Abstract
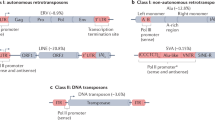
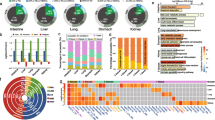
Transposable elements (TEs) are major components of the human genome constituting at least half of it. More than half a century ago, Barbara McClintock and later Roy Britten and Eric Davidson have postulated that they might be major players in the host gene regulation. We have scanned a large amount of data produced by ENCODE project for active transcription binding sites (TFBSs) located in TE-originated parts of polymerase II promoters. In total, more than 35,000 promoters in six different tissues were analyzed and over 26,000 of them harbored TEs. Moreover, these TEs usually provide one or more of TFBSs in the host promoters, which resulted in more than 6% of active TFBSs in these regions located in the TE-originated sequences. Rewiring of transcription circuits played a major role in mammalian evolution and consequently increased their functional and morphological diversity. In this large-scale analysis, we have demonstrated that TEs contributed a large fraction of human TFBSs. Interestingly, these TFBSs usually act in a tissue-specific manner. Thus, our study clearly showed that TEs played a significant role in shaping expression pattern in mammals and humans in particular. Furthermore, since several TE families are still active in our genome, they continue to influence not only our genome architecture but also gene functioning in a broader sense.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banville, D., and Boie, Y. (1989). Retroviral long terminal repeat is the promoter of the gene encoding the tumor-associated calcium-binding protein oncomodulin in the rat. J Mol Biol 207, 481–490.
Britten, R.J., and Davidson, E.H. (1969). Gene regulation for higher cells: a theory. Science 165, 349–357.
Britten, R.J., and Kohne, D.E. (1968). Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science 161, 529–540.
Brosius, J. (1991). Retroposons—seeds of evolution. Science 251, 753.
Chuong, E.B., Rumi, M.A.K., Soares, M.J., and Baker, J.C. (2013). Endogenous retroviruses function as species-specific enhancer elements in the placenta. Nat Genet 45, 325–329.
Cordaux, R., and Batzer, M.A. (2009). The impact of retrotransposons on human genome evolution. Nat Rev Genet 10, 691–703.
de Koning, A.P.J., Gu, W., Castoe, T.A., Batzer, M.A., and Pollock, D.D. (2011). Repetitive elements may comprise over two-thirds of the human genome. PLoS Genet 7, e1002384.
Doolittle, W.F., and Sapienza, C. (1980). Selfish genes, the phenotype paradigm and genome evolution. Nature 284, 601–603.
Feschotte, C. (2008). Transposable elements and the evolution of regulatory networks. Nat Rev Genet 9, 397–405.
Feschotte, C. (2008). Transposable elements and the evolution of regulatory networks. Nat Rev Genet 9, 397–405.
Hamdi, H.K., Nishio, H., Tavis, J., Zielinski, R., and Dugaiczyk, A. (2000). Alu-mediated phylogenetic novelties in gene regulation and development. J Mol Biol 299, 931–939.
Harrow, J., Frankish, A., Gonzalez, J.M., Tapanari, E., Diekhans, M., Kokocinski, F., Aken, B.L., Barrell, D., Zadissa, A., Searle, S., et al. (2012). GENCODE: the reference human genome annotation for The ENCODE Project. Genome Res 22, 1760–1774.
Hickey, D.A. (1982). Selfish DNA: a sexually-transmitted nuclear parasite. Genetics 101, 519–531.
Jordan, I.K., Rogozin, I.B., Glazko, G.V., and Koonin, E.V. (2003). Origin of a substantial fraction of human regulatory sequences from transposable elements. Trends Genets 19, 68–72.
Kanehisa, M., Furumichi, M., Tanabe, M., Sato, Y., and Morishima, K. (2017). KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res 45, D353–D361.
Kazazian, H.H., and Moran, J.V. (1998). The impact of L1 retrotransposons on the human genome. Nat Genet 19, 19–24.
King, M.C., and Wilson, A.C. (1975). Evolution at two levels in humans and chimpanzees. Science 188, 107–116.
Korenberg, J.R., and Rykowski, M.C. (1988). Human genome organization: Alu, lines, and the molecular structure of metaphase chromosome bands. Cell 53, 391–400.
Kunarso, G., Chia, N.Y., Jeyakani, J., Hwang, C., Lu, X., Chan, Y.S., Ng, H.H., and Bourque, G. (2010). Transposable elements have rewired the core regulatory network of human embryonic stem cells. Nat Genet 42, 631–634.
Lander, E.S., Linton, L.M., Birren, B., Nusbaum, C., Zody, M.C., Baldwin, J., Devon, K., Dewar, K., Doyle, M., FitzHugh, W., et al. (2001). Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409, 860–921.
Lynch, V.J., Leclerc, R.D., May, G., and Wagner, G.P. (2011). Transposon-mediated rewiring of gene regulatory networks contributed to the evolution of pregnancy in mammals. Nat Genet 43, 1154–1159.
Makalowski, W. (1995). SINEs as a genomic scrap yard: an essay on genomic evolution. In The Impact of Short Interspersed Elements (SINEs) on the Host Genome, R. Maraia, ed. (Austin TX: R.G. Landes), pp. 81–104.
Makalowski, W. (2000). Genomic scrap yard: how genomes utilize all that junk. Gene 259, 61–67.
Malamy, M.H., Fiandt, M., and Szybalski, W. (1972). Electron-microscopy of polar insertions in lac Operon of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 119, 207–222.
McClintock, B. (1950). The origin and behavior of mutable loci in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 36, 344–355.
McClintock, B. (1956). Intranuclear systems controlling gene action and mutation. Brookhaven Symp Biol, 58–74.
Orgel, L.E., and Crick, F.H.C. (1980). Selfish DNA: the ultimate parasite. Nature 284, 604–607.
Simonti, C.N., Pavlicev, M., and Capra, J.A. (2017). Transposable element exaptation into regulatory regions is rare, influenced by evolutionary age, and subject to pleiotropic constraints. Mol Biol Evol 34, 2856–2869.
Sloan, C.A., Chan, E.T., Davidson, J.M., Malladi, V.S., Strattan, J.S., Hitz, B.C., Gabdank, I., Narayanan, A.K., Ho, M., Lee, B.T., et al. (2016). ENCODE data at the ENCODE portal. Nucleic Acids Res 44, D726–D732.
Thornburg, B.G., Gotea, V., and Makalowski, W. (2006). Transposable elements as a significant source of transcription regulating signals. Gene 365, 104–110.
Trizzino, M., Kapusta, A., and Brown, C.D. (2018). Transposable elements generate regulatory novelty in a tissue-specific fashion. BMC Genomics 19, 468.
Venter, J.C., Adams, M.D., Myers, E.W., Li, P.W., Mural, R.J., Sutton, G. G., Smith, H.O., Yandell, M., Evans, C.A., Holt, R.A., et al. (2001). The sequence of the human genome. Science 291, 1304–1351.
Wang, J., Vasaikar, S., Shi, Z., Greer, M., and Zhang, B. (2017). WebGestalt 2017: a more comprehensive, powerful, flexible and interactive gene set enrichment analysis toolkit. Nucleic Acids Res 45, W130–W137.
Waring, M., and Britten, R.J. (1966). Nucleotide sequence repetition: a rapidly reassociating fraction of mouse DNA. Science 154, 791–794.
Wicker, T., Sabot, F., Hua-Van, A., Bennetzen, J.L., Capy, P., Chalhoub, B., Flavell, A., Leroy, P., Morgante, M., Panaud, O., et al. (2007). A unified classification system for eukaryotic transposable elements. Nat Rev Genet 8, 973–982.
Wingender, E., Schoeps, T., Haubrock, M., Krull, M., and Dönitz, J. (2018). TFClass: expanding the classification of human transcription factors to their mammalian orthologs. Nucleic Acids Res 46, D343–D347.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Institute of Bioinformatics, Muenster, Germany. We acknowledge support by Open Access Publication Fund of University of Muenster.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kellner, M., Makałowski, W. Transposable elements significantly contributed to the core promoters in the human genome. Sci. China Life Sci. 62, 489–497 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-018-9449-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-018-9449-0