Abstract
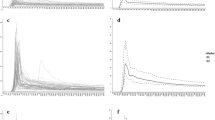
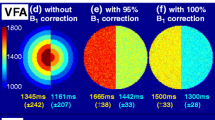
This experiment aimed to compare the ionic (Gadodiamide, Gd-DTPA-BMA) and non-ionic (Gadopentetate dimeglumine, Gd-DTPA) gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) in the quantitative evaluation of C6 glioma with dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI). A C6 glioma model was established in 12 Wistar rats, and magnetic resonance (MR) scans were performed six days after tumor implantation. Imaging was performed using a 3.0-T MR scanner with a 7-inch handmade circular coil. Pre-contrast T1 mapping and dynamic contrast-enhanced T1WI after a bolus injection (0.2 mL s−1) of GBCA at 0.4 mmol kg−1 were performed. Each rat received two DCE-MRI scans, 24 h apart. The first and second scans were performed using Gd-DTPA-BMA and Gd-DTPA, respectively. Image data were processed using the Patlak model. Both K trans and V p maps were generated. Tumors were manually segmented on all 3D K trans and V p maps. Pixel counts and mean values were recorded for use in a paired t-test. Three radiologists independently performed the tumor segmentation and value calculation. The agreements from different observers were subjective to the intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC). Readers demonstrated that the pixel counts of tumors in K trans maps were higher with Gd-DTPA-BMA than with Gd-DTPA (P<0.001, all readers). Although the K trans values were higher with Gd-DTPA-BMA than with Gd-DTPA, there was no statistical significance (P>0.05, all readers). The pixel counts of tumors in V p maps, as well as V p values, showed no obvious difference between the two agents (P>0.05, all readers). Excellent interobserver measurement reproducibility and reliability were demonstrated in the ICC tests. The Gd-DTPA-BMA contrast agent had significantly higher pixel counts of glioma in the K trans maps, and an increased tendency for average K trans values, indicating that DCE-MRI with Gd-DTPA-BMA may be more suitable and sensitive for the evaluation of glioma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allegrini, P.R., Weidensteiner, C., and McSheehy, P.M. (2006). Direct comparison of macromolecular contrast agent Vistarem with Dotarem for detecting drug effects on tumor vasculature by DCE MRI. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med 14, 2907.
Allhenn, D., Shetab Boushehri, M.A., and Lamprecht, A. (2012). Drug delivery strategies for the treatment of malignant gliomas. Int J Pharmaceut 436, 299–310.
Barboriak, D.P., MacFall, J.R., and Padua, A.O. (2004). Standardized software for calculation of K trans and Vp from dynamic T1-weighted MR images. In Proceedings of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Workshop on MR in Drug Development: From Discovery to Clinical Therapeutic Trials, McLean Va, USA. 4.
Bayer Schering Pharma AG. (2008). MAGNEVIST® (Gadopentetic Acid Dimeglumine Salt Injection). Germany.
Blasiak, B., Tomanek, B., Abulrob, A., Iqbal, U., Stanimirovic, D., Albaghdadi, H., Foniok, T., Lun, X., Forsyth, P., and Sutherland, G.R. (2010). Detection of T2 changes in an early mouse brain tumor. Magn Reson Imaging 28, 784–789.
Brown, G.L., Echley, M., and Wargo, K.A. (2010). A review of glioblastoma multiforme. US Pharmacist 35, 3–10.
Daldrup-Link, H.E., Kaiser, A., Helbich, T., Werner, M., Bjørnerud, A., Link, T.M., and Rummeny, E.J. (2003). Macromolecular contrast medium (feruglose) versus small molecular contrast medium (gadopentetate) enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Acad Radiol 10, 1237–1246.
Doblas, S., Saunders, D., Kshirsagar, P., Pye, Q., Oblander, J., Gordon, B., Kosanke, S., Floyd, R.A., and Towner, R.A. (2008). Phenyl-tert-butylnitrone induces tumor regression and decreases angiogenesis in a C6 rat glioma model. Free Radic Biol Med 44, 63–72.
Feng, Y., Jeong, E.K., Mohs, A.M., Emerson, L., and Lu, Z.R. (2008). Characterization of tumor angiogenesis with dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and biodegradable macromolecular contrast agents in mice. Magn Reson Med 60, 1347–1352.
Gao, X. (2015). Model animals and their applications. Sci China Life Sci 58, 319–320.
GE Healthcare. (2007). Omniscantm (Gadadiamide Injection). USA.
Gordon, Y., Partovi, S., and Müller-Eschner, M. (2014). Dynamic contrastenhanced magnetic resonance imaging: fundamentals and application to the evaluation of the peripheral perfusion. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther 4, 147–164.
Gutmann, D.H., Baker, S.J., Giovannini, M., Garbow, J., and Weiss, W. (2003). Mouse models of human cancer consortium symposium on nervous system tumors. Cancer Res 63, 3001–3004.
Jackson, A., Buckley, D.L., and Parker, G.J.M. (2005). Dynamic Contrast- Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Oncology (Medical Radiology/ Diagnostic Imaging). (Heidelberg: Springer).
Liang, J., Sammet, S., Yang, X., Jia, G., Takayama, Y., and Knopp, M.V. (2010). Intraindividual in vivo comparison of gadolinium contrast agents for pharmacokinetic analysis using dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 45, 233–244.
O’Connor, J.P.B., Jackson, A., Parker, G.J.M., and Jayson, G.C. (2007). DCE-MRI biomarkers in the clinical evaluation of antiangiogenic and vascular disrupting agents. Br J Cancer 96, 189–195.
Quick, A., Patel, D., Hadziahmetovic, M., Chakravarti, A., and Mehta, M. (2010). Current therapeutic paradigms in glioblastoma. Rev Recent Clin Trials 5, 14–27.
Tofts, P. (2004). Quantitative MRI of the Brain: Measuring Changes Caused by Disease. (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd).
Zhang, X., Wu, J., Gao, D., Fei, Z., Qu, Y., and Jing, J. (2002). Development of a rat C6 brain tumor model. Chin Med J 115, 455–457.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Liu, G., Lou, X. et al. Intra-individual comparison of different gadolinium-based contrast agents in the quantitative evaluation of C6 glioma with dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Sci. China Life Sci. 60, 11–15 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-016-0386-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-016-0386-2