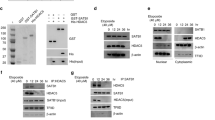
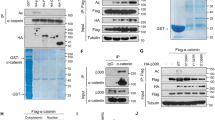
Abstract
Large tumor suppressor 1 (LATS1) is the key kinase controlling activation of Hippo signalling pathway. Post-translational modifications of LATS1 modulate its kinase activity. However, detailed mechanism underlying LATS1 stability and activation remains elusive. Here we report that LATS1 is acetylated by acetyltransferase CBP at K751 and is deacetylated by deacetylases SIRT3 and SIRT4. Acetylation at K751 stabilized LATS1 by decreasing LATS1 ubiquitination and inhibited LATS1 activation by reducing its phosphorylation. Mechanistically, LATS1 acetylation resulted in inhibition of YAP phosphorylation and degradation, leading to increased YAP nucleus translocation and promoted target gene expression. Functionally, LATS1-K751Q, the acetylation mimic mutant potentiated lung cancer cell migration, invasion and tumor growth, whereas LATS1-K751R, the acetylation deficient mutant inhibited these functions. Taken together, we demonstrated a previously unidentified post-translational modification of LATS1 that converts LATS1 from a tumor suppressor to a tumor promoter by suppression of Hippo signalling through acetylation of LATS1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai, J., Zhang, N., Zheng, Y., de Wilde, R.F., Maitra, A., and Pan, D. (2010). The Hippo signaling pathway restricts the oncogenic potential of an intestinal regeneration program. Genes Dev 24, 2383–2388.
Chan, E.H.Y., Nousiainen, M., Chalamalasetty, R.B., Schäfer, A., Nigg, E. A., and Silljé, H.H.W. (2005). The Ste20-like kinase Mst2 activates the human large tumor suppressor kinase Lats1. Oncogene 24, 2076–2086.
Cong, L., Ran, F.A., Cox, D., Lin, S., Barretto, R., Habib, N., Hsu, P.D., Wu, X., Jiang, W., Marraffini, L.A., et al. (2013). Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 339, 819–823.
Dai, X., Xin, Y., Xu, W., Tian, X., Wei, X., and Zhang, H. (2020). CBP-mediated Slug acetylation stabilizes Slug and promotes EMT and migration of breast cancer cells. Sci China Life Sci doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1736-5.
Halder, G., and Johnson, R.L. (2011). Hippo signaling: growth control and beyond. Development 138, 9–22.
He, M., Zhou, Z., Shah, A.A., Hong, Y., Chen, Q., and Wan, Y. (2016). New insights into posttranslational modifications of Hippo pathway in carcinogenesis and therapeutics. Cell Div 11, 4.
Ho, K.C., Zhou, Z., She, Y.M., Chun, A., Cyr, T.D., and Yang, X. (2011). Itch E3 ubiquitin ligase regulates large tumor suppressor 1 stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 4870–4875.
Huang, J., Wu, S., Barrera, J., Matthews, K., and Pan, D. (2005). The Hippo signaling pathway coordinately regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by inactivating Yorkie, the Drosophila Homolog of YAP. Cell 122, 421–434.
Jiang, L., Kon, N., Li, T., Wang, S.J., Su, T., Hibshoosh, H., Baer, R., and Gu, W. (2015). Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature 520, 57–62.
Justice, R.W., Zilian, O., Woods, D.F., Noll, M., and Bryant, P.J. (1995). The Drosophila tumor suppressor gene warts encodes a homolog of human myotonic dystrophy kinase and is required for the control of cell shape and proliferation. Genes Dev 9, 534–546.
Latham, J.A., and Dent, S.Y.R. (2007). Cross-regulation of histone modifications. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14, 1017–1024.
Lei, Q.Y., Zhang, H., Zhao, B., Zha, Z.Y., Bai, F., Pei, X.H., Zhao, S., Xiong, Y., and Guan, K.L. (2008). TAZ promotes cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and is inhibited by the Hippo pathway. Mol Cell Biol 28, 2426–2436.
Li, W., Cooper, J., Zhou, L., Yang, C., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Zagzag, D., Snuderl, M., Ladanyi, M., Hanemann, C.O., Zhou, P., et al. (2014). Merlin/NF2 loss-driven tumorigenesis linked to CRL4DCAF1-mediated inhibition of the Hippo pathway kinases Lats1 and 2 in the nucleus. Cancer Cell 26, 48–60.
Ma, B., Chen, Y., Chen, L., Cheng, H., Mu, C., Li, J., Gao, R., Zhou, C., Cao, L., Liu, J., et al. (2015). Hypoxia regulates Hippo signalling through the SIAH2 ubiquitin E3 ligase. Nat Cell Biol 17, 95–103.
Matallanas, D., Romano, D., Hamilton, G., Kolch, W., and O’Neill, E. (2008). A Hippo in the ointment: MST signalling beyond the fly. Cell Cycle 7, 879–884.
Mei, L., Yuan, L., Shi, W., Fan, S., Tang, C., Fan, X., Yang, W., Qian, Y., Hussain, M., and Wu, X. (2017). SUMOylation of large tumor suppressor 1 at Lys751 attenuates its kinase activity and tumor-suppressor functions. Cancer Lett 386, 1–11.
Meng, Z., Moroishi, T., and Guan, K.L. (2016). Mechanisms of Hippo pathway regulation. Genes Dev 30, 1–17.
Nterma, P., Panopoulou, E., Papadaki-Petrou, E., and Assimakopoulou, M. (2020). Immunohistochemical profile of tumor suppressor proteins RASSF1A and LATS1/2 in relation to p73 and YAP expression, of human inflammatory bowel disease and normal intestine. Pathol Oncol Res 26, 567–574.
Oka, T., Mazack, V., and Sudol, M. (2008). Mst2 and Lats kinases regulate apoptotic function of yes kinase-associated protein (YAP). J Biol Chem 283, 27534–27546.
Pan, B., Yang, Y., Li, J., Wang, Y., Fang, C., Yu, F.X., and Xu, Y. (2020). USP47-mediated deubiquitination and stabilization of YAP contributes to the progression of colorectal cancer. Protein Cell 11, 138–143.
Siegel, R.L., Fedewa, S.A., Miller, K.D., Goding-Sauer, A., Pinheiro, P.S., Martinez-Tyson, D., and Jemal, A. (2015). Cancer statistics for Hispanics/Latinos, 2015. CA-A Cancer J Clinicians 65, 457–480.
Wan, J., Zhan, J., Li, S., Ma, J., Xu, W., Liu, C., Xue, X., Xie, Y., Fang, W., Chin, Y.E., et al. (2015). PCAF-primed EZH2 acetylation regulates its stability and promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression. Nucleic Acids Res 43, 3591–3604.
Wan, J., Xu, W., Zhan, J., Ma, J., Li, X., Xie, Y., Wang, J., Zhu, W.G., Luo, J., and Zhang, H. (2016). PCAF-mediated acetylation of transcriptional factor HOXB9 suppresses lung adenocarcinoma progression by targeting oncogenic protein JMJD6. Nucleic Acids Res 44, 10662–10675.
Xu, T., Wang, W., Zhang, S., Stewart, R.A., and Yu, W. (1995). Identifying tumor suppressors in genetic mosaics: The Drosophila lats gene encodes a putative protein kinase. Development 121, 1053–1063.
Yang, X.J., and Seto, E. (2008). Lysine acetylation: codified crosstalk with other posttranslational modifications. Mol Cell 31, 449–461.
Yeung, B., Ho, K.C., and Yang, X. (2013). WWP1 E3 ligase targets LATS1 for ubiquitin-mediated degradation in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 8, e61027.
Yu, F.X., and Guan, K.L. (2013). The Hippo pathway: regulators and regulations. Genes Dev 27, 355–371.
Yu, F.X., Zhao, B., and Guan, K.L. (2015). Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue homeostasis, and cancer. Cell 163, 811–828.
Zhang, J., Smolen, G.A., and Haber, D.A. (2008). Negative regulation of YAP by LATS1 underscores evolutionary conservation of the Drosophila Hippo pathway. Cancer Res 68, 2789–2794.
Zhao, B., Wei, X., Li, W., Udan, R.S., Yang, Q., Kim, J., Xie, J., Ikenoue, T., Yu, J., Li, L., et al. (2007). Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev 21, 2747–2761.
Zhao, B., Ye, X., Yu, J., Li, L., Li, W., Li, S., Yu, J., Lin, J.D., Wang, C.Y., Chinnaiyan, A.M., et al. (2008). TEAD mediates YAP-dependent gene induction and growth control. Genes Dev 22, 1962–1971.
Zhao, B., Lei, Q., and Guan, K.L. (2009). Mst out and HCC in. Cancer Cell 16, 363–364.
Zhao, B., Li, L., Lei, Q., and Guan, K.L. (2010). The Hippo-YAP pathway in organ size control and tumorigenesis: an updated version. Genes Dev 24, 862–874.
Zhao, B., Tumaneng, K., and Guan, K.L. (2011). The Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue regeneration and stem cell self-renewal. Nat Cell Biol 13, 877–883.
Zhou, D., Conrad, C., Xia, F., Park, J.S., Payer, B., Yin, Y., Lauwers, G.Y., Thasler, W., Lee, J.T., Avruch, J., et al. (2009). Mst1 and Mst2 maintain hepatocyte quiescence and suppress hepatocellular carcinoma development through inactivation of the Yap1 oncogene. Cancer Cell 16, 425–438.
Zhou, Q., Li, L., Zhao, B., and Guan, K.L. (2015). The Hippo pathway in heart development, regeneration, and diseases. Circ Res 116, 1431–1447.
Acknowldgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81730071, 81972616, 81230051, 81472734, 31170711 and 81773199), the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2016YFC1302103 and 2015CB553906), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7120002 and 7171005), and Peking University (BMU2018JC004, BMU20120314 and BMU20130364).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Xu, W., Liu, C. et al. LATS1 K751 acetylation blocks activation of Hippo signalling and switches LATS1 from a tumor suppressor to an oncoprotein. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 129–141 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1914-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1914-3