Abstract
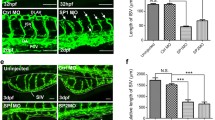
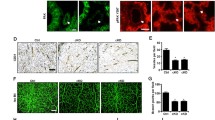
Angiogenic factor with G-patch and FHA domains 1 (AGGF1) exhibits a dynamic distribution from the nucleus to the cytoplasm in endothelial cells during angiogenesis, but the biological significance and underlying mechanism of this nucleocytoplasmic transport remains unknown. Here, we demonstrate that the dynamic distribution is essential for AGGF1 to execute its angiogenic function. To search the structural bases for this nucleocytoplasmic transport, we characterized three potential nuclear localization regions, one potential nuclear export region, forkhead-associated (FHA), and G-patch domains to determine their effects on nucleocytoplasmic transport and angiogenesis, and we show that AGGF1 remains intact during the dynamic subcellular distribution and the region from 260 to 288 amino acids acts as a signal for its nuclear localization. The distribution of AGGF1 in cytoplasm needs both FHA domain and 14-3-3α/β. Binding of AGGF1 via FHA domain to 14-3-3α/β is required to complete the transport. Thus, we for the first time established structural bases for the nucleocytoplasmic transport of AGGF1 and revealed that the FHA domain of AGGF1 is essential for its nucleocytoplasmic transport and angiogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, A.K., and Webb, A.E. (2018). Regulation of FOXO factors in mammalian cells. Curr Top Dev Biol 127, 165–192.
Chevalier, S.A., Meertens, L., Calattini, S., Gessain, A., Kiemer, L., and Mahieux, R. (2005). Presence of a functional but dispensable nuclear export signal in the HTLV-2 Tax protein. Retrovirology 2, 70.
Cook, A., Bono, F., Jinek, M., and Conti, E. (2007). Structural biology of nucleocytoplasmic transport. Annu Rev Biochem 76, 647–671.
Deak, J.C., Cross, J.V., Lewis, M., Qian, Y., Parrott, L.A., Distelhorst, C. W., and Templeton, D.J. (1998). Fas-induced proteolytic activation and intracellular redistribution of the stress-signaling kinase MEKK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95, 5595–5600.
Durocher, D., Smerdon, S.J., Yaffe, M.B., and Jackson, S.P. (2000). The FHA domain in DNA repair and checkpoint signaling. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quantitat Biol 65, 423–432.
Fei, H.R., Cui, L.Y., Zhang, Z.R., Zhao, Y., and Wang, F.Z. (2012). Caudatin inhibits carcinomic human alveolar basal epithelial cell growth and angiogenesis through modulating GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. J Cell Biochem 113, 3403–3410.
Han, D.C., Shen, T.L., Miao, H., Wang, B., and Guan, J.L. (2002). EphB1 associates with Grb7 and regulates cell migration. J Biol Chem 277, 45655–45661.
Hu, F.Y., Wu, C., Li, Y., Xu, K., Wang, W.J., Cao, H., and Tian, X.L. (2013). AGGF1 is a novel anti-inflammatory factor associated with TNF-α-induced endothelial activation. Cell Signal 25, 1645–1653.
Kaffman, A., Rank, N.M., and O’Shea, E.K. (1998). Phosphorylation regulates association of the transcription factor Pho4 with its import receptor Pse1/Kap121. Genes Dev 12, 2673–2683.
Kashiwada, T., Fukuhara, S., Terai, K., Tanaka, T., Wakayama, Y., Ando, K., Nakajima, H., Fukui, H., Yuge, S., Saito, Y., et al. (2015). β-catenin-dependent transcription is central to Bmp-mediated formation of venous vessels. Development 142, 497–509.
Kumagai, A., and Dunphy, W.G. (1999). Binding of 14-3-3β proteins and nuclear export control the intracellular localization of the mitotic inducer Cdc25. Genes Dev 13, 1067–1072.
Kumar, S., Saradhi, M., Chaturvedi, N.K., and Tyagi, R.K. (2006). Intracellular localization and nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of steroid receptors: an overview. Mol Cell Endocrinol 246, 147–156.
la Cour, T., Kiemer, L., Mølgaard, A., Gupta, R., Skriver, K., and Brunak, S. (2004). Analysis and prediction of leucine-rich nuclear export signals. Protein Eng Des Sel 17, 527–536.
Lee, J.C., Kim, D.S., Moon, D.C., Lee, J.H., Kim, M.J., Lee, S.M., Lee, Y. S., Kang, S.W., Lee, E.J., Kang, S.S., et al. (2009). Prediction of bacterial proteins carrying a nuclear localization signal and nuclear targeting of HsdM from Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Microbiol 47, 641–645.
Li, J., Lee, G.I., Van Doren, S.R., and Walker, J.C. (2000). The FHA domain mediates phosphoprotein interactions. J Cell Sci 113 Pt 23, 4143–4149.
Li, L., Chen, D., Li, J., Wang, X., Wang, N., Xu, C., and Wang, Q.K. (2014). AGGF1 acts at the top of the genetic regulatory hierarchy in specification of hemangioblasts in zebrafish. Blood 123, 501–508.
Lu, Q., Yao, Y., Yao, Y., Liu, S., Huang, Y., Lu, S., Bai, Y., Zhou, B., Xu, Y., Li, L., et al. (2012). Angiogenic factor AGGF1 promotes therapeutic angiogenesis in a mouse limb ischemia model. PLoS ONE 7, e46998.
Major, M.B., Roberts, B.S., Berndt, J.D., Marine, S., Anastas, J., Chung, N., Ferrer, M., Yi, X.H., Stoick-Cooper, C.L., von Haller, P.D., et al. (2008). New regulators of Wnt/β-catenin signaling revealed by integrative molecular screening. Sci Signal 1, ra12.
Manning, B.D., and Cantley, L.C. (2007). AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129, 1261–1274.
Montenarh, M. (2014). Protein kinase CK2 and angiogenesis. Adv Clin Exp Med 23, 153–158.
Muslin, A.J., Tanner, J.W., Allen, P.M., and Shaw, A.S. (1996). Interaction of 14-3-3 with signaling proteins is mediated by the recognition of phosphoserine. Cell 84, 889–897.
Muslin, A., and Xing, H.M. (2000). 14-3-3 proteins: regulation of subcellular localization by molecular interference. Cell Signal 12, 703–709.
Nigg, E.A. (1997). Nucleocytoplasmic transport: signals, mechanisms and regulation. Nature 386, 779–787.
Olsnes, S., Klingenberg, O., and Wiçdłocha, A. (2003). Transport of exogenous growth factors and cytokines to the cytosol and to the nucleus. Physiol Rev 83, 163–182.
Planque, N. (2006). Nuclear trafficking of secreted factors and cell-surface receptors: new pathways to regulate cell proliferation and differentiation, and involvement in cancers. Cell Commun Signal 4, 7.
Rivière, Y., Blank, V., Kourilsky, P., and Israël, A. (1991). Processing of the precursor of NF-κB by the HIV-1 protease during acute infection. Nature 350, 625–626.
Rousseau, A., and Bertolotti, A. (2018). Regulation of proteasome assembly and activity in health and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19, 697–712.
Scott, M.S., Troshin, P.V., and Barton, G.J. (2011). NoD: a nucleolar localization sequence detector for eukaryotic and viral proteins. BMC Bioinformatics 12, 317.
Smith, G.A., Fearnley, G.W., Abdul-Zani, I., Wheatcroft, S.B., Tomlinson, D.C., Harrison, M.A., and Ponnambalam, S. (2016). VEGFR2 trafficking, signaling and proteolysis is regulated by the ubiquitin isopeptidase USP8. Traffic 17, 53–65.
Sørensen, V., Nilsen, T., and Wiedlocha, A. (2006). Functional diversity of FGF-2 isoforms by intracellular sorting. Bioessays 28, 504–514.
Sorokin, A.V., Kim, E.R., and Ovchinnikov, L.P. (2007). Nucleocytoplasmic transport of proteins. Biochem Moscow 72, 1439–1457.
Tian, X.L., Kadaba, R., You, S.A., Liu, M., Timur, A.A., Yang, L., Chen, Q., Szafranski, P., Rao, S., Wu, L., et al. (2004). Identification of an angiogenic factor that when mutated causes susceptibility to Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome. Nature 427, 640–645.
Valovka, T., and Hottiger, M.O. (2011). p65 controls NF-κB activity by regulating cellular localization of IκBβ. Biochem J 434, 253–263.
Wiedlocha, A., and Sorensen, V. (2004). Signaling, internalization, and intracellular activity of fibroblast growth factor. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology 286, 45–79.
Woerner, A.C., Frottin, F., Hornburg, D., Feng, L.R., Meissner, F., Patra, M., Tatzelt, J., Mann, M., Winklhofer, K.F., Hartl, F.U., et al. (2016). Cytoplasmic protein aggregates interfere with nucleocytoplasmic transport of protein and RNA. Science 351, 173–176.
Yang, J., Winkler, K., Yoshida, M., and Kornbluth, S. (1999). Maintenance of G2 arrest in the Xenopus oocyte: a role for 14-3-3-mediated inhibition of Cdc25 nuclear import. EMBO J 18, 2174–2183.
Yao, Y., Lu, Q., Hu, Z., Yu, Y., Chen, Q., and Wang, Q.K. (2017). A non-canonical pathway regulates ER stress signaling and blocks ER stress-induced apoptosis and heart failure. Nat Commun 8, 133.
Zabriskie, M.S., Antelope, O., Verma, A.R., Draper, L.R., Eide, C.A., Pomicter, A.D., Tran, T.H., Druker, B.J., Tyner, J.W., Miles, R.R., et al. (2018). A novel AGGF1-PDGFRb fusion in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 103, e87–e91.
Zhan, M., Hori, Y., Wada, N., Ikeda, J.I., Hata, Y., Osuga, K., and Morii, E. (2016). Angiogenic factor with G-patch and FHA domain 1 (AGGF1) expression in human vascular lesions. Acta Histochem Cytochem 49, 75–81.
Zhang, K., Daigle, J.G., Cunningham, K.M., Coyne, A.N., Ruan, K., Grima, J.C., Bowen, K.E., Wadhwa, H., Yang, P., Rigo, F., et al. (2018a). Stress granule assembly disrupts nucleocytoplasmic transport. Cell 173, 958–971.e17.
Zhang, T., He, P., and Wang, Q. (2008). AGGF1 is essential for embryonic and pathological angiogenesis. Circulation 118, S461–S462.
Zhang, T., Yao, Y., Wang, J., Li, Y., He, P., Pasupuleti, V., Hu, Z., Jia, X., Song, Q., Tian, X.L., et al. (2016). Haploinsufficiency of Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome gene Aggf1 inhibits developmental and pathological angiogenesis by inactivating PI3K and AKT and disrupts vascular integrity by activating VE-cadherin. Hum Mol Genet 25, 5094–5110.
Zhang, Y., Gao, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, J., He, F., Hnízda, A., Qian, M., Liu, X., Gocho, Y., Pui, C.H., et al. (2018b). PDGFRB mutation and tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in Ph-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 131, 2256–2261.
Zhou, B., Zeng, S., Li, N., Yu, L., Yang, G., Yang, Y., Zhang, X., Fang, M., Xia, J., and Xu, Y. (2017). Angiogenic factor with G patch and FHA domains 1 is a novel regulator of vascular injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 37, 675–684.
Zhou, Q., Heinke, J., Vargas, A., Winnik, S., Krauss, T., Bode, C., Patterson, C., and Moser, M. (2007). ERK signaling is a central regulator for BMP-4 dependent capillary sprouting. Cardiovasc Res 76, 390–399.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30730047, 81070262, 81130003 and 81630034). We acknowledge Mei-Qin Hu from Department of Cellular Biophysical and Neurodegenerative Disease Mechanisms (Institute of Molecular Medicine, Peking University) for his kind gifts of plasmids: pmCherry-N1 and pEGFP-C1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, CF., Wang, HM., Wu, A. et al. FHA domain of AGGF1 is essential for its nucleocytoplasmic transport and angiogenesis. Sci. China Life Sci. 64, 1884–1894 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1844-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1844-0