Abstract
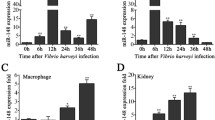
Inflammation is a self-protection mechanism that can be triggered when innate immune cells detect infection. Eradication of pathogen infection requires appropriate immune and inflammatory responses, but excessive inflammatory responses can cause uncontrolled inflammation, autoimmune diseases, or pathogen dissemination. Mounting evidence has shown that microRNAs (miRNAs) in mammals act as important and versatile regulators of innate immunity and inflammation. However, miRNA-mediated regulation networks are largely unknown in inflammatory responses in lower vertebrates. Here miR-144 and miR-217 are identified as negative regulators in teleost inflammatory responses. We find that Vibrio harveyi and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment significantly upregulate the expression of fish miR-144 and miR-217. Upregulated miR-144 and miR-217 suppress LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine expression by targeting nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 1 (NOD1), thereby avoiding excessive inflammatory responses. In addition, miR-144 and miR-217 regulate inflammatory responses through NOD1-induced nuclear factor kappa (NF-kB) signaling pathways. These findings demonstrate that miR-144 and miR-217 play regulatory roles in inflammatory responses by modulating the NOD1-induced NF-κB signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akira, S., Takeda, K., and Kaisho, T. (2001). Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat Immunol 2, 675–680.
Austin, B., and Zhang, X.H. (2006). Vibrio harveyi: a significant pathogen of marine vertebrates and invertebrates. Lett Appl Microbiol 43, 119–124.
Baltimore, D., Boldin, M.P., O’Connell, R.M., Rao, D.S., and Taganov, K. D. (2008). MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat Immunol 9, 839–845.
Bertin, J., Nir, W.J., Fischer, C.M., Tayber, O.V., Errada, P.R., Grant, J.R., Keilty, J.J., Gosselin, M.L., Robison, K.E., Wong, G.H.W., et al. (1999). Human CARD4 protein is a novel CED-4/Apaf-1 cell death family member that activates NF-kB. J Biol Chem 274, 12955–12958.
Bi, D., Gao, Y., Chu, Q., Cui, J., and Xu, T. (2017). NOD1 is the innate immune receptor for iE-DAP and can activate NF-κB pathway in teleost fish. Dev Comp Immunol 76, 238–246.
Bi, D., Wang, Y., Gao, Y., Li, X., Chu, Q., Cui, J., and Xu, T. (2018). Recognition of lipopolysaccharide and activation of NF-κB by cytosolic sensor NOD1 in teleost fish. Front Immunol 9, 1413.
Chu, Q., and Xu, T. (2016). miR-192 targeting IL-1RI regulates the immune response in miiuy croaker after pathogen infection in vitro and in vivo. Fish Shellfish Immunol 54, 537–543.
Chu, Q., Song, W., Cui, J., and Xu, T. (2017a). Genome-guided transcriptome analysis of miiuy croaker provides insights into pattern recognition receptors and cytokines in response to Vibrio anguillarum. Dev Comp Immunol 73, 72–78.
Chu, Q., Sun, Y., Cui, J., and Xu, T. (2017b). MicroRNA-3570 modulates the NF-κB pathway in teleost fish by targeting MyD88. J Immunol 198, 3274–3282.
Chu, Q., Yan, X., Liu, L., and Xu, T. (2019). The inducible microRNA-21 negatively modulates the inflammatory response in teleost fish via targeting IRAK4. Front Immunol 10, 1623.
Chuang, A.Y., Chuang, J.C., Zhai, Z., Wu, F., and Kwon, J.H. (2014). NOD2 expression is regulated by microRNAs in colonic epithelial HCT116 cells. Inflamm Bowel Dis 20, 126–135.
da Silva Correia, J., Miranda, Y., Leonard, N., and Ulevitch, R. (2007). SGT1 is essential for Nod1 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 6764–6769.
Denli, A.M., Tops, B.B.J., Plasterk, R.H.A., Ketting, R.F., and Hannon, G. J. (2004). Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature 432, 231–235.
Dryden, N.H., Sperone, A., Martin-Almedina, S., Hannah, R.L., Birdsey, G. M., Khan, S.T., Layhadi, J.A., Mason, J.C., Haskard, D.O., Göttgens, B., et al. (2012). The transcription factor Erg controls endothelial cell quiescence by repressing activity of nuclear factor (NF)-κB p65. J Biol Chem 287, 12331–12342.
Friedman, R.C., Farh, K.K.H., Burge, C.B., and Bartel, D.P. (2009). Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets ofmicroRNAs. Genome Res 19, 92–105.
Girardin, S.E., Boneca, I.G., Carneiro, L.A.M., Antignac, A., Jéhanno, M., Viala, J., Tedin, K., Taha, M.K., Labigne, A., Zähringer, U., et al. (2003). Nod1 detects a unique muropeptide from gram-negative bacterial peptidoglycan. Science 300, 1584–1587.
Girardin, S.E., Jéhanno, M., Mengin-Lecreulx, D., Sansonetti, P.J., Alzari, P.M., and Philpott, D.J. (2005). Identification of the critical residues involved in peptidoglycan detection by Nod1. J Biol Chem 280, 38648–38656.
Hahn, J.S. (2005). Regulation of Nod1 by Hsp90 chaperone complex. FEBS Lett 579, 4513–1519.
Hasegawa, M., Fujimoto, Y., Lucas, P.C., Nakano, H., Fukase, K., Núñez, G., and Inohara, N. (2008). A critical role of RICK/RIP2 polyubiquitination in Nod-induced NF-κB activation. EMBO J 27, 373–383.
He, Y., Pan, H., Zhang, G., and He, S. (2019). Comparative study on pattern recognition receptors in non-teleost ray-finned fishes and their evolutionary significance in primitive vertebrates. Sci China Life Sci 62, 566–578.
Hua, Y., Zhang, J., Jia, Z., Li, J., Xiong, X., and Xiong, Y. (2019). Immune-related genes response to stimulation ofmiR-155 overexpression in CIK (ctenopharyngodon idella kidney) cells and zebrafish. Fish Shellfish Immunol 94, 142–148.
Inohara, N., Chamaillard, M., McDonald, C., and Nuñez, G. (2005). NOD-LRR proteins: role in host-microbial interactions and inflammatory disease. Annu Rev Biochem 74, 355–383.
Janeway Jr, C.A., and Medzhitov, R. (2002). Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 20, 197–216.
John, B., Enright, A.J., Aravin, A., Tuschl, T., Sander, C., and Marks, D.S. (2004). Human microRNA targets. PLoS Biol 2, e363.
Kang, H., Park, Y., Lee, A., Seo, H., Kim, M.J., Choi, J., Jo, H.N., Jeong, H.N., Cho, J.G., Chang, W., et al. (2017). Negative regulation of NOD1 mediated angiogenesis by PPARy-regulated miR-125a. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 482, 28–34.
Kawai, T., and Akira, S. (2010). The role ofpattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 11, 373–384.
Kwak, J.S., Kim, M.S., and Kim, K.H. (2019). Generation of microRNA-30e-producing recombinant viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus (VHSV) and its effect on in vitro immune responses. Fish Shellfish Immunol 94, 381–388.
Lewis, B.P., Shih, I., Jones-Rhoades, M.W., Bartel, D.P., and Burge, C.B. (2003). Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115, 787–798.
Li, J., Gao, Y., and Xu, T. (2015a). Comparative genomic and evolution of vertebrate NOD1 and NOD2 genes and their immune response in miiuy croaker. Fish Shellfish Immunol 46, 387–397.
Li, J., Kong, L., Gao, Y., Wu, C and Xu, T. (2015b). Characterization of NLR-A subfamily members in miiuy croaker and comparative genomics revealed NLRX1 underwent duplication and lose in actinopterygii. Fish Shellfish Immunol 47, 397–406.
Livak, K.J., and Schmittgen, T.D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 25, 402–408.
Luo, G., Sun, Y., Huang, L., Su, Y., Zhao, L., Qin Y., Xu, X., and Yan, Q. (2020). Time-resolved dual RNA-seq of tissue uncovers Pseudomonas plecoglossicida key virulence genes in host-pathogen interaction with Epinephelus coioides. Environ Microbiol 22, 677–693.
Magnadóttir, B. (2006). Innate immunity of fish (overview). Fish Shellfish Immunol 20, 137–151.
Medzhitov, R. (2001). Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 1, 135–145.
Ogura, Y., Bonen, D.K., Inohara, N., Nicolae, D.L., Chen, F.F., Ramos, R., Britton, H., Moran, T., Karaliuskas, R., Duerr, R.H., et al. (2001). A frameshift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Nature 411, 603–606.
Park, J.H., Kim, Y.G., McDonald, C., Kanneganti, T.D., Hasegawa, M., Body-Malapel, M., Inohara, N and Núñez, G. (2007). RICK/RIP2 mediates innate immune responses induced through Nod1 and Nod2 but not TLRs. J Immunol 178, 2380–2386.
Park, S.B., Hikima, J., Suzuki, Y., Ohtani, M., Nho, S.W., Cha, I.S., Jang, H.B., Kondo, H., Hirono, I., Aoki, T., et al. (2012). Molecular cloning and functional analysis of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 1 (NOD1) in olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Dev Comp Immunol 36, 680–687.
Rusinov, V., Baev, V., Minkov, I.N., and Tabler, M. (2005). MicroInspector: a web tool for detection of miRNA binding sites in an RNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 33, W696–W700.
Swain, B., Basu, M., and Samanta, M. (2013). NOD1 and NOD2 receptors in mrigal (Cirrhinus mrigala): inductive expression and downstream signalling in ligand stimulation and bacterial infections. J Biosci 38, 533–548.
Takeuchi, O., and Akira, S. (2010). Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 140, 805–820.
Xiao, C., and Rajewsky, K. (2009). MicroRNA control in the immune system: basic principles. Cell 136, 26–36.
Xu, T., Chu, Q., Cui, J., and Bi, D. (2018a). Inducible MicroRNA-3570 feedback inhibits the RIG-I-dependent innate immune response to rhabdovirus in teleost fish by targeting MAVS/IPS-1. J Virol 92.
Xu, T., Chu, Q., Cui, J., and Zhao, X. (2018b). The inducible microRNA-203 in fish represses the inflammatory responses to Gram-negative bacteria by targeting IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4. J Biol Chem 293, 1386–1396.
Xu, T., Chu, Q., Cui, J., and Huo, R. (2018c). MicroRNA-216a inhibits NF-κB-mediated inflammatory cytokine production in teleost fish by modulating p65. Infect Immun 86, e00256.
Xu, T., Xu, G., Che, R., Wang, R., Wang, Y., Li, J., Wang, S., Shu, C., Sun, Y., Liu, T., et al. (2016). The genome of the miiuy croaker reveals well-developed innate immune and sensory systems. Sci Rep 6, 21902.
Yamamoto-Furusho, J.K., Barnich, N., Xavier, R., Hisamatsu, T., and Podolsky, D.K. (2006). Centaurin β1 down-regulates nucleotide-binding oligomerization domains 1- and 2-dependent NF-κB activation. J Biol Chem 281, 36060–36070.
Zhang, B., Luo, G., Zhao, L., Huang, L., Qin, Y., Su, Y., and Yan, Q. (2018). Integration of RNAi and RNA-seq uncovers the immune responses of Epinephelus coioides to L321RS19110 gene of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida. Fish Shellfish Immunol 81, 121–129.
Zhang, F., Peng, Z., Zhang, J., Liu, M., Fu R., and Luo, H. (2010). Isolation and identification of the pathogenic strain of Vibrio harveyi from Miichthys miiuy (in Chinese). Acta Micrbiol Sin 50, 304–309.
Zhang, R., Zhao, J., Song, Y., Wang, X., Wang, L., Xu, J., Song, C., and Liu, F. (2014). The E3 ligase RNF34 is anovel negative regulator of the NOD1 pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 33, 1954–1962.
Zou, J., and Secombes, C.J. (2011). Teleost fish interferons and their role in immunity. Dev Comp Immunol 35, 1376–1387.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31822057) and the National Key Research and Development Project (2018YFD0900503).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, Q., Bi, D., Zheng, W. et al. MicroRNA negatively regulates NF-κB-mediated immune responses by targeting NOD1 in the teleost fish Miichthys miiuy. Sci. China Life Sci. 64, 803–815 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1777-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1777-y