Abstract
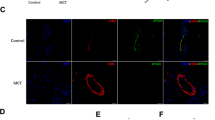
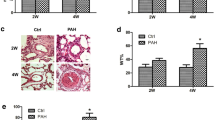
Clinical cases have reported pulmonary arterial structural and functional abnormalities in patients with Kawasaki disease (KD); however, the underlying mechanisms are unclear. In this study, a KD rat model was established via the intraperitoneal injection of Lactobacillus casei cell wall extract (LCWE). The results showed that pulmonary arterial functional and structural abnormalities were observed in KD rats. Furthermore, proliferative endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress) was observed in the pulmonary arteries of KD rats. Notably, the level of lipocalin-2 (Lcn 2), a trigger factor of inflammation, was remarkably elevated in the plasma and lung tissues of KD rats; increased Lcn 2 levels following LCWE stimulation may result from polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs). Correspondingly, in cultured pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs), Lcn 2 markedly augmented the cleavage and nuclear localization of activating transcription factor-6 (ATF6), upregulated the transcription of glucose regulated protein 78 (GRP78) and neurite outgrowth inhibitor (NOGO), and promoted PASMCs proliferation. However, proapoptotic C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) and caspase 12 levels were not elevated. Treatment with 4-phenyl butyric acid (4-PBA, a specific inhibitor of ER stress) inhibited PASMCs proliferation induced by Lcn 2 and attenuated pulmonary arterial abnormalities and right ventricular hypertrophy and reduced right ventricular systolic pressure in KD rats. In conclusion, Lcn 2 remarkably facilitates proliferative ER stress in PASMCs, which probably accounts for KD-related pulmonary arterial abnormalities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand, A., and Anand, A. (1995). Coronary artery involvement in Kawasaki disease—diagnosis and treatment. West J Med 163, 393.
Biezeveld, M.H., van Mierlo, G., Lutter, R., Kuipers, I.M., Dekker, T., Hack, C.E., Newburger, J.W., and Kuijpers, T.W. (2005). Sustained activation of neutrophils in the course of Kawasaki disease: an association with matrix metalloproteinases. Clin Exp Immunol 141, 183–188.
Briceno-Medina, M., Perez, M., Waller, B.R., and Sathanandam, S. (2016). Systemic and pulmonary artery aneurysms in incomplete Kawasaki disease. J Cardiol Cases 13, 185–188.
Brogan, P.A., Bose, A., Burgner, D., Shingadia, D., Tulloh, R., Michie, C., Klein, N., Booy, R., Levin, M., and Dillon, M.J. (2002). Kawasaki disease: an evidence based approach to diagnosis, treatment, and proposals for future research. Arch Dis Childhood 86, 286–290.
Chung, T.W., Choi, H.J., Kim, C.H., Jeong, H.S., and Ha, K.T. (2013). Lipocalin-2 elicited by advanced glycation end-products promotes the migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1833, 3386–3395.
da Silva, M.H., Peçanha, F.L.M., de Oliveira, A.M., and da-Silva, W.S. (2017). 4-Phenyl butyric acid increases particulate hexokinase activity and protects against ROS injury in L6 myotubes. Life Sci 179, 98–102.
Ding, G., Wang, J., Feng, C., Jiang, H., Xu, J., and Ding, Q. (2016). Lipocalin 2 over-expression facilitates progress of castration-resistant prostate cancer via improving androgen receptor transcriptional activity. Oncotarget 7, 64309–64317.
Dromparis, P., Paulin, R., Stenson, T.H., Haromy, A., Sutendra, G., and Michelakis, E.D. (2013). Attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress as a novel therapeutic strategy in pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 127, 115–125.
Dromparis, P., Sutendra, G., and Michelakis, E.D. (2010). The role of mitochondria in pulmonary vascular remodeling. J Mol Med 88, 1003–1010.
Eilenberg, W., Stojkovic, S., Piechota-Polanczyk, A., Kaider, A., Kozakowski, N., Weninger, W.J., Nanobachvili, J., Wojta, J., Huk, I., Demyanets, S., et al. (2017). Neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) is elevated in type 2 diabetics with carotid artery stenosis and reduced under metformin treatment. Cardiovasc Diabetol 16, 98.
Eilenberg, W., Stojkovic, S., Piechota-Polanczyk, A., Kaun, C., Rauscher, S., Gröger, M., Klinger, M., Wojta, J., Neumayer, C., Huk, I., et al. (2016). Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is associated with symptomatic carotid atherosclerosis and drives pro-inflammatory state in vitro. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 51, 623–631.
Escalon, J.G., Wu, X., Drexler, I.R., Lief, L., Plataki, M., Bender, M., and Gruden, J.F. (2018). Rare case of pulmonary involvement in an adult with Kawasaki disease. Clin Imag 47, 1–3.
Giaginis, C., Zira, A., Katsargyris, A., Klonaris, C., and Theocharis, S. (2010). Clinical implication of plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) concentrations in patients with advanced carotid atherosclerosis. Clin Chem Lab Med 48, 1035–1041.
Hotamisligil, G.S. (2010). Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 140, 900–917.
Huang, Y., Liu, M., Dong, M., Yang, W., Zhang, B., Luan, L., Dong, H., Xu, M., Wang, Y., Liu, L., et al. (2009). Effects of sodium tanshinone II A sulphonate on hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in rats in vivo and on Kv2.1 expression in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells in vitro. J EthnoPharmacol 125, 436–443.
Ibrahim, J., Al Amri, A., and Ghatasheh, G. (2017). Transfusion-related acute lung injury after immunoglobulin infusion for Kawasaki disease: a case report and literature review. Glob Pediatr Health 4, 2333794X1774654.
Jung, M., Ören, B., Mora, J., Mertens, C., Dziumbla, S., Popp, R., Weigert, A., Grossmann, N., Fleming, I., and Brüne, B. (2016). Lipocalin 2 from macrophages stimulated by tumor cell-derived sphingosine 1-phosphate promotes lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Sci Signal 9, ra64.
Kjeldsen, L., Bainton, D.F., Sengelov, H., and Borregaard, N. (1994). Identification of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a novel matrix protein of specific granules in human neutrophils. Blood 83, 799–807.
Kjeldsen, L., Johnsen, A.H., Sengelov, H., and Borregaard, N. (1993). Isolation and primary structure of NGAL, a novel protein associated with human neutrophil gelatinase. J Biol Chem 268, 10425–10432.
Ko, E.A., Song, M.Y., Donthamsetty, R., Makino, A., and Yuan, J.X.J. (2010). Tension measurement in isolated rat and mouse pulmonary artery. Drug Discov Today Dis Model 7, 123–130.
Koyama, M., Furuhashi, M., Ishimura, S., Mita, T., Fuseya, T., Okazaki, Y., Yoshida, H., Tsuchihashi, K., and Miura, T. (2014). Reduction of endoplasmic reticulum stress by 4-phenylbutyric acid prevents the development of hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 306, H1314–H1323.
Lee, Y., Schulte, D.J., Shimada, K., Chen, S., Crother, T.R., Chiba, N., Fishbein, M.C., Lehman, T.J.A., and Arditi, M. (2012). Interleukin-1β is crucial for the induction of coronary artery inflammation in a mouse model of Kawasaki disease. Circulation 125, 1542–1550.
Li, C., Yu, L., Xue, H., Yang, Z., Yin, Y., Zhang, B., Chen, M., and Ma, H. (2017). Nuclear AMPK regulated CARM1 stabilization impacts autophagy in aged heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 486, 398–405.
Lin, I.C., Sheen, J.M., Tain, Y.L., Chou, M.H., Huang, L.T., and Yang, K.D. (2014). Vascular endothelial growth factor-a in lactobacillus casei cell wall extract-induced coronary arteritis of a murine model. Circ J 78, 752–762.
Masuda, H., Shozawa, T., Naoe, S., and Tanaka, N. (1986). The intercostal artery in Kawasaki disease. A pathologic study of 17 autopsy cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med 110, 1136–1142.
McCrindle, B.W., Rowley, A.H., Newburger, J.W., Burns, J.C., Bolger, A. F., Gewitz, M., Baker, A.L., Jackson, M.A., Takahashi, M., Shah, P.B., et al. (2017). Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 135, e927.
Michelakis, E.D., Wilkins, M.R., and Rabinovitch, M. (2008). Emerging concepts and translational priorities in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation 118, 1486–1495.
Minamino, T., and Kitakaze, M. (2010). ER stress in cardiovascular disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol 48, 1105–1110.
Nicholson, G.T., Samai, C., and Kanaan, U. (2013). Pulmonary hypertension in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 34, 1966–1968.
Nilsen-Hamilton, M., Liu, Q., Ryon, J., Bendickson, L., Lepont, P., and Chang, Q. (2003). Tissue involution and the acute phase response. Ann New York Acad Sci 995, 94–108.
Numano, F., Shimizu, C., Tremoulet, A.H., Dyar, D., Burns, J.C., and Printz, B.F. (2016). Pulmonary artery dilation and right ventricular function in acute Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 37, 482–490.
Oakes, S.A., and Papa, F.R. (2015). The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu Rev Pathol Mech Dis 10, 173–194.
Paulin, R., and Michelakis, E.D. (2014). The metabolic theory of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ Res 115, 148–164.
Quintero, O.A., and Wright, J.R. (2002). Clearance of surfactant lipids by neutrophils and macrophages isolated from the acutely inflamed lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282, L330–L339.
Senzaki, H., Chen, C.H., Ishido, H., Masutani, S., Matsunaga, T., Taketazu, M., Kobayashi, T., Sasaki, N., Kyo, S., and Yokote, Y. (2005). Arterial hemodynamics in patients after Kawasaki disease. Circulation 111, 2119–2125.
Singer, E., Markó, L., Paragas, N., Barasch, J., Dragun, D., Müller, D.N., Budde, K., and Schmidt-Ott, K.M. (2013). Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: pathophysiology and clinical applications. Acta Physiol 207, 663–672.
Singh, S., Gupta, A., Jindal, A.K., Gupta, A., Suri, D., Rawat, A., Vaidya, P. C., and Singh, M. (2018). Pulmonary presentation of Kawasaki disease—A diagnostic challenge. Pediatr Pulmonol 53, 103–107.
Sittiwangkul, R., Pongprot, Y., Silvilairat, S., and Phornphutkul, C. (2011). Delayed diagnosis of Kawasaki disease: risk factors and outcome of treatment. Ann Trop Paediatr 31, 109–114.
Sugimoto, M., Ishido, H., Seki, M., Masutani, S., Tamai, A., and Senzaki, H. (2012). Findings in the pulmonary vascular bed in the remote phase after Kawasaki disease. Am J Cardiol 109, 1219–1222.
Sutendra, G., Dromparis, P., Wright, P., Bonnet, S., Haromy, A., Hao, Z., McMurtry, M.S., Michalak, M., Vance, J.E., Sessa, W.C., et al. (2011). The role of Nogo and the mitochondria-endoplasmic reticulum unit in pulmonary hypertension. Sci Transl Med 3, 88ra55.
Szegezdi, E., Logue, S.E., Gorman, A.M., and Samali, A. (2006). Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep 7, 880–885.
Takahashi K., O.T., Yokouchi Y., and Enomoto Y. (2017). Histopathological characteristics of noncardiac organs in Kawasaki disease. In Kawasaki Disease, N.J. Saji B., Burns J., Takahashi M., ed. (Tokyo: Springer), pp. 17–22.
Ugi, J., Lepper, P.M., Witschi, M., Maier, V., Geiser, T., and Ott, S.R. (2010). Nonresolving pneumonia and rash in an adult: pulmonary involvements in Kawasaki’s disease. Eur Respir J 35, 452–454.
Umezawa, T., Saji, T., Matsuo, N., and Odagiri, K. (1989). Chest x-ray findings in the acute phase of Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Radiol 20, 48–51.
Vaidya, P.C., Narayanan, K., Suri, D., Rohit, M.K., Gupta, A., Singh, S., and Singh, M. (2017). Pulmonary presentation of Kawasaki disease: an unusual occurrence. Int J Rheum Dis 20, 2227–2229.
Wang, G., Liu, S., Wang, L., Meng, L., Cui, C., Zhang, H., Hu, S., Ma, N., and Wei, Y. (2017a). Lipocalin-2 promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress and proliferation by augmenting intracellular iron in human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Int J Biol Sci 13, 135–144.
Wang, G., Liu, X., Meng, L., Liu, S., Wang, L., Li, J., Cui, C., Meng, J., Hu, S., and Wei, Y. (2014). Up-regulated lipocalin-2 in pulmonary hypertension involving in pulmonary artery SMC resistance to apoptosis. Int J Biol Sci 10, 798–806.
Wang, G., Ma, N., Meng, L., Wei, Y., and Gui, J. (2015). Activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway is involved in lipocalin-2-promoted human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation. Mol Cell Biochem 410, 207–213.
Wang, J.J., Zuo, X.R., Xu, J., Zhou, J.Y., Kong, H., Zeng, X.N., Xie, W.P., and Cao, Q. (2016). Evaluation and treatment of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in right ventricular dysfunction during monocrotaline-induced rat pulmonary arterial hypertension. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 30, 587–598.
Wang, Y., Wu, Z.Z., and Wang, W. (2017b). Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress alleviates cigarette smoke-induced airway inflammation and emphysema. Oncotarget 8, 77685–77695.
Xu, D.Q., Luo, Y., Liu, Y., Wang, J., Zhang, B., Xu, M., Wang, Y.X., Dong, H.Y., Dong, M.Q., Zhao, P.T., et al. (2010). Beta-estradiol attenuates hypoxic pulmonary hypertension by stabilizing the expression of p27kip1 in rats. Respir Res 11, 182.
Yoshida, H. (2007). ER stress and diseases. FEBS J 274, 630–658.
Zhang, B., Niu, W., Xu, D., Li, Y., Liu, M., Wang, Y., Luo, Y., Zhao, P., Liu, Y., Dong, M., et al. (2014). Oxymatrine prevents hypoxia- and monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Free Rad Biol Med 69, 198–207.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the following grants: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91749108, 31671424, and 81322004 to H.M., 81200036 to M.L., and 81102006 to J.Z.), the Science and Technology Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province, China (2018SF-101 to N.M. and 2019SF-008 to M.L.), and the Youth Innovation Team of Shaanxi Universities, China (to H.M., Y.Y., N.M., Y.W., and J.Z.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Z., Yin, Y., Li, C. et al. Lipocalin-2-induced proliferative endoplasmic reticulum stress participates in Kawasaki disease-related pulmonary arterial abnormalities. Sci. China Life Sci. 64, 1000–1012 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-019-1772-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-019-1772-8