Abstract
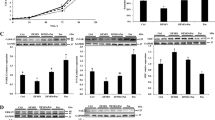
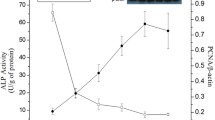
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) has been shown to improve piglet intestinal morphology and epithelial recovery. In an attempt to further understand the mechanisms behind these improvements, this study tested the hypothesis that dietary EGF may affect intestinal morphology by stimulating the proliferation and differentiation of enterocytes in weaning piglets. In piglets receiving 200 µg kg−1 EGF, crypt depth and villus height increased (P<0.05). Adding 400 µg kg−1 EGF increased villus height-to-crypt depth ratio (P<0.05), but reduced crypt depth (P<0.05). Dietary supplementation with 200 µg kg−1 EGF significantly increased the number of Ki67-positive cells (P<0.01) and tended to increase the mRNA level of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (P<0.10). However, this supplementation decreased the expression level of intestinal fatty acid-binding protein (P<0.05). Piglets fed with 400 µg kg−1 EGF had an increased mRNA level of intestinal alkaline phosphatase (P<0.05). The phosphorylation of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) was observed in the 200 µg kg−1 EGF group. These results suggest that dietary supplementation with a low level of EGF improved piglet intestinal morphology through stimulating the proliferation and differentiation of enterocytes, and the mTOR signaling pathway may partly be involved in this process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriaanse, M.P.M., Tack, G.J., Passos, V.L., Damoiseaux, J.G.M.C., Schreurs, M.W.J., van Wijck, K., Riedl, R.G., Masclee, A.A.M., Buurman, W.A., Mulder, C.J.J., et al. (2013). Serum I-FABP as marker for enterocyte damage in coeliac disease and its relation to villous atrophy and circulating autoantibodies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 37, 482–490.
Atshaves, B.P., Foxworth, W.B., Frolov, A., Roths, J.B., Kier, A.B., Oetama, B.K., Piedrahita, J.A., and Schroeder, F. (1998). Cellular differentiation and I-FABP protein expression modulate fatty acid uptake and diffusion. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 274, C633–C644.
Avissar, N.E., Wang, H.T., Miller, J.H., Iannoli, P., and Sax, H.C. (2000). Epidermal growth factor receptor is increased in rabbit intestinal brush border membrane after small bowel resection. Digest Dis Sci 45, 1145–1152.
Bedford, A., Chen, T., Huynh, E., Zhu, C., Medeiros, S., Wey, D., de Lange, C., and Li, J. (2015). Epidermal growth factor containing culture supernatant enhances intestine development of early-weaned pigs in vivo: potential mechanisms involved. J Biotech 196–197, 9–19.
Biteau, B., and Jasper, H. (2011). EGF signaling regulates the proliferation of intestinal stem cells in Drosophila. Development 138, 1045–1055.
Canesi, L., Malatesta, M., Battistelli, S., Ciacci, C., Gallo, G., and Gazzanelli, G. (2000). Immunoelectron microscope analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in isolated Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lam.) digestive gland cells: Evidence for ligand-induced changes in EGFR intracellular distribution. J Exp Zool 286, 690–698.
Cheng, Z., Liu, F., Li, X., Dai, M., Wu, J., Guo, X., Tian, H., Heng, Z., Lu, Y., Chai, X., et al. (2017). EGF-mediated EGFR/ERK signaling pathway promotes germinative cell proliferation in Echinococcus multilocularis that contributes to larval growth and development. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 11, e0005418.
Cheung, Q.C.K., Yuan, Z., Dyce, P.W., Wu, D., DeLange, K., and Li, J. (2009). Generation of epidermal growth factor-expressing Lactococcus lactis and its enhancement on intestinal development and growth of early-weaned mice. Am J Clin Nutrit 89, 871–879.
Chiu, T., Santiskulvong, C., and Rozengurt, E. (2005). EGF receptor transactivation mediates ANG II-stimulated mitogenesis in intestinal epithelial cells through the PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR/p70S6K1 signaling pathway. Am J Physiol Gastrointestinal Liver Physiol 288, G182–G194.
Crasméneur, C., Elghazi, L., Czernichow, P., and Scharfmann, R. (2001). Epidermal growth factor increases undifferentiated pancreatic embryonic cells in vitro: a balance between proliferation and differentiation. Diabetes 50, 1571–1579.
Darimont, C., Gradoux, N., and De, P.A. (1999). Epidermal growth factor regulates fatty acid uptake and metabolism in Caco-2 cells. Am J Physiol 276, 606–612.
Dignass, A.U., and Sturm, A. (2001). Peptide growth factors in the intestine. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 13, 763–770.
Fleet, J.C., Wang, L., Vitek, O., Craig, B.A., and Edenberg, H.J. (2003). Gene expression profiling of Caco-2 BBe cells suggests a role for specific signaling pathways during intestinal differentiation. Physiol Genomics 13, 57–68.
Gainza, G., Bonafonte, D.C., Moreno, B., Aguirre, J.J., Gutierrez, F.B., Villullas, S., Pedraz, J.L., Igartua, M., and Hernandez, R.M. (2015). The topical administration of rhEGF-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (rhEGF-NLC) improves healing in a porcine full-thickness excisional wound model. J Control Release 197, 41–47.
Galbaugh, T., Cerrito, M.G., Jose, C.C., and Cutler, M.L. (2006). EGF-induced activation of Akt results in mTOR-dependent p70S6 kinase phosphorylation and inhibition of HC11 cell lactogenic differentiation. BMC Cell Biol 7, 34.
Grosse, A.S., Pressprich, M.F., Curley, L.B., Hamilton, K.L., Margolis, B., Hildebrand, J.D., and Gumucio, D.L. (2011). Cell dynamics in fetal intestinal epithelium: implications for intestinal growth and morphogenesis. Development 138, 4423–4432.
Henson, E.S., and Gibson, S.B. (2006). Surviving cell death through epidermal growth factor (EGF) signal transduction pathways: implications for cancer therapy. Cell Signal 18, 2089–2097.
Jaeger, L.A., Lamar, C.H., Cline, T.R., and Cardona, C.J. (1990). Effect of orally administered epidermal growth factor on the jejunal mucosa of weaned pigs. Am J Vet Res 51, 471–474.
Jung, K., Kang, B.K., Kim, J.Y., Shin, K.S., Lee, C.S., and Song, D.S. (2008). Effects of epidermal growth factor on atrophic enteritis in piglets induced by experimental porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus. Vet J 177, 231–235.
Kang, P., Toms, D., Yin, Y., Cheung, Q., Gong, J., De Lange, K., and Li, J. (2010). Epidermal growth factor-expressing Lactococcus lactis enhances intestinal development of early-weaned pigs. J Nutrit 140, 806–811.
Lee, D.N., Chuang, Y.S., Chiou, H.Y., Wu, F.Y., Yen, H.T., and Weng, C.F. (2008). Oral administration recombinant porcine epidermal growth factor enhances the jejunal digestive enzyme genes expression and activity of early-weaned piglets. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutrit 92, 463–470.
Li, J., Tan, B., Tang, Y., Liao, P., Yao, K., Ji, P., and Yin, Y. (2018). Extraction and identification of the chyme proteins in the digestive tract of growing pigs. Sci China Life Sci 61, 1396–1406.
Liu, S., Wang, L., Liu, G., Tang, D., Fan, X., Zhao, J., Jiao, H., Wang, X., Sun, S., and Lin, H. (2017). Leucine alters immunoglobulin a secretion and inflammatory cytokine expression induced by lipopolysaccharide via the nuclear factor-κB pathway in intestine of chicken embryos. Animal 22, 1–9.
Lv, D., Xiong, X., Yang, H., Wang, M., He, Y., Liu, Y., and Yin, Y. (2018). Effect of dietary soy oil, glucose, and glutamine on growth performance, amino acid profile, blood profile, immunity, and antioxidant capacity in weaned piglets. Sci China Life Sci 61, 1233–1242.
Murthy, S., Mathur, S., Bishop, W.P., and Field, E.J. (1997). Inhibition of apolipoprotein B secretion by IL-6 is mediated by EGF or an EGF-like molecule in CaCo-2 cells. J Lipid Res 38, 206–216.
Nakamura, A., Hara, K., Yamamoto, K., Yasuda, H., Moriyama, H., Hirai, M., Nagata, M., and Yokono, K. (2012). Role of the mTOR complex 1 pathway in the in vivo maintenance of the intestinal mucosa by oral intake of amino acids. Geriatr Gerontol Int 12, 131–139.
National Research Council. (2012). Nutrient Requirements of Swine. 11th ed. (Washington, DC: Natinal. Academies Press).
Petersen, Y.M., Hartmann, B., Holst, J.J., Le Huerou-Luron, I., Bjørnvad, C.R., and Sangild, P.T. (2003). Introduction of enteral food increases plasma GLP-2 and decreases GLP-2 receptor mRNA abundance during pig development. J Nutrit 133, 1781–1786.
Shin, J., Carr, A., Corner, G.A., Tögel, L., Dávalos-Salas, M., Dávaos-Salas, M., Tran, H., Chueh, A.C., Al-Obaidi, S., Chionh, F., et al. (2015). The intestinal epithelial cell differentiation marker intestinal alkaline phosphatase (ALPi) is selectively induced by histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) in colon cancer cells in a Kruppel-like factor 5 (KLF5)-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 289, 25306–25316.
Smith, F., Clark, J.E., Overman, B.L., Tozel, C.C., Huang, J.H., Rivier, J.E. F., Blikslager, A.T., and Moeser, A.J. (2010). Early weaning stress impairs development of mucosal barrier function in the porcine intestine. Am J Physiol Gastrointestinal Liver Physiol 298, G352–G363.
Sobolewska, A., Gajewska, M., Zarzyńska, J., Gajkowska, B., and Motyl, T. (2009). IGF-I, EGF, and sex steroids regulate autophagy in bovine mammary epithelial cells via the mTOR pathway. Eur J Cell Biol 88, 117–130.
Tang, X., Liu, H., Yang, S., Li, Z., Zhong, J., and Fang, R. (2016). Epidermal growth factor and intestinal barrier function. Mediat Inflamm 2016, 1–9.
Turner, J.R. (2009). Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9, 799–809.
Wang, L., Yan, S., Li, J., Li, Y., Ding, X., Yin, J., Xiong, X., Yin, Y., and Yang, H. (2019a). Rapid Communication: The relationship of enterocyte proliferation with intestinal morphology and nutrient digestibility in weaning piglets. J Anim Sci 97, 353–358.
Wang, L., Zhu, F., Yang, H., Li, J., Li Y., Ding, X., Xiong, X., and Yin, Y. (2019b). Effects of dietary supplementation with epidermal growth factor on nutrient digestibility, intestinal development and expression of nutrient transporters in early-weaned piglets. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 2019, 1–8.
Wang, S., Zhou, L., Chen, H., Cao, Y., Zhang, Z., Yang, J., Huang, Y., and Guo, C. (2015). Analysis of the biological activities of Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing intracellular EGF, extracellular EGF, and tagged EGF in early-weaned rats. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 2179–2189.
Wallace, L.E., Chung, B.M., Hardin, J.A., and Gall, D.G. (2000). Expression of EGF and Erbb receptor proteins in jejunal epithelium. Gastroenterology 118, A556.
Xu, S., Wang, D., Zhang, P., Lin, Y., Fang, Z., Che, L., and Wu, D. (2015). Oral administration of Lactococcus lactis-expressed recombinant porcine epidermal growth factor stimulates the development and promotes the health of small intestines in early-weaned piglets. J Appl Microbiol 119, 225–235.
Yang, H., Li, F., Kong, X., Yuan, X., Wang, W., Huang, R., Li, T., Geng, M., Wu, G., and Yin, Y. (2012). Chemerin regulates proliferation and differentiation of myoblast cells via ERK1/2 and mTOR signaling pathways. Cytokine 60, 646–652.
Yang, H.S., Wu, F., Long, L.N., Li, T.J., Xiong, X., Liao, P., Liu, H.N., and Yin, Y.L. (2016). Effects of yeast products on the intestinal morphology, barrier function, cytokine expression, and antioxidant system of weaned piglets. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 17, 752–762.
Yang, H., Wang, X., Xiong, X., and Yin, Y. (2016a). Energy metabolism in intestinal epithelial cells during maturation along the crypt-villus axis. Sci Rep 6, 31917.
Yang, H., Xiong, X., Li, T., and Yin, Y. (2016b). Ethanolamine enhances the proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells via the mTOR signaling pathway and mitochondrial function. Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 52, 562–567.
Yang, H., Xiong, X., Wang, X., Li, T., and Yin, Y. (2016c). Effects of weaning on intestinal crypt epithelial cells in piglets. Sci Rep 6, 36939.
Zhang, S., Ren, M., Zeng, X., He, P., Ma, X., and Qiao, S. (2014). Leucine stimulates ASCT2 amino acid transporter expression in porcine jejunal epithelial cell line (IPEC-J2) through PI3K/Akt/mTOR and ERK signaling pathways. Amino Acids 46, 2633–2642.
Zhao, D., Zhang, C., Yang, R., Chen, J., Ma, L., Liu, G., and Yang, X. (2017). Effect of 1,25(OH2D3) on the proliferation of human mesangial cells and their expression of Ki67. Genet Mol Res 16, 16029191.
Zijlstra, R.T., Odle, J., Hall, W.F., Petschow, B.W., Gelberg, H.B., and Litov, R.E. (1994). Effect of orally administered epidermal growth factor on intestinal recovery of neonatal pigs infected with rotavirus. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutrit 19, 382–390.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Key Programs of Frontier Scientific Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (QYZDY-SSW-SMC008), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2017JJ1020), Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST (YESS20160086).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Zhu, F., Yang, H. et al. Epidermal growth factor improves intestinal morphology by stimulating proliferation and differentiation of enterocytes and mTOR signaling pathway in weaning piglets. Sci. China Life Sci. 63, 259–268 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-018-9519-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-018-9519-6