Abstract
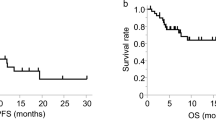
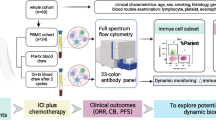
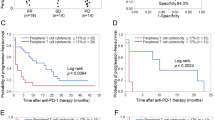
Limited benefit population of immune checkpoint inhibitors makes it urgent to screen predictive biomarkers for stratifying the patients. Herein, we have investigated peripheral CD4+ T cell signatures in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients receiving anti-PD-1/PD-L1 treatments. It was found that the percentages of IFN-γ and IL-17A secreting naïve CD4+ T cells (Tn), and memory CD4+ T cells (Tm) expressing PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA-4 were significantly higher in responder (R) than non-responder (NonR) NSCLC patients associated with a longer progression free survival (PFS). Logistic regression analysis revealed that the baseline IFN-γ-producing CD4+ Tn cells and PD-1+CD4+ Tm cells were the most significant signatures with the area under curve (AUC) value reaching 0.849. This was further validated in another anti-PD-1 monotherapy cohort. Conversely, high percentage of CTLA-4+CD4+ Tm cells was associated with a shorter PFS in patients receiving anti-PD-L1 monotherapy. Our study therefore elucidates the significance of functional CD4+ Tn and Tm subpopulations before the treatment in predicting the responses to anti-PD-1 treatment in Chinese NSCLC patients. The fact that there display distinct CD4+ T cell signatures in the prediction to anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 monotherapy from our study provides preliminary evidence on the feasibility of anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 combination therapy for advanced NSCLC patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrends, T., Spanjaard, A., Pilzecker, B., Bąbała, N., Bovens, A., Xiao, Y., Jacobs, H., and Borst, J. (2017). CD4+ T cell help confers a cytotoxic T cell effector program including coinhibitory receptor downregulation and increased tissue invasiveness. Immunity 47, 848–861.e5.
Alspach, E., Lussier, D.M., Miceli, A.P., Kizhvatov, I., DuPage, M., Luoma, A.M., Meng, W., Lichti, C.F., Esaulova, E., Vomund, A.N., et al. (2019). MHC-II neoantigens shape tumour immunity and response to immunotherapy. Nature 574, 696–701.
Binnewies, M., Mujal, A.M., Pollack, J.L., Combes, A.J., Hardison, E.A., Barry, K.C., Tsui, J., Ruhland, M.K., Kersten, K., Abushawish, M.A., et al. (2019). Unleashing type-2 dendritic cells to drive protective antitumor CD4+ T cell immunity. Cell 177, 556–571.e16.
Brahmer, J., Reckamp, K.L., Baas, P., Crinò, L., Eberhardt, W.E.E., Poddubskaya, E., Antonia, S., Pluzanski, A., Vokes, E.E., Holgado, E., et al. (2015). Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 373, 123–135.
Butte, M.J., Keir, M.E., Phamduy, T.B., Sharpe, A.H., and Freeman, G.J. (2007). Programmed death-1 ligand 1 interacts specifically with the B7-1 costimulatory molecule to inhibit T cell responses. Immunity 27, 111–122.
Carroll, K.L., Avery, L., Treat, B.R., Kane, L.P., Kinchington, P.R., Hendricks, R.L., and St Leger, A.J. (2020). Differential expression of immune checkpoint molecules on CD8+ T cells specific for immunodominant and subdominant herpes simplex virus 1 epitopes. J Virol 94.
Gandini, S., Massi, D., and Mandalà, M. (2016). PD-L1 expression in cancer patients receiving anti PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncol 100, 88–98.
Garon, E.B., Hellmann, M.D., Rizvi, N.A., Carcereny, E., Leighl, N.B., Ahn, M.J., Eder, J.P., Balmanoukian, A.S., Aggarwal, C., Horn, L., et al. (2019). Five-year overall survival for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with pembrolizumab: results from the phase I KEYNOTE-001 study. J Clin Oncol 37, 2518–2527.
Gettinger, S., Horn, L., Jackman, D., Spigel, D., Antonia, S., Hellmann, M., Powderly, J., Heist, R., Sequist, L.V., Smith, D.C., et al. (2018). Five-year follow-up of nivolumab in previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results from the CA209-003 study. J Clin Oncol 36, 1675–1684.
Gide, T.N., Quek, C., Menzies, A.M., Tasker, A.T., Shang, P., Holst, J., Madore, J., Lim, S.Y., Velickovic, R., Wongchenko, M., et al. (2019). Distinct immune cell populations define response to anti-PD-1 monotherapy and anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4 combined therapy. Cancer Cell 35, 238–255.e6.
Goodman, A.M., Kato, S., Bazhenova, L., Patel, S.P., Frampton, G.M., Miller, V., Stephens, P.J., Daniels, G.A., and Kurzrock, R. (2017). Tumor mutational burden as an independent predictor of response to immunotherapy in diverse cancers. Mol Cancer Ther 16, 2598–2608.
Hellmann, M.D., Ciuleanu, T.E., Pluzanski, A., Lee, J.S., Otterson, G.A., Audigier-Valette, C., Minenza, E., Linardou, H., Burgers, S., Salman, P., et al. (2018). Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in lung cancer with a high tumor mutational burden. N Engl J Med 378, 2093–2104.
Hellmann, M.D., Paz-Ares, L., Bernabe Caro, R., Zurawski, B., Kim, S.W., Carcereny Costa, E., Park, K., Alexandru, A., Lupinacci, L., de la Mora Jimenez, E., et al. (2019). Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 381, 2020–2031.
Herbst, R.S., Baas, P., Kim, D.W., Felip, E., Pérez-Gracia, J.L., Han, J.Y., Molina, J., Kim, J.H., Arvis, C.D., Ahn, M.J., et al. (2016). Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 387, 1540–1550.
Huang, A.C., Postow, M.A., Orlowski, R.J., Mick, R., Bengsch, B., Manne, S., Xu, W., Harmon, S., Giles, J.R., Wenz, B., et al. (2017). T-cell invigoration to tumour burden ratio associated with anti-PD-1 response. Nature 545, 60–65.
Jacquelot, N., Roberti, M.P., Enot, D.P., Rusakiewicz, S., Ternès, N., Jegou, S., Woods, D.M., Sodré, A.L., Hansen, M., Meirow, Y., et al. (2017). Predictors of responses to immune checkpoint blockade in advanced melanoma. Nat Commun 8, 592.
Jin, Y., Dong, H., Xia, L., Yang, Y., Zhu, Y., Shen, Y., Zheng, H., Yao, C., Wang, Y., and Lu, S. (2019). The diversity of gut microbiome is associated with favorable responses to anti-programmed death 1 immunotherapy in Chinese patients with NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol 14, 1378–1389.
Juliá, E.P., Mandé, P., Rizzo, M.M., Cueto, G.R., Tsou, F., Luca, R., Pupareli, C., Bravo, A.I., Astorino, W., Mordoh, J., et al. (2019). Peripheral changes in immune cell populations and soluble mediators after anti-PD-1 therapy in non-small cell lung cancer and renal cell carcinoma patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 68, 1585–1596.
Kagamu, H., Kitano, S., Yamaguchi, O., Yoshimura, K., Horimoto, K., Kitazawa, M., Fukui, K., Shiono, A., Mouri, A., Nishihara, F., et al. (2020). CD4+ T-cell immunity in the peripheral blood correlates with response to anti-PD-1 therapy. Cancer Immunol Res 8, 334–344.
Kamphorst, A.O., Pillai, R.N., Yang, S., Nasti, T.H., Akondy, R.S., Wieland, A., Sica, G.L., Yu, K., Koenig, L., Patel, N.T., et al. (2017). Proliferation of PD-1+ CD8 T cells in peripheral blood after PD-1-targeted therapy in lung cancer patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114, 4993–4998.
Koyama, S., Akbay, E.A., Li, Y.Y., Herter-Sprie, G.S., Buczkowski, K.A., Richards, W.G., Gandhi, L., Redig, A.J., Rodig, S.J., Asahina, H., et al. (2016). Adaptive resistance to therapeutic PD-1 blockade is associated with upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints. Nat Commun 7, 10501.
Krieg, C., Nowicka, M., Guglietta, S., Schindler, S., Hartmann, F.J., Weber, L.M., Dummer, R., Robinson, M.D., Levesque, M.P., and Becher, B. (2018). High-dimensional single-cell analysis predicts response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy. Nat Med 24, 144–153.
Lee, J., Ahn, E., Kissick, H.T., and Ahmed, R. (2015). Reinvigorating exhausted T cells by blockade of the PD-1 pathway. For Immunopathol Dis Therap 6, 7–17.
Marty Pyke, R., Thompson, W.K., Salem, R.M., Font-Burgada, J., Zanetti, M., and Carter, H. (2018). Evolutionary pressure against MHC class II binding cancer mutations. Cell 175, 416–428.e13.
Oh, D.Y., Kwek, S.S., Raju, S.S., Li, T., McCarthy, E., Chow, E., Aran, D., Ilano, A., Pai, C.C.S., Rancan, C., et al. (2020). Intratumoral CD4+ T cells mediate anti-tumor cytotoxicity in human bladder cancer. Cell 181, 1612–1625.e13.
Remon, J., Passiglia, F., Ahn, M.J., Barlesi, F., Forde, P.M., Garon, E.B., Gettinger, S., Goldberg, S.B., Herbst, R.S., Horn, L., et al. (2020). Immune checkpoint inhibitors in thoracic malignancies: Review of the existing evidence by an IASLC expert panel and recommendations. J Thorac Oncol 15, 914–947.
Rittmeyer, A., Barlesi, F., Waterkamp, D., Park, K., Ciardiello, F., von Pawel, J., Gadgeel, S.M., Hida, T., Kowalski, D.M., Dols, M.C., et al. (2017). Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 389, 255–265.
Rizvi, N.A., Hellmann, M.D., Snyder, A., Kvistborg, P., Makarov, V., Havel, J.J., Lee, W., Yuan, J., Wong, P., Ho, T.S., et al. (2015). Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science 348, 124–128.
Routy, B., Le Chatelier, E., Derosa, L., Duong, C.P.M., Alou, M.T., Daillère, R., Fluckiger, A., Messaoudene, M., Rauber, C., Roberti, M.P., et al. (2018). Gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1-based immunotherapy against epithelial tumors. Science 359, 91–97.
Sharpe, A.H., and Pauken, K.E. (2018). The diverse functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat Rev Immunol 18, 153–167.
Shin, D.S., and Ribas, A. (2015). The evolution of checkpoint blockade as a cancer therapy: what’s here, what’s next? Curr Opin Immunol 33, 23–35.
Spitzer, M.H., Carmi, Y., Reticker-Flynn, N.E., Kwek, S.S., Madhireddy, D., Martins, M.M., Gherardini, P.F., Prestwood, T.R., Chabon, J., Bendall, S.C., et al. (2017). Systemic immunity is required for effective cancer immunotherapy. Cell 168, 487–502.e15.
Spranger, S., Spaapen, R.M., Zha, Y., Williams, J., Meng, Y., Ha, T.T., and Gajewski, T.F. (2013). Up-regulation of PD-L1, IDO, and Tregs in the melanoma tumor microenvironment is driven by CD8+ T cells. Sci Transl Med 5, 200ra116.
Subrahmanyam, P.B., Dong, Z., Gusenleitner, D., Giobbie-Hurder, A., Severgnini, M., Zhou, J., Manos, M., Eastman, L.M., Maecker, H.T., and Hodi, F.S. (2018). Distinct predictive biomarker candidates for response to anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma patients. J Immunother Cancer 6, 18.
Thommen, D.S., Koelzer, V.H., Herzig, P., Roller, A., Trefny, M., Dimeloe, S., Kiialainen, A., Hanhart, J., Schill, C., Hess, C., et al. (2018). A transcriptionally and functionally distinct PD-1+ CD8+ T cell pool with predictive potential in non-small-cell lung cancer treated with PD-1 blockade. Nat Med 24, 994–1004.
Togashi, Y., Shitara, K., and Nishikawa, H. (2019). Regulatory T cells in cancer immunosuppression—Implications for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 16, 356–371.
Wistuba-Hamprecht, K., Martens, A., Heubach, F., Romano, E., Geukes Foppen, M., Yuan, J., Postow, M., Wong, P., Mallardo, D., Schilling, B., et al. (2017). Peripheral CD8 effector-memory type 1 T-cells correlate with outcome in ipilimumab-treated stage IV melanoma patients. Eur J Cancer 73, 61–70.
Wu, S.P., Liao, R.Q., Tu, H.Y., Wang, W.J., Dong, Z.Y., Huang, S.M., Guo, W.B., Gou, L.Y., Sun, H.W., Zhang, Q., et al. (2018). Stromal PD-L1-positive regulatory T cells and PD-1-positive CD8-positive T cells define the response of different subsets of non-small cell lung cancer to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade immunotherapy. J Thorac Oncol 13, 521–532.
Xia, L., Liu, Y., and Wang, Y. (2019). PD-1/PD-L1 blockade therapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: current status and future directions. Oncol 24, S31.
Yang, Y., Yu, Y., and Lu, S. (2020). Effectiveness of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in the treatment of lung cancer: Brightness and challenge. Sci China Life Sci 63, 1499–1514.
Zander, R., Schauder, D., Xin, G., Nguyen, C., Wu, X., Zajac, A., and Cui, W. (2019). CD4+ T cell help is required for the formation of a cytolytic CD8+ T cell subset that protects against chronic infection and cancer. Immunity 51, 1028–1042.e4.
Zappasodi, R., Budhu, S., Hellmann, M.D., Postow, M.A., Senbabaoglu, Y., Manne, S., Gasmi, B., Liu, C., Zhong, H., Li, Y., et al. (2018). Non-conventional Inhibitory CD4+Foxp3−PD-1hi T cells as a biomarker of immune checkpoint blockade activity. Cancer Cell 33, 1017–1032.e7.
Zuazo, M., Arasanz, H., Fernández-Hinojal, G., García-Granda, M.J., Gato, M., Bocanegra, A., Martínez, M., Hernández, B., Teijeira, L., Morilla, I., et al. (2019). Functional systemic CD4 immunity is required for clinical responses to PD-L1/PD-1 blockade therapy. EMBO Mol Med 11, e10293.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC1303303), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82073152, 81802264), Technology Innovation Program of Shanghai (19411950500), Talent Training Program of Shanghai Chest Hospital in 2019, and Incubation Project Plan for Research in Shanghai Chest Hospital (2019YNJCM07). We also appreciated Core Facility of Basic Medical Sciences in Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine for their technical supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest. All samples were collected in accordance with the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Chest Hospital-approved protocol. All patients have provided written consent prior to blood collection.
Electronic supplementary material
11427_2020_1861_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Peripheral CD4+ T cell signatures in predicting the responses to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy for Chinese advanced non-small cell lung cancer, approximately 120 KB.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, L., Wang, H., Sun, M. et al. Peripheral CD4+ T cell signatures in predicting the responses to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy for Chinese advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. China Life Sci. 64, 1590–1601 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1861-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1861-5