Abstract
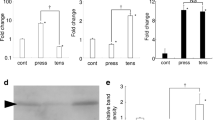
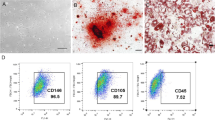
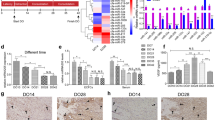
Osteoclastogenesis in alveolar bone induced by compression stress triggers orthodontic tooth movement. Compression stress also stimulates angiogenesis, which is essential for osteoclastogenesis. However, the effects of osteoclastogenesis induced by compression on angiogenesis are poorly understood. In vivo, we found the markers of angiogenesis increased during orthodontic bone remodeling. In vitro, osteoclast-derived exosomes increased proliferation, migration, and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), as well as expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and CD31. The promotive effects of exosomes derived from compressed osteoclasts were greater than those derived from osteoclasts without compression. Next, we analyzed changes in the microRNA transcriptome after compression stress and focused on microRNA146a-5p (miR-146a), which was significantly decreased by compression. Transfection of an inhibitor of miR-146a stimulated angiogenesis of HUVECs while miR-146a mimics repressed angiogenesis. Adiponectin (ADP) was confirmed to be a target of miR-146a by dual luciferase reporter assay. In HUVECs treated with exosomes, we detected increased ADP which promoted angiogenesis. Knockdown of ADP in HUVECs reduced the promotive effects of exosomes. Our results demonstrate that the decreased miR-146a observed in osteoclasts after compression promotes angiogenesis by targeting ADP, suggesting a novel method to interfere with bone remodeling induced by compression stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Samra, M., Selvais, C.M., Dubuisson, N., and Brichard, S.M. (2020). Adiponectin and its mimics on skeletal muscle: insulin sensitizers, fat burners, exercise mimickers, muscling pills … or everything together? Int J Mol Sci 21, 2620.
Adu-Gyamfi, E.A., Fondjo, L.A., Owiredu, W.K.B.A., Czika, A., Nelson, W., Lamptey, J., Wang, Y.X., and Ding, Y.B. (2020). The role of adiponectin in placentation and preeclampsia. Cell Biochem Funct 38, 106–117.
Azad, T., Ghahremani, M., and Yang, X. (2019). The role of YAP and TAZ in angiogenesis and vascular mimicry. Cells 8, 407.
Barwari, T., Joshi, A., and Mayr, M. (2016). MicroRNAs in cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 68, 2577–2584.
Behera, J., and Tyagi, N. (2018). Exosomes: mediators of bone diseases, protection, and therapeutics potential. Oncoscience 5, 181–195.
Bråkenhielm, E., Veitonmäki, N., Cao, R., Kihara, S., Matsuzawa, Y., Zhivotovsky, B., Funahashi, T., and Cao, Y. (2004). Adiponectininduced antiangiogenesis and antitumor activity involve caspasemediated endothelial cell apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101, 2476–2481.
Essandoh, K., Yang, L., Wang, X., Huang, W., Qin, D., Hao, J., Wang, Y., Zingarelli, B., Peng, T., and Fan, G.C. (2015). Blockade of exosome generation with GW4869 dampens the sepsis-induced inflammation and cardiac dysfunction. Biochim Biophys Acta, S0925443915002379.
Foulquier, S., Daskalopoulos, E.P., Lluri, G., Hermans, K.C.M., Deb, A., and Blankesteijn, W.M. (2018). WNT signaling in cardiac and vascular disease. Pharmacol Rev 70, 68–141.
Francisco, C., Neves, J.S., Falcão-Pires, I., and Leite-Moreira, A. (2016). Can adiponectin help us to target diastolic dysfunction? Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 30, 635–644.
Fruebis, J., Tsao, T.S., Javorschi, S., Ebbets-Reed, D., Erickson, M.R.S., Yen, F.T., Bihain, B.E., and Lodish, H.F. (2001). Proteolytic cleavage product of 30-kDa adipocyte complement-related protein increases fatty acid oxidation in muscle and causes weight loss in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 2005–2010.
Gao, Y., Wang, B., Shen, C., and Xin, W. (2018). Overexpression of miR-146a blocks the effect of LPS on RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Mol Med Report 18, 5481–5488.
Götz, W., Reichert, C., Canullo, L., Jäger, A., and Heinemann, F. (2012). Coupling of osteogenesis and angiogenesis in bone substitute healing—A brief overview. Ann Anat 194, 171–173.
Guo, B.B., Bellingham, S.A., and Hill, A.F. (2015). The neutral sphingomyelinase pathway regulates packaging of the prion protein into exosomes. J Biol Chem 290, 3455–3467.
Hayakawa, T., Yoshimura, Y., Kikuiri, T., Matsuno, M., Hasegawa, T., Fukushima, K., Shibata, K., Deyama, Y., Suzuki, K., and Iida, J. (2015). Optimal compressive force accelerates osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cells. Mol Med Rep 12, 5879–5885.
Heuslein, J.L., McDonnell, S.P., Song, J., Annex, B.H., and Price, R.J. (2018). MicroRNA-146a regulates perfusion recovery in response to arterial occlusion via arteriogenesis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 6, 1.
Holliday, L.S., McHugh, K.P., Zuo, J., Aguirre, J.I., Neubert, J.K., and Rody Jr, W.J. (2017). Exosomes: novel regulators of bone remodelling and potential therapeutic agents for orthodontics. Orthod Craniofac Res 20, 95–99.
Huang, Y., Han, Y., Guo, R., Liu, H., Li, X., Jia, L., Zheng, Y., and Li, W. (2020). Long non-coding RNA FER1L4 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stromal cells via miR-874-3p and vascular endothelial growth factor A. Stem Cell Res Ther 11, 5.
Hulsmans, M., Van Dooren, E., Mathieu, C., and Holvoet, P. (2012). Decrease of miR-146b-5p in monocytes during obesity is associated with loss of the anti-inflammatory but not insulin signaling action of adiponectin. PLoS ONE 7, e32794.
Huynh, N., VonMoss, L., Smith, D., Rahman, I., Felemban, M.F., Zuo, J., Rody Jr, W.J., McHugh, K.P., and Holliday, L.S. (2016). Characterization of regulatory extracellular vesicles from osteoclasts. J Dent Res 95, 673–679.
Jiang, N., Xiang, L., He, L., Yang, G., Zheng, J., Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, S., Zhou, Y., Sheu, T.J., et al. (2017). Exosomes mediate epithelium-mesenchyme crosstalk in organ development. ACS Nano 11, 7736–7746.
Jing, D., Hao, J., Shen, Y., Tang, G., Li, M.L., Huang, S.H., and Zhao, Z.H. (2015). The role of microRNAs in bone remodeling. Int J Oral Sci 7, 131–143.
Rody Jr, W.J., King, G.J., and Gu, G. (2001). Osteoclast recruitment to sites of compression in orthodontic tooth movement. Am J Orthodontics Dentofacial Orthopedics 120, 477–489.
Kacso, T., Bondor, C.I., Rusu, C.C., Moldovan, D., Trinescu, D., Coman, L. A., Ticala, M., Gavrilas, A.M., and Potra, A.R. (2018). Adiponectin is related to markers of endothelial dysfunction and neoangiogenesis in diabetic patients. Int Urol Nephrol 50, 1661–1666.
Kishida, K., Nagaretani, H., Kondo, H., Kobayashi, H., Tanaka, S., Maeda, N., Nagasawa, A., Hibuse, T., Ohashi, K., Kumada, M., et al. (2003). Disturbed secretion of mutant adiponectin associated with the metabolic syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 306, 286–292.
Lee, H.P., Lin, C.Y., Shih, J.S., Fong, Y.C., Wang, S.W., Li, T.M., and Tang, C.H. (2015). Adiponectin promotes VEGF-A-dependent angiogenesis in human chondrosarcoma through PI3K, Akt, mTOR, and HIF-α pathway. Oncotarget 6, 36746–36761.
Liu, L., Liu, M., Li, R., Liu, H., Du, L., Chen, H., Zhang, Y., Zhang, S., and Liu, D. (2017). MicroRNA-503-5p inhibits stretch-induced osteogenic differentiation and bone formation. Cell Biol Int 41, 112–123.
Liu, M.Y., Sun, F., Feng, Y.X., Sun, X.Y., Li, J., Fan, Q., and Liu, M. (2019). MicroRNA-132-3p represses Smad5 in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells under cyclic tensile stress. Mol Cell Biochem 458, 143–157.
Luo, J., Zhan, J., You, H., and Cheng, X. (2018). MicroRNA-146a/Toll-like receptor 4 signaling protects against severe burn-induced remote acute lung injury in rats via anti-inflammation. Mol Med Report 17, 8377–8384.
Majidinia, M., and Yousefi, B. (2016). DNA damage response regulation by microRNAs as a therapeutic target in cancer. DNA Repair 47, 1–11.
Miyagawa, A., Chiba, M., Hayashi, H., and Igarashi, K. (2009). Compressive force induces VEGF production in periodontal tissues. J Dent Res 88, 752–756.
Niklas, A., Proff, P., Gosau, M., and Römer, P. (2013). The role of hypoxia in orthodontic tooth movement. Int J Dentistry 2013, 1–7.
Oshima, K., Nampei, A., Matsuda, M., Iwaki, M., Fukuhara, A., Hashimoto, J., Yoshikawa, H., and Shimomura, I. (2005). Adiponectin increases bone mass by suppressing osteoclast and activating osteoblast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331, 520–526.
Ouchi, N., Kobayashi, H., Kihara, S., Kumada, M., Sato, K., Inoue, T., Funahashi, T., and Walsh, K. (2004). Adiponectin stimulates angiogenesis by promoting cross-talk between AMP-activated protein kinase and Akt signaling in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 279, 1304–1309.
Palanisamy, K., Nareshkumar, R.N., Sivagurunathan, S., Raman, R., Sulochana, K.N., and Chidambaram, S. (2019). Anti-angiogenic effect of adiponectin in human primary microvascular and macrovascular endothelial cells. Microvasc Res 122, 136–145.
Peng, Y., Wu, S., Li, Y., and Crane, J.L. (2020). Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics 10, 426–436.
Pethő, A., Chen, Y., and George, A. (2018). Exosomes in extracellular matrix bone biology. Curr Osteoporos Rep 16, 58–64.
Quan, H., Liang, M., Li, N., Dou, C., Liu, C., Bai, Y., Luo, W., Li, J., Kang, F., Cao, Z., et al. (2018). LncRNA-AK131850 sponges miR-93-5p in newborn and mature osteoclasts to enhance the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor a promoting vasculogenesis of endothelial progenitor cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 46, 401–417.
Ratajczak, J., Vangansewinkel, T., Gervois, P., Merckx, G., Hilkens, P., Quirynen, M., Lambrichts, I., and Bronckaers, A. (2018). Angiogenic properties of ‘leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin’. Sci Rep 8, 14632.
Rumney, R.M.H., Lanham, S.A., Kanczler, J.M., Kao, A.P., Thiagarajan, L., Dixon, J.E., Tozzi, G., and Oreffo, R.O.C. (2019). In vivo delivery of VEGF RNA and protein to increase osteogenesis and intraosseous angiogenesis. Sci Rep 9, 17745.
Sato, K., Suematsu, A., Nakashima, T., Takemoto-Kimura, S., Aoki, K., Morishita, Y., Asahara, H., Ohya, K., Yamaguchi, A., Takai, T., et al. (2006). Regulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the CaMK-CREB pathway. Nat Med 12, 1410–1416.
Schröder, A., Bauer, K., Spanier, G., Proff, P., Wolf, M., and Kirschneck, C. (2018). Expression kinetics of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts in the early phases of orthodontic tooth movement. J Orofac Orthop 79, 337–351.
Shinoda, Y., Yamaguchi, M., Ogata, N., Akune, T., Kubota, N., Yamauchi, T., Terauchi, Y., Kadowaki, T., Takeuchi, Y., Fukumoto, S., et al. (2006). Regulation of bone formation by adiponectin through autocrine/paracrine and endocrine pathways. J Cell Biochem 99, 196–208.
Sirois, I., Groleau, J., Pallet, N., Brassard, N., Hamelin, K., Londono, I., Pshezhetsky, A.V., Bendayan, M., and Hébert, M.J. (2012). Caspase activation regulates the extracellular export of autophagic vacuoles. Autophagy 8, 927–937.
Soma, S., Iwamoto, M., Higuchi, Y., and Kurisu, K. (1999). Effects of continuous infusion of PTH on experimental tooth movement in rats. J Bone Miner Res 14, 546–554.
Stephens, E., Roy, M., Bisson, M., Nguyen, H.D., Scott, M.S., Boire, G., Bouchard, L., and Roux, S. (2020). Osteoclast signaling-targeting miR-146a-3p and miR-155-5p are downregulated in Paget’s disease of bone. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1866, 165852.
Su, P., Tian, Y., Yang, C., Ma, X., Wang, X., Pei, J., and Qian, A. (2018). Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration during Bone Formation and Bone Diseases Therapy. IJMS 19, 2343.
Sun, M., Zhou, X., Chen, L., Huang, S., Leung, V., Wu, N., Pan, H., Zhen, W., Lu, W., and Peng, S. (2016). The Regulatory Roles of MicroRNAs in Bone Remodeling and Perspectives as Biomarkers in Osteoporosis. Biomed Res Int 2016, 1–11.
Thayanithy, V., O’Hare, P., Wong, P., Zhao, X., Steer, C.J., Subramanian, S., and Lou, E. (2017). A transwell assay that excludes exosomes for assessment of tunneling nanotube-mediated intercellular communication. Cell Commun Signal 15, 46.
Wu, Y., Ou, Y., Liao, C., Liang, S., and Wang, Y. (2019). High-throughput sequencing analysis of the expression profile of microRNAs and target genes in mechanical force-induced osteoblastic/cementoblastic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. Am J Transl Res 11, 3398–3411.
Xie, H., Cui, Z., Wang, L., Xia, Z., Hu, Y., Xian, L., Li, C., Xie, L., Crane, J., Wan, M., et al. (2014). PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis. Nat Med 20, 1270–1278.
Xie, Q., Wei, W., Ruan, J., Ding, Y., Zhuang, A., Bi, X., Sun, H., Gu, P., Wang, Z., and Fan, X. (2017). Effects of miR-146a on the osteogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and bone regeneration. Sci Rep 7, 42840.
Yamaguchi, N., Kukita, T., Li, Y.J., Kamio, N., Fukumoto, S., Nonaka, K., Ninomiya, Y., Hanazawa, S., and Yamashita, Y. (2008). Adiponectin inhibits induction of TNF-α/RANKL-stimulated NFATc1 via the AMPK signaling. FEBS Lett 582, 451–456.
Yao, Y., Jia, T., Pan, Y., Gou, H., Li, Y., Sun, Y., Zhang, R., Zhang, K., Lin, G., Xie, J., et al. (2015). Using a novel microRNA delivery system to inhibit osteoclastogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 16, 8337–8350.
Yin, Y., Tang, L., Chen, J., and Lu, X. (2017). MiR-30a attenuates osteoclastogenesis via targeting DC-STAMP-c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling. Am J Transl Res 9, 5743–5753.
Zheng, Y., Li, X., Huang, Y., Jia, L., and Li, W. (2017). The circular RNA landscape of periodontal ligament stem cells during osteogenesis. J Periodontol 88, 906–914.
Zhu, D., Johnson, T.K., Wang, Y., Thomas, M., Huynh, K., Yang, Q., Bond, V.C., Chen, Y.E., and Liu, D. (2020). Macrophage M2 polarization induced by exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells contributes to the exosomal proangiogenic effect on mouse ischemic hindlimb. Stem Cell Res Ther 11, 162.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81700938, 81670957). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or the preparation of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. The results of microRNA sequencing are available on www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Traces/study/?acc=PRJNA629042&o=acc_s%3Aa.
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest. Animal experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Use and Care Committee of Peking University (LA2020033).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zheng, Y. & Li, W. Compression loading of osteoclasts attenuated microRNA-146a-5p expression, which promotes angiogenesis by targeting adiponectin. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 151–166 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1869-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1869-7