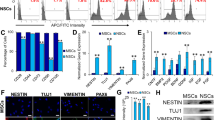
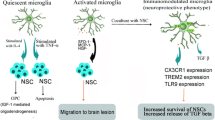
Abstract
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (CNS), with focal T lymphocytic infiltration and damage of myelin and axons. The underlying mechanism of pathogenesis remains unclear and there are currently no effective treatments. The development of neural stem cell (NSC) transplantation provides a promising strategy to treat neurodegenerative disease. However, the limited availability of NSCs prevents their application in neural disease therapy. In this study, we generated NSCs from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and transplanted these cells into mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a model of MS. The results showed that transplantation of iPSC-derived NSCs dramatically reduced T cell infiltration and ameliorated white matter damage in the treated EAE mice. Correspondingly, the disease symptom score was greatly decreased, and motor ability was dramatically rescued in the iPSC-NSC-treated EAE mice, indicating the effectiveness of using iPSC-NSCs to treat MS. Our study provides pre-clinical evidence to support the feasibility of treating MS by transplantation of iPSC-derived NSCs.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Ager, R.R., Davis, J.L., Agazaryan, A., Benavente, F., Poon, W.W., La- Ferla, F.M., and Blurton-Jones, M. (2015). Human neural stem cells improve cognition and promote synaptic growth in two complementary transgenic models of Alzheimer’s disease and neuronal loss. Hippocampus 25, 813–826.
Araki, R., Uda, M., Hoki, Y., Sunayama, M., Nakamura, M., Ando, S., Sugiura, M., Ideno, H., Shimada, A., Nifuji, A., and Abe, M. (2013). Negligible immunogenicity of terminally differentiated cells derived from induced pluripotent or embryonic stem cells. Nature 494, 100–104.
Arima, Y., Harada, M., Kamimura, D., Park, J.H., Kawano, F., Yull, F.E., Kawamoto, T., Iwakura, Y., Betz, U.A.K. and Abe, M. (2013). Negligible immunogenicity of terminally differendefines a gateway for autoreactive T cells to cross the blood-brain barrier. Cell 148, 447–457.
Bai, L., Hecker, J., Kerstetter, A., and Miller, R.H. (2013). Myelin repair and functional recovery mediated by neural cell transplantation in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Neurosci Bull 29, 239–250.
Beare, J., E., Morehouse, J., R., DeVries, W., H., Enzmann, G., U., Burke, D., A., Magnuson, D., S.K., and Whittemore, S., R. (2009). Gait analysis in normal and spinal cotused mice using the treadscan system. J Neurotrauma 11, 2045–2056.
Ben-Hur, T., Idelson, M., Khaner, H., Pera, M., Reinhartz, E., Itzik, A., and Reubinoff, B.E. (2004). Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural progenitors improves behavioral deficit in Parkinsonian rats. Stem Cells 22, 1246–1255.
Cao, J., Li, X., Lu, X., Zhang, C., Yu, H., and Zhao, T. (2014). Cells derived from iPSC can be immunogenic—yes or no? Protein Cell 5, 1–3.
Compston, A., and Coles, A. (2008). Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 372, 1502–1517.
Constantinescu, C.S., Farooqi, N., O’Brien, K., and Gran, B. (2011). Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) as a model for multiple sclerosis (MS). Br J Pharmacol 164, 1079–1106.
Crusio, W., E. (2001). Genetic dissection of mouse exploratory behaviour. Behav Brain Res 125, 127–132.
Cundiff, P.E., and Anderson, S.A. (2011). Impact of induced pluripotent stem cells on the study of central nervous system disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev 21, 354–361.
de Almeida, P.E., Meyer, E.H., Kooreman, N.G., Diecke, S., Dey, D., Sanchez-Freire, V., Hu, S., Ebert, A., Odegaard, J., Mordwinkin, N.M., Brouwer, T.P., Lo, D., Montoro, D.T., Longaker, M.T., Negrin, R.S., and Wu, J.C. (2014). Transplanted terminally differentiated induced pluripotent stem cells are accepted by immune mechanisms similar to self-tolerance. Nat Commun 5, 3903.
Durnaoglu, S., Genc, S., and Genc, K. (2011). Patient-specific pluripotent stem cells in neurological diseases. Stem Cells Int 2011, 212487.
Einstein, O., Karussis, D., Grigoriadis, N., Mizrachi-Kol, R., Reinhartz, E., Abramsky, O., and Ben-Hur, T. (2003). Intraventricular transplantation of neural precursor cell spheres attenuates acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Mol Cell Neurosci 24, 1074–1082.
Fassas, A., Anagnostopoulos, A., and Tsompanakou, A. (1997). Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in the treatment of progressive multiple sclerosis: first results of a pilot study. Bone Marrow Transplant 20, 631–638.
Fisher-Shoval, Y., Barhum, Y., Sadan, O., Yust-Katz, S., Ben-Zur, T., Lev, N., Benkler, C., Hod, M., Melamed, E., and Offen, D. (2012). Transplantation of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the EAE mouse model of MS.J Mol Neurosci 48, 176–184.
Harris, V.K., Yan, Q.J., Vyshkina, T., Sahabi, S., Liu, X., and Sadiq, S.A. (2012). Clinical and pathological effects of intrathecal injection of mesenchymal stem cell-derived neural progenitors in an experimental model of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 313, 167–177.
Huang, S., and Fu, X. (2014). Stem cell therapies and regenerative medicine in China. Sci China Life Sci 57, 157–161.
Israel, M.A., Yuan, S.H., Bardy, C., Reyna, S.M., Mu, Y., Herrera, C., Hefferan, M.P., Van Gorp, S., Nazor, K.L., Boscolo, F.S., Carson, C.T., Laurent, L.C., Marsala, M., Gage, F.H., Remes, A.M., Koo, E.H., and Goldstein, L.S. (2012). Probing sporadic and familial Alzheimer’s disease using induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 482, 216–220.
Jelinek, G.A., Weiland, T.J., Hadgkiss, E.J., Marck, C.H., Pereira, N., and van der Meer, D.M. (2015). Medication use in a large international sample of people with multiple sclerosis: associations with quality of life, relapse rate and disability. Neurol Res 37, 662–673.
Kim, H., Walczak, P., Kerr, C., Galpoththawela, C., Gilad, A.A., Muja, N., and Bulte, J.W. (2012). Immunomodulation by transplanted human embryonic stem cell-derived oligodendroglial progenitors in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Stem Cells 30, 2820–2829.
Kim, J.H., Auerbach, J.M., Rodriguez-Gomez, J.A., Velasco, I., Gavin, D., Lumelsky, N., Lee, S.H., Nguyen, J., Sanchez-Pernaute, R., Bankiewicz, K., and McKay, R. (2002). Dopamine neurons derived from embryonic stem cells function in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Nature 418, 50–56.
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K., and Tyler K. L. (2005). Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy complicating treatment with natalizumab and interferon beta-1a for multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 353, 369–374.
Lajimi, A.A., Hagh, M.F., Saki, N., Mortaz, E., Soleimani, M., and Rahim, F. (2012). Feasibility of cell therapy in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review of 83 studies. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res 7, 15–33.
Lee, S.T., Chu, K., Park, J.E., Lee, K., Kang, L., Kim, S.U., and Kim, M. (2005). Intravenous administration of human neural stem cells induces functional recovery in Huntington’s disease rat model. Neurosci Res 52, 243–249.
Liu, K., Song, Y., Yu, H., and Zhao, T. (2014). Understanding the roadmaps to induced pluripotency. Cell Death Dis 5, e1232.
Lu, X., and Zhao, T. (2013). Clinical therapy using iPSCs: hopes and challenges. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 11, 294–298.
Okabe, S., Nilsson, K., F., Spiro, A. C., Segal, M., and McKay, R., D.G (1996). Development of neuronal precursor cells and functional postmitotic neurons from embryonic stem cells in vitro. Mech Dev 59, 89–102.
Pluchino, S., Gritti, A., Blezer, E., Amadio, S., Brambilla, E., Borsellino, G., Cossetti, C., Del Carro, U., Comi, G., Hart, B., Vescovi, A., and Martino, G. (2009). Human neural stem cells ameliorate autoimmune encephalomyelitis in non-human primates. Ann Neurol 66, 343–354.
Pluchino, S., and Martino, G. (2008). The therapeutic plasticity of neural stem/precursor cells in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 265, 105–110.
Pluchino, S., Quattrini, A., Brambilla, E., Gritti, A., Salani, G., Dina, G., Galli, R., Del Carro, U., Amadio, S., and Bergami, A. (2003). Injection of adult neurospheres induces recovery in a chronic model of multiple sclerosis. Nature 422, 688–694.
Redmond, D.E., Bjugstad, K.B., Teng, Y.D., Ourednik, V., Ourednik, J., Wakeman, D.R., Parsons, X.H., Gonzalez, R., Blanchard, B.C., Kim, S.U., Gu, Z., Lipton, S.A., Markakis, E.A., Roth, R.H., Elsworth, J.D., Sladek, J.R., Sidman, R.L., and Snyder, E.Y. (2007). Behavioral improvement in a primate Parkinson’s model is associated with multiple homeostatic effects of human neural stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104, 12175–12180.
Takahashi, K., and Yamanaka, S. (2006). Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126, 663–676.
Viglietta, V., Baecher-Allan, C., Weiner, H.L., and Hafler, D.A. (2004). Loss of functional suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med 199, 971–979.
Wu, S., Li, K., Yan, Y., Gran, B., Han, Y., Zhou, F., Guan, Y.T., Rostami, A., and Zhang, G.X. (2013). Intranasal delivery of neural stem cells: a CNS-specific, non-invasive cell-based therapy for experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Clin Cell Immunol 4, doi: 10.4172/2155-9899.1000142.
Ying, Q.L., Stavridis, M., Griffiths, D., Li, M., and Smith, A. (2003). Conversion of embryonic stem cells into neuroectodermal precursors in adherent monoculture. Nat Biotechnol 21, 183–186.
Zhao, T., Zhang, Z.N., Rong, Z., and Xu, Y. (2011). Immunogenicity of induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 474, 212–215.
Zhao, T., Zhang, Z.N., Westenskow, P.D., Todorova, D., Hu, Z., Lin, T., Rong, Z., Kim, J., He, J., Wang, M., Clegg, D.O., Yang, Y.G., Zhang, K., Friedlander, M., and Xu, Y. (2015). Humanized mice reveal differential immunogenicity of cells derived from autologous induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 17, 353–359.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This article is published with open access at link.springer.com
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Cao, J., Li, X. et al. Treatment of multiple sclerosis by transplantation of neural stem cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci. China Life Sci. 59, 950–957 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-016-0114-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-016-0114-9