serra, D., Mayr, U., Boni, A., Lukonin, I., Rempfler, M., Challet Meylan, L., Stadler, M.B., Strnad, P., Papasaikas, P., Vischi, D., et al. (2019). Self-organization and symmetry breaking in intestinal organoid development. Nature 569, 66–72.
Varelas, X., Miller, B.W., Sopko, R., Song, S., Gregorieff, A., Fellouse, F. A., Sakuma, R., Pawson, T., Hunziker, W., McNeill, H., et al. (2010). The Hippo pathway regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Dev Cell 18, 579–591.
Wang, Q., Gao, X., Yu, T., Yuan, L., Dai, J., Wang, W., Chen, G., Jiao, C., Zhou, W., Huang, Q., et al. (2018). REGγ controls Hippo signaling and reciprocal NF-κB-YAP regulation to promote colon cancer. Clin Cancer Res 24, 2015–2025.
Xu, J., Zhou, L., Ji, L., Chen, F., Fortmann, K., Zhang, K., Liu, Q., Li, K., Wang, W., Wang, H., et al. (2016). The REGγ-proteasome forms a regulatory circuit with IκB and NFκB in experimental colitis. Nat Commun 7, 10761.
Yan, K.S., Janda, C.Y., Chang, J., Zheng, G.X.Y., Larkin, K.A., Luca, V.C., Chia, L.A., Mah, A.T., Han, A., Terry, J.M., et al. (2017). Non-equivalence of Wnt and R-spondin ligands during Lgr5+ intestinal stem-cell self-renewal. Nature 545, 238–242.
Yao, L., Zhou, L., Xuan, Y., Zhang, P., Wang, X., Wang, T., Meng, T., Xue, Y., Ma, X., Shah, A.S., et al. (2019). The proteasome activator REGγ counteracts immunoproteasome expression and autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 103, 102282.
Yilmaz, Ö.H., Katajisto, P., Lamming, D.W., Gültekin, Y., Bauer-Rowe, K. E., Sengupta, S., Birsoy, K., Dursun, A., Yilmaz, V.O., Selig, M., et al. (2012). mTORC1 in the Paneth cell niche couples intestinal stem-cell function to calorie intake. Nature 486, 490–495.
Yu, F.X., Zhao, B., and Guan, K.L. (2015). Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue homeostasis, and cancer. Cell 163, 811–828.
Zhang, Y., Liu, S., Zuo, Q., Wu, L., Ji, L., Zhai, W., Xiao, J., Chen, J., and Li, X. (2015). Oxidative challenge enhances REGγ-proteasome-dependent protein degradation. Free Radical Biol Med 82, 42–49.
Zhao, B., Tumaneng, K., and Guan, K.L. (2011). The Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue regeneration and stem cell self-renewal. Nat Cell Biol 13, 877–883.
Zhou, D., Zhang, Y., Wu, H., Barry, E., Yin, Y., Lawrence, E., Dawson, D., Willis, J.E., Markowitz, S.D., Camargo, F.D., et al. (2011). Mst1 and Mst2 protein kinases restrain intestinal stem cell proliferation and colonic tumorigenesis by inhibition of Yes-associated protein (Yap) overabundance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, E1312–E1320.
Zhou, W.J., Geng, Z.H., Spence, J.R., and Geng, J.G. (2013). Induction of intestinal stem cells by R-spondin 1 and Slit2 augments chemoradioprotection. Nature 501, 107–111.
Zhu, X., Tian, X., Yang, M., Yu, Y., Zhou, Y., Gao, Y., Zhang, L., Li, Z., Xiao, Y., Moses, R.E., et al. (2021). Procyanidin B2 promotes intestinal injury repair and attenuates colitis-associated tumorigenesis via suppression of oxidative stress in mice. Antioxid Redox Signal 35, 75–92.
Zou, W.Y., Blutt, S.E., Zeng, X.L., Chen, M.S., Lo, Y.H., Castillo-Azofeifa, D., Klein, O.D., Shroyer, N.F., Donowitz, M., and Estes, M.K. (2018). Epithelial WNT ligands are essential drivers of intestinal stem cell activation. Cell Rep 22, 1003–1015.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82073483, 31730017, 82022051), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (19JC1411900, 20s11901500), Changning Maternity and Infant Health Hospital PI team building project (311–20031). We also thank ECNU Multifunctional Platform for Innovation (011) for keeping and raising mice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Yang, M., Lin, Z. et al. REGγ drives Lgr5+ stem cells to potentiate radiation induced intestinal regeneration. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 1608–1623 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-2018-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-2018-7