Abstract
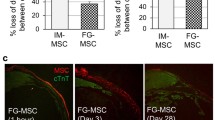
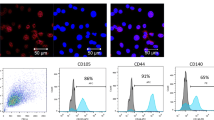
Stem cell therapy is an attractive approach for recovery from myocardial infarction (MI) but faces the challenges of rapid diffusion and poor survival after transplantation. Here we developed an injectable collagen scaffold to promote the long-term retention of transplanted cells in chronic MI. Forty-five minipigs underwent left anterior descending artery (LAD) ligation and were equally divided into three groups 2 months later (collagen scaffold loading with human umbilical mesenchymal stem cell (hUMSC) group, hUMSC group, and placebo group (only phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) injection)). Immunofluorescence staining indicated that the retention of transplanted cells was promoted by the collagen scaffold. Echocardiography and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR) showed much higher left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and lower infarct size percentage in the collagen/hUMSC group than in the hUMSC and placebo groups at 12 months after treatment. There were also higher densities of vWf-, α-sma-, and cTnT-positive cells in the infarct border zone in the collagen/cell group, as revealed by immunohistochemical analysis, suggesting better angiogenesis and more cardiomyocyte survival after MI. Thus, the injectable collagen scaffold was safe and effective on a large animal myocardial model, which is beneficial for constructing a favorable microenvironment for applying stem cells in clinical MI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araña, M., Gavira, J.J., Peña, E., González, A., Abizanda, G., Cilla, M., Pérez, M.M., Albiasu, E., Aguado, N., Casado, M., et al. (2014). Epicardial delivery of collagen patches with adipose-derived stem cells in rat and minipig models of chronic myocardial infarction. Biomaterials 35, 143–151.
Araña, M., Peña, E., Abizanda, G., Cilla, M., Ochoa, I., Gavira, J.J., Espinosa, G., Doblaré, M., Pelacho, B., and Prosper, F. (2013). Preparation and characterization of collagen-based ADSC-carrier sheets for cardiovascular application. Acta Biomater 9, 6075–6083.
Behfar, A., Crespo-Diaz, R., Terzic, A., and Gersh, B.J. (2014). Cell therapy for cardiac repair—Lessons from clinical trials. Nat Rev Cardiol 11, 232–246.
Beltrami, A.P., Urbanek, K., Kajstura, J., Yan, S.M., Finato, N., Bussani, R., Nadal-Ginard, B., Silvestri, F., Leri, A., Beltrami, C.A., et al. (2001). Evidence that human cardiac myocytes divide after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 344, 1750–1757.
Blackburn, N.J.R., Sofrenovic, T., Kuraitis, D., Ahmadi, A., McNeill, B., Deng, C., Rayner, K.J., Zhong, Z., Ruel, M., and Suuronen, E.J. (2015). Timing underpins the benefits associated with injectable collagen biomaterial therapy for the treatment of myocardial infarction. Biomaterials 39, 182–192.
Bollini, S., Smits, A.M., Balbi, C., Lazzarini, E., and Ameri, P. (2018). Triggering endogenous cardiac repair and regeneration via extracellular vesicle-mediated communication. Front Physiol 9, 1497.
Buikema, J.W., Van Der Meer, P., Sluijter, J.P.G., and Domian, I.J. (2013). Concise review: Engineering myocardial tissue: The convergence of stem cells biology and tissue engineering technology. Stem Cells 31, 2587–2598.
Chachques, J.C., Trainini, J.C., Lago, N., Masoli, O.H., Barisani, J.L., Cortes-Morichetti, M., Schussler, O., and Carpentier, A. (2007). Myocardial assistance by grafting a new bioartificial upgraded myocardium (magnum clinical trial): One year follow-up. Cell Transplant 16, 927–934.
Chachques, J.C., Trainini, J.C., Lago, N., Cortes-Morichetti, M., Schussler, O., and Carpentier, A. (2008). Myocardial assistance by grafting a new bioartificial upgraded myocardium (magnum trial): Clinical feasibility study. Ann Thorac Surg 85, 901–908.
Chang, M.Y., Huang, T.T., Chen, C.H., Cheng, B., Hwang, S.M., and Hsieh, P.C.H. (2016). Injection of human cord blood cells with hyaluronan improves postinfarction cardiac repair in pigs. Stem Cells Transl Med 5, 56–66.
Chen, A.J., Pi, J.K., Hu, J.G., Huang, Y.Z., Gao, H.W., Li, S.F., Li-Ling, J., and Xie, H.Q. (2020). Identification and characterization of two morphologically distinct stem cell subpopulations from human urine samples. Sci China Life Sci 62, 712–723.
Chen, C.H., Chang, M.Y., Wang, S.S., and Hsieh, P.C.H. (2014). Injection of autologous bone marrow cells in hyaluronan hydrogel improves cardiac performance after infarction in pigs. Am J Physiol-Heart Circ Physiol 306, H1078–H1086.
Chiu, L.L.Y., Reis, L.A., Momen, A., and Radisic, M. (2012). Controlled release of thymosin β4 from injected collagen-chitosan hydrogels promotes angiogenesis and prevents tissue loss after myocardial infarction. Regen Med 7, 523–533.
Christman, K.L., Vardanian, A.J., Fang, Q., Sievers, R.E., Fok, H.H., and Lee, R.J. (2004). Injectable fibrin scaffold improves cell transplant survival, reduces infarct expansion, and induces neovasculature formation in ischemic myocardium. J Am Coll Cardiol 44, 654–660.
Dixit, P., and Katare, R. (2015). Challenges in identifying the best source of stem cells for cardiac regeneration therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther 6, 26.
Eschenhagen, T., Bolli, R., Braun, T., Field, L.J., Fleischmann, B.K., Frisén, J., Giacca, M., Hare, J.M., Houser, S., Lee, R.T., et al. (2017). Cardiomyocyte regeneration: A consensus statement. Circulation 136, 680–686.
Fukushima, S., Sawa, Y., and Suzuki, K. (2013). Choice of cell-delivery route for successful cell transplantation therapy for the heart. Future Cardiol 9, 215–227.
Gaballa, M.A., Sunkomat, J.N.E., Thai, H., Morkin, E., Ewy, G., and Goldman, S. (2006). Grafting an acellular 3-dimensional collagen scaffold onto a non-transmural infarcted myocardium induces neo-angiogenesis and reduces cardiac remodeling. J Heart Lung Transplant 25, 946–954.
Gao, J., Liu, J., Gao, Y., Wang, C., Zhao, Y., Chen, B., Xiao, Z., Miao, Q., and Dai, J. (2011). A myocardial patch made of collagen membranes loaded with collagen-binding human vascular endothelial growth factor accelerates healing of the injured rabbit heart. Tissue Eng Part A 17, 2739–2747.
Gautam, S., Chou, C.F., Dinda, A.K., Potdar, P.D., and Mishra, N.C. (2014). Surface modification of nanofibrous polycaprolactone/gelatin composite scaffold by collagen type I grafting for skin tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C 34, 402–409.
Gelse, K., Pöschl, E., and Aigner, T. (2003). Collagens—Structure, function, and biosynthesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55, 1531–1546.
Golpanian, S., Wolf, A., Hatzistergos, K.E., and Hare, J.M. (2016). Rebuilding the damaged heart: Mesenchymal stem cells, cell-based therapy, and engineered heart tissue. Physiol Rev 96, 1127–1168.
Han, S., Xiao, Z., Li, X., Zhao, H., Wang, B., Qiu, Z., Li, Z., Mei, X., Xu, B., Fan, C., et al. (2018). Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells loaded on linear ordered collagen scaffold improves functional recovery after completely transected spinal cord injury in canine. Sci China Life Sci 61, 2–13.
Holladay, C.A., Duffy, A.M., Chen, X., Sefton, M.V., O’Brien, T.D., and Pandit, A.S. (2012). Recovery of cardiac function mediated by MSC and interleukin-10 plasmid functionalised scaffold. Biomaterials 33, 1303–1314.
Hou, D., Youssef, E.A., Brinton, T.J., Zhang, P., Rogers, P., Price, E.T., Yeung, A.C., Johnstone, B.H., Yock, P.G. and March, K.L. (2005). Radiolabeled cell distribution after intramyocardial, intracoronary, and interstitial retrograde coronary venous delivery: Implications for current clinical trials. Circulation 112, 1150–1156.
Jansen Of Lorkeers, S.J., Eding, J.E.C., Vesterinen, H.M., van der Spoel, T. I.G., Sena, E.S., Duckers, H.J., Doevendans, P.A., Macleod, M.R., and Chamuleau, S.A.J. (2015). Similar effect of autologous and allogeneic cell therapy for ischemic heart disease. Circ Res 116, 80–86.
Jeevanantham, V., Butler, M., Saad, A., Abdel-Latif, A., Zuba-Surma, E.K., and Dawn, B. (2012). Adult bone marrow cell therapy improves survival and induces long-term improvement in cardiac parameters. Circulation 126, 551–568.
Jiang, P., Tang, X., Wang, H., Dai, C., Su, J., Zhu, H., Song, M., Liu, J., Nan, Z., Ru, T., et al. (2019). Collagen-binding basic fibroblast growth factor improves functional remodeling of scarred endometrium in uterine infertile women: A pilot study. Sci China Life Sci 62, 1617–1629.
Keith, M.C.L., Tang, X.L., Tokita, Y., Li, Q., Ghafghazi, S., Moore Joseph, I., Hong, K.U., Elmore, B., Amraotkar, A., Ganzel, B.L., et al. (2015). Safety of intracoronary infusion of 20 million C-kit positive human cardiac stem cells in pigs. PLoS ONE 10, e0124227.
Kellar, R.S., Landeen, L.K., Shepherd, B.R., Naughton, G.K., Ratcliffe, A., and Williams, S.K. (2001). Scaffold-based three-dimensional human fibroblast culture provides a structural matrix that supports angiogenesis in infarcted heart tissue. Circulation 104, 2063–2068.
Kijeńska, E., Prabhakaran, M.P., Swieszkowski, W., Kurzydlowski, K.J., and Ramakrishna, S. (2012). Electrospun bio-composite P(LLA-CL)/collagen I/collagen III scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res 100B, 1093–1102.
Lin, H. (2019). Transplantation of adult spinal cord tissue: Transection spinal cord repair and potential clinical translation. Sci China Life Sci 62, 870–872.
Lin, Y.D., Yeh, M.L., Yang, Y.J., Tsai, D.C., Chu, T.Y., Shih, Y.Y., Chang, M.Y., Liu, Y.W., Tang, A.C.L., Chen, T.Y., et al. (2010). Intramyocardial peptide nanofiber injection improves postinfarction ventricular remodeling and efficacy of bone marrow cell therapy in pigs. Circulation 122, S132–S141.
Liu, B., Duan, C.Y., Luo, C.F., Ou, C.W., Wu, Z.Y., Zhang, J.W., Ni, X.B., Chen, P.Y., and Chen, M.S. (2016). Impact of timing following acute myocardial infarction on efficacy and safety of bone marrow stem cells therapy: A network meta-analysis. Stem Cells Int 2016, 1–11.
Mahmoudi, M., Yu, M., Serpooshan, V., Wu, J.C., Langer, R., Lee, R.T., Karp, J.M., and Farokhzad, O.C. (2017). Multiscale technologies for treatment of ischemic cardiomyopathy. Nat Nanotech 12, 845–855.
Marquardt, L.M., and Heilshorn, S.C. (2016). Design of injectable materials to improve stem cell transplantation. Curr Stem Cell Rep 2, 207–220.
Martin-Rendon, E., Brunskill, S.J., Hyde, C.J., Stanworth, S.J., Mathur, A., and Watt, S.M. (2008). Autologous bone marrow stem cells to treat acute myocardial infarction: A systematic review. Eur Heart J 29, 1807–1818.
Maureira, P., Marie, P. Y., Yu, F., Poussier, S., Liu, Y., Groubatch, F., Falanga, A., and Tran, N. (2012). Repairing chronic myocardial infarction with autologous mesenchymal stem cells engineered tissue in rat promotes angiogenesis and limits ventricular remodeling. J Biomed Sci 19, 93.
Mokashi, S.A., Guan, J., Wang, D., Tchantchaleishvili, V., Brigham, M., Lipsitz, S., Lee, L.S., Schmitto, J.D., Bolman III, R.M., Khademhosseini, A., et al. (2010). Preventing cardiac remodeling: The combination of cell-based therapy and cardiac support therapy preserves left ventricular function in rodent model of myocardial ischemia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 140, 1374–1380.
Nguyen, P.K., Neofytou, E., Rhee, J.W., and Wu, J.C. (2016). Potential strategies to address the major clinical barriers facing stem cell regenerative therapy for cardiovascular disease. JAMA Cardiol 1, 953–962.
Paiva, L., Providência, R., Barra, S., Dinis, P., Faustino, A.C., and Gonçalves, L. (2015). Universal definition of myocardial infarction: Clinical insights. Cardiology 131, 13–21.
Perea-Gil, I., Prat-Vidal, C., and Bayes-Genis, A. (2015). In vivo experience with natural scaffolds for myocardial infarction: The times they are a-changin. Stem Cell Res Ther 6, 248.
Radhakrishnan, J., Krishnan, U.M., and Sethuraman, S. (2014). Hydrogel based injectable scaffolds for cardiac tissue regeneration. Biotech Adv 32, 449–461.
Sanganalmath, S.K., and Bolli, R. (2013). Cell therapy for heart failure. Circ Res 113, 810–834.
Sepantafar, M., Maheronnaghsh, R., Mohammadi, H., Rajabi-Zeleti, S., Annabi, N., Aghdami, N., and Baharvand, H. (2016). Stem cells and injectable hydrogels: Synergistic therapeutics in myocardial repair. Biotech Adv 34, 362–379
Serpooshan, V., Zhao, M., Metzler, S.A., Wei, K., Shah, P.B., Wang, A., Mahmoudi, M., Malkovskiy, A.V., Rajadas, J., Butte, M.J., et al. (2013). The effect of bioengineered acellular collagen patch on cardiac remodeling and ventricular function post myocardial infarction. Biomaterials 34, 9048–9055.
Shafy, A., Fink, T., Zachar, V., Lila, N., Carpentier, A., and Chachques, J.C. (2013). Development of cardiac support bioprostheses for ventricular restoration and myocardial regeneration. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 43, 1211–1219.
Shen, H., Chen, X., Li, X., Jia, K., Xiao, Z., and Dai, J. (2019). Transplantation of adult spinal cord grafts into spinal cord transected rats improves their locomotor function. Sci China Life Sci 62, 725–733.
Shi, C., Li, Q., Zhao, Y., Chen, W., Chen, B., Xiao, Z., Lin, H., Nie, L., Wang, D., and Dai, J. (2011). Stem-cell-capturing collagen scaffold promotes cardiac tissue regeneration. Biomaterials 32, 2508–2515.
Shiba, Y., Gomibuchi, T., Seto, T., Wada, Y., Ichimura, H., Tanaka, Y., Ogasawara, T., Okada, K., Shiba, N., Sakamoto, K., et al. (2016). Allogeneic transplantation of iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes regenerates primate hearts. Nature 538, 388–391.
Thygesen, K., Alpert, J.S., Jaffe, A.S., Simoons, M.L., Chaitman, B.R., White, H.D., Thygesen, K., Alpert, J.S., White, H.D., Jaffe, A.S., et al. (2012). Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 60, 1581–1598.
Wall, S.T., Yeh, C.C., Tu, R.Y.K., Mann, M.J., and Healy, K.E. (2010). Biomimetic matrices for myocardial stabilization and stem cell transplantation. J Biomed Mater Res 95A, 1055–1066.
Wang, B., Han, J., Gao, Y., Xiao, Z., Chen, B., Wang, X., Zhao, W., and Dai, J. (2007). The differentiation of rat adipose-derived stem cells into OEC-like cells on collagen scaffolds by co-culturing with OECs. Neurosci Lett 421, 191–196.
Wu, W.Q., Peng, S., Song, Z.Y., and Lin, S. (2019). Collagen biomaterial for the treatment of myocardial infarction: An update on cardiac tissue engineering and myocardial regeneration. Drug Deliv Transl Res 9, 920–934.
Xiang, Z., Liao, R., Kelly, M.S., and Spector, M. (2006). Collagen-GAG scaffolds grafted onto myocardial infarcts in a rat model: A delivery vehicle for mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng 12, 2467–2478.
Xu, J., Xiong, Y.Y., Li, Q., Hu, M.J., Huang, P.S., Xu, J.Y., Tian, X.Q., Jin, C., Liu, J.D., Qian, L., et al. (2019). Optimization of timing and times for administration of atorvastatin-pretreated mesenchymal stem cells in a preclinical model of acute myocardial infarction. Stem Cells Transl Med 8, 1068–1083.
Xu, Y., Dong, S., Zhou, Q., Mo, X., Song, L., Hou, T., Wu, J., Li, S., Li, Y., Li, P., et al. (2014). The effect of mechanical stimulation on the maturation of tdscs-poly(l-lactide-co-e-caprolactone)/collagen scaffold constructs for tendon tissue engineering. Biomaterials 35, 2760–2772.
Zhao, Y., Tang, F., Xiao, Z., Han, G., Wang, N., Yin, N., Chen, B., Jiang, X., Yun, C., Han, W., et al. (2017). Clinical study of neuroregen scaffold combined with human mesenchymal stem cells for the repair of chronic complete spinal cord injury. Cell Transplant 26, 891–900.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (ZDRW-ZS-2016-2-2), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC1000808), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81370239), the Key Project supported by Medical Science and Technology Development Foundation, Nanjing Department of Health (201605016), the Key Project supported by Nanjing Medical Science and Technique Development Foundation (QRX17044), and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS Project (2016096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest. All animal and human protocols were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital affiliated with Nanjing University Medical School, and conformed with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975 (as revised in 2008) concerning human and animal rights. We also followed our policy concerning informed consent, as can be seen at Springer.com.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., He, X., Wang, B. et al. Injectable collagen scaffold promotes swine myocardial infarction recovery by long-term local retention of transplanted human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Sci. China Life Sci. 64, 269–281 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-019-1575-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-019-1575-x