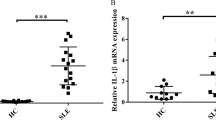
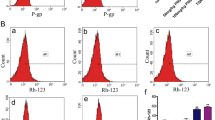
Abstract
Kidney is a major target organ in both antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The etiology of antiphospholipid syndrome nephropathy associated lupus nephritis (APSN-LN) is intricate and remains largely unrevealed. We proposed in present work, that generation of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPLs), especially those directed towards the oxidized neoepitopes, are largely linked with the redox status along with disease progression. Moreover, we observed that compromised antioxidative capacity coincided with turbulence of inflammatory cytokine profile in the kidney of male NZW×BXSB F1 mice suffered from APSN-LN. SM934 is an artemisinin derivative that has been proved to have potent immunosuppressive properties. In current study, we elaborated the therapeutic benefits of SM934 in male NZW×BXSB F1 mice, a murine model develops syndrome resembled human APS associated with SLE, for the first time. SM934 treatment comprehensively impeded autoantibodies production, inflammatory cytokine accumulation and excessive oxidative stress in kidney. Among others, we interpreted in present work that both anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects of SM934 is closely correlated with the enhancement of Nrf2 signaling and expression of its targets. Collectively, our finding confirmed that therapeutic strategy simultaneously exerting antioxidant and anti-inflammatory efficacy provide a novel feasible remedy for treating APSN-LN.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames, P., Matsuura, E., Batuca, J.R., Ciampa, A., Lopez, L.L., Ferrara, F., Iannaccone, L., and Delgado Alves, J. (2010). High-density lipoprotein inversely relates to its specific autoantibody favoring oxidation in thrombotic primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus 19, 711–716.
Biswas, S.K. (2016). Does the Interdependence between Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Explain the Antioxidant Paradox? Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016, 5698931.
Córdova, E.J., Velázquez-Cruz, R., Centeno, F., Baca, V., and Orozco, L. (2010). The NRF2 gene variant, -653G/A, is associated with nephritis in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 19, 1237–1242.
Castellani, P., Balza, E., and Rubartelli, A. (2014). Inflammation, DAMPs, tumor development, and progression: a vicious circle orchestrated by redox signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal 20, 1086–1097.
Charakida, M., Besler, C., Batuca, J.R., Sangle, S., Marques, S., Sousa, M., Wang, G., Tousoulis, D., Delgado, A.J., Loukogeorgakis, S.P., et al. (2009). Vascular abnormalities, paraoxonase activity, and dysfunctional HDL in primary antiphospholipid syndrome. JAMA 302, 1210–1217.
Dahdah, A., Habir, K., Nandakumar, K.S., Saxena, A., Xu, B., Holmdahl, R., and Malin, S. (2018). Germinal center B cells are essential for collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 70, 193–203.
DeFranco, A.L. (2016). Germinal centers and autoimmune disease in humans and mice. Immunol Cell Biol 94, 918–924.
Gharavi, A.E., Sammaritano, L.R., Wen, J., and Elkon, K.B. (1992). Induction of antiphospholipid autoantibodies by immunization with beta 2 glycoprotein I (apolipoprotein H). J Clin Invest 90, 1105–1109.
Gong, W., Li, J., Chen, Z., Huang, J., Chen, Q., Cai, W., Liu, P., and Huang, H. (2017). Polydatin promotes Nrf2-ARE anti-oxidative pathway through activating CKIP-1 to resist HG-induced up-regulation of FN and ICAM-1 in GMCs and diabetic mice kidneys. Free Radic Biol Med 106, 393–405.
Hörkkö, S., Miller, E., Dudl, E., Reaven, P., Curtiss, L.K., Zvaifler, N.J., Terkeltaub, R., Pierangeli, S.S., Branch, D.W., Palinski, W., et al. (1996). Antiphospholipid antibodies are directed against epitopes of oxidized phospholipids. Recognition of cardiolipin by monoclonal antibodies to epitopes of oxidized low density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest 98, 815–825.
Hahn, B.H., McMahon, M.A., Wilkinson, A., Wallace, W.D., Daikh, D.I., FitzGerald, J.D., Karpouzas, G.A., Merrill, J.T., Wallace, D.J., Yazdany, J., et al. (2012). American College of Rheumatology guidelines for screening, treatment, and management of lupus nephritis. Arthritis Care Res 64, 797–808.
Hao, F., Tian, M., Feng, Y., Quan, C., Chen, Y., Chen, S., and Wei, M. (2018). Abrogation of lupus nephritis in somatic hypermutation-deficient MRL-Faslpr/J mice. J Immunol 200, 3905–3912.
He, S., Lin, Z., Wu, Y., Bai, B., Yang, X., He, P., Zhu, F., Tang, W., and Zuo, J. (2014). Therapeutic effects of DZ2002, a reversible SAHH inhibitor, on lupus-prone NZB×NZW F1 mice via interference with TLR-mediated APC response. Acta Pharmacol Sin 35, 219–229.
Hou, L.F., He, S.J., Li, X., Yang, Y., He, P.L., Zhou, Y., Zhu, F.H., Yang, Y. F., Li, Y., Tang, W., et al. (2011). Oral administration of artemisinin analog SM934 ameliorates lupus syndromes in MRL/lpr mice by inhibiting Th1 and Th17 cell responses. Arthritis Rheum 63, 2445–2455.
Hou, L.F., He, S.J., Li, X., Wan, C.P., Yang, Y., Zhang, X.H., He, P.L., Zhou, Y., Zhu, F.H., Yang, Y.F., et al. (2012). SM934 treated lupus-prone NZB×NZW F1 mice by enhancing macrophage interleukin-10 production and suppressing pathogenic T cell development. PLoS ONE 7, e32424.
Kaul, A., Gordon, C., Crow, M.K., Touma, Z., Urowitz, M.B., van Vollenhoven, R., Ruiz-Irastorza, G., and Hughes, G. (2016). Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2, 16039.
Kobayashi, K., Kishi, M., Atsumi, T., Bertolaccini, M.L., Makino, H., Sakairi, N., Yamamoto, I., Yasuda, T., Khamashta, M.A., Hughes, G.R.V., et al. (2003). Circulating oxidized LDL forms complexes with β2-glycoprotein I. J Lipid Res 44, 716–726.
Kronbichler, A., and Mayer, G. (2013). Renal involvement in autoimmune connective tissue diseases. BMC Med 11, 95.
López-Pedrera, C., Barbarroja, N., Jimenez-Gomez, Y., Collantes-Estevez, E., Aguirre, M.A., and Cuadrado, M.J. (2016). Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of atherothrombosis associated with anti-phospholipid syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus: new therapeutic approaches. Rheumatology 55, 2096–2108.
Lamb, R.E., and Goldstein, B.J. (2008). Modulating an oxidative-inflammatory cascade: potential new treatment strategy for improving glucose metabolism, insulin resistance, and vascular function. Int J Clin Pract 62, 1087–1095.
Li, X., Li, T.T., Zhang, X.H., Hou, L.F., Yang, X.Q., Zhu, F.H., Tang, W., and Zuo, J.P. (2013). Artemisinin analogue SM934 ameliorates murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through enhancing the expansion and functions of regulatory T cell. PLoS ONE 8, e74108.
Li, Y. (2012). Qinghaosu (artemisinin): chemistry and pharmacology. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33, 1141–1146.
Lin, Z.M., Yang, X.Q., Zhu, F.H., He, S.J., Tang, W., and Zuo, J.P. (2016). Artemisinin analogue SM934 attenuate collagen-induced arthritis by suppressing T follicular helper cells and T helper 17 cells. Sci Rep 6, 38115.
Liu, X., Ward, K., Xavier, C., Jann, J., Clark, A.F., Pang, I.H., and Wu, H. (2016). The novel triterpenoid RTA 408 protects human retinal pigment epithelial cells against H2O2-induced cell injury via NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) activation. Redox Biol 8, 98–109.
Lu, H., Wang, B., Cui, N., and Zhang, Y. (2018). Artesunate suppresses oxidative and inflammatory processes by activating Nrf2 and ROS-dependent p38 MAPK and protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep 17, 6639–6646.
Luo, J.F., Shen, X.Y., Lio, C.K., Dai, Y., Cheng, C.S., Liu, J.X., Yao, Y.D., Yu, Y., Xie, Y., Luo, P., et al. (2018). Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 pathway by nardochinoid C inhibits inflammation and oxidative stress in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Front Pharmacol 9, 911.
Martínez-Flores, J., Serrano, M., Morales, J., and Serrano, A. (2016). Antiphospholipid syndrome and kidney involvement: new insights. Antibodies 5, 17.
Misasi, R., Capozzi, A., Longo, A., Recalchi, S., Lococo, E., Alessandri, C., Conti, F., Valesini, G., and Sorice, M. (2015). “New” antigenic targets and methodological approaches for refining laboratory diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome. J Immunol Res 2015, 1–13.
Mittal, M., Siddiqui, M.R., Tran, K., Reddy, S.P., and Malik, A.B. (2014). Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid Redox Signal 20, 1126–1167.
Perez-Sanchez, C., Ruiz-Limon, P., Aguirre, M.A., Bertolaccini, M.L., Khamashta, M.A., Rodriguez-Ariza, A., Segui, P., Collantes-Estevez, E., Barbarroja, N., Khraiwesh, H., et al. (2012). Mitochondrial dysfunction in antiphospholipid syndrome: implications in the pathogenesis of the disease and effects of coenzyme Q10 treatment. Blood 119, 5859–5870.
Pizzino, G., Irrera, N., Cucinotta, M., Pallio, G., Mannino, F., Arcoraci, V., Squadrito, F., Altavilla, D., and Bitto, A. (2017). Oxidative stress: harms and benefits for human health. Oxid Med Cell Long 2017, 1–13.
Pons-Estel, G.J., Andreoli, L., Scanzi, F., Cervera, R., and Tincani, A. (2017). The antiphospholipid syndrome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun 76, 10–20.
Ratliff, B.B., Abdulmahdi, W., Pawar, R., and Wolin, M.S. (2016). Oxidant mechanisms in renal injury and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 25, 119–146.
Ruiz-Irastorza, G., Ramos-Casals, M., Brito-Zeron, P., and Khamashta, M. A. (2010). Clinical efficacy and side effects of antimalarials in systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis 69, 20–28.
Savelli, S.L., Roubey, R.A.S., Kitzmiller, K.J., Zhou, D., Nagaraja, H.N., Mulvihill, E., Barbar-Smiley, F., Ardoin, S.P., Wu, Y.L., and Yu, C.Y. (2019). Opposite profiles of complement in antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) among patients with antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL). Front Immunol 10, 885.
Schreiber, K., Sciascia, S., de Groot, P.G., Devreese, K., Jacobsen, S., Ruiz-Irastorza, G., Salmon, J.E., Shoenfeld, Y., Shovman, O., and Hunt, B.J. (2018). Antiphospholipid syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers 4, 17103.
Shah, D., Mahajan, N., Sah, S., Nath, S.K., and Paudyal, B. (2014). Oxidative stress and its biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Biomed Sci 21, 23.
Smallwood, M.J., Nissim, A., Knight, A.R., Whiteman, M., Haigh, R., and Winyard, P.G. (2018). Oxidative stress in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Free Radic Biol Med 125, 3–14.
Turrent-Carriles, A., Herrera-Félix, J.P., and Amigo, M.C. (2018). Renal involvement in antiphospholipid syndrome. Front Immunol 9, 1008.
Vomund, S., Schäfer, A., Parnham, M., Brüne, B., and von Knethen, A. (2017). Nrf2, the master regulator of anti-oxidative responses. Int J Mol Sci 18, 2772.
Wang, J., Xu, C., Wong, Y.K., Li, Y., Liao, F., Jiang, T., and Tu, Y. (2019). Artemisinin, the magic drug discovered from traditional chinese medicine. Engineering 5, 32–39.
Wang, Y., Xiao, C.Y., Lin, H.Q., Hu, J.S., Ip, T.M., and Chi-Cheong Wan, D. (2020). Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Keap1-Nrf2 interaction inhibitors identification. Redox Biol 34, 101573.
Willis, R., Smikle, M., DeCeulaer, K., Romay-Penabad, Z., Papalardo, E., Jajoria, P., Harper, B., Murthy, V., Petri, M., and Gonzalez, E.B. (2017). Clinical associations of proinflammatory cytokines, oxidative biomarkers and vitamin D levels in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 26, 1517–1527.
Wu, Y., He, S., Bai, B., Zhang, L., Xue, L., Lin, Z., Yang, X., Zhu, F., He, P., Tang, W., et al. (2016). Therapeutic effects of the artemisinin analog SM934 on lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice via inhibition of TLR-triggered B-cell activation and plasma cell formation. Cell Mol Immunol 13, 379–390.
Yung, S., Yap, D.Y., and Chan, T.M. (2017). Recent advances in the understanding of renal inflammation and fibrosis in lupus nephritis. F1000Research 6, 874.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81903882 and 81871240), the National Science and Technology Major Project “New Drug Creation and Manufacturing Program” (2018ZX09711002-014-001), the Personalized Medicines—“Molecular Signature-based Drug Discovery and Development”, Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA12020107 and XDA12020369).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Z., Liu, Y., Chen, L. et al. Artemisinin analogue SM934 protects against lupus-associated antiphospholipid syndrome via activation of Nrf2 and its targets. Sci. China Life Sci. 64, 1702–1719 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1840-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1840-1