Abstract
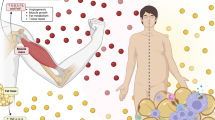
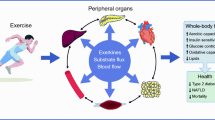
Skeletal muscle fitness plays vital roles in human health and disease and is determined by developmental as well as physiological inputs. These inputs control and coordinate muscle fiber programs, including capacity for fuel burning, mitochondrial ATP production, and contraction. Recent studies have demonstrated crucial roles for nuclear receptors and their co-activators, and microRNAs (miRNAs) in the regulation of skeletal muscle energy metabolism and fiber type determination. In this review, we present recent progress in the study of nuclear receptor signaling and miRNA networks in muscle fiber type switching. We also discuss the therapeutic potential of nuclear receptors and miRNAs in disease states that are associated with loss of muscle fitness.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Schiaffino S, Reggiani C. Fiber types in mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev, 2011, 91: 1447–1531
Zierath JR, Hawley JA. Skeletal muscle fiber type: influence on contractile and metabolic properties. PLoS Biol, 2004, 2: e348
Saltin B, Henriksson J, Nygaard E, Andersen P, Jansson E. Fiber types and metabolic potentials of skeletal muscles in sedentary man and endurance runners. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1977, 301: 3–29
Holloszy JO, Coyle EF. Adaptations of skeletal muscle to endurance exercise and their metabolic consequences. J Appl Physiol, 1984, 56: 831–838
Yan Z, Okutsu M, Akhtar YN, Lira VA. Regulation of exercise-induced fiber type transformation, mitochondrial biogenesis, and angiogenesis in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985), 2011, 110: 264–274
Pette D, Staron RS. Myosin isoforms, muscle fiber types, and transitions. Microsc Res Tech, 2000, 50: 500–509
Lillioja S, Young AA, Culter CL, Ivy JL, Abbott WG, Zawadzki JK, Yki-Jarvinen H, Christin L, Secomb TW, Bogardus C. Skeletal muscle capillary density and fiber type are possible determinants of in vivo insulin resistance in man. J Clin Invest, 1987, 80: 415–424
Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN. Signaling pathways in skeletal muscle remodeling. Ann Rev Biochem, 2006, 75: 19–37
Potthoff MJ, Wu H, Arnold MA, Shelton JM, Backs J, McAnally J, Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN. Histone deacetylase degradation and MEF2 activation promote the formation of slow-twitch myofibers. J Clin Invest, 2007, 117: 2459–2467
Desvergne B, Wahli W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocrine Rev, 1999, 20: 649–688
Hong SH, Ahmadian M, Yu RT, Atkins AR, Downes M, Evans RM. Nuclear receptors and metabolism: from feast to famine. Diabetologia, 2014, 57: 860–867
Fan W, Atkins AR, Yu RT, Downes M, Evans RM. Road to exercise mimetics: targeting nuclear receptors in skeletal muscle. J Mol Endocrinol, 2013, 51: T87–100
Madrazo JA, Kelly DP. The PPAR trio: regulators of myocardial energy metabolism in health and disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2008, 44: 968–975
Lefebvre P, Chinetti G, Fruchart JC, Staels B. Sorting out the roles of PPAR alpha in energy metabolism and vascular homeostasis. J Clin Invest, 2006, 116: 571–580
Gulick T, Cresci S, Caira T, Moore DD, Kelly DP. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor regulates mitochondrial fatty acid oxidative enzyme gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1994, 91: 11012–11016
Barish GD, Narkar VA, Evans RM. PPAR delta: a dagger in the heart of the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest, 2006, 116: 590–597
Nielsen R, Pedersen TA, Hagenbeek D, Moulos P, Siersbaek R, Megens E, Denissov S, Borgesen M, Francoijs KJ, Mandrup S, Stunnenberg HG. Genome-wide profiling of PPARgamma:RXR and RNA polymerase II occupancy reveals temporal activation of distinct metabolic pathways and changes in RXR dimer composition during adipogenesis. Genes Dev, 2008, 22: 2953–2967
Finck BN, Bernal-Mizrachi C, Han DH, Coleman T, Sambandam N, LaRiviere LL, Holloszy JO, Semenkovich CF, Kelly DP. A potential link between muscle peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha signaling and obesity-related diabetes. Cell Metab, 2005, 1: 133–144
Gan Z, Burkart-Hartman EM, Han DH, Finck B, Leone TC, Smith EY, Ayala JE, Holloszy J, Kelly DP. The nuclear receptor PPARbeta/delta programs muscle glucose metabolism in cooperation with AMPK and MEF2. Genes Dev, 2011, 25: 2619–2630
Gan Z, Rumsey J, Hazen BC, Lai L, Leone TC, Vega RB, Xie H, Conley KE, Auwerx J, Smith SR, Olson EN, Kralli A, Kelly DP. Nuclear receptor/microRNA circuitry links muscle fiber type to energy metabolism. J Clin Invest, 2013, 123: 2564–2575
Leone TC, Weinheimer CJ, Kelly DP. A critical role for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) in the cellular fasting response: the PPARalpha-null mouse as a model of fatty acid oxidation disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999, 96: 7473–7478
Burkart EM, Sambandam N, Han X, Gross RW, Courtois M, Gierasch CM, Shoghi K, Welch MJ, Kelly DP. Nuclear receptors PPARbeta/delta and PPARalpha direct distinct metabolic regulatory programs in the mouse heart. J Clin Invest, 2007, 117: 3930–3939
Narkar VA, Downes M, Yu RT, Embler E, Wang YX, Banayo E, Mihaylova MM, Nelson MC, Zou Y, Juguilon H, Kang H, Shaw RJ, Evans RM. AMPK and PPARdelta agonists are exercise mimetics. Cell, 2008, 134: 405–415
Luquet S, Lopez-Soriano J, Holst D, Fredenrich A, Melki J, Rassoulzadegan M, Grimaldi PA. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta controls muscle development and oxidative capability. FASEB J, 2003, 17: 2299–2301
Wang YX, Zhang CL, Yu RT, Cho HK, Nelson MC, Bayuga-Ocampo CR, Ham J, Kang H, Evans RM. Regulation of muscle fiber type and running endurance by PPARdelta. PLoS Biol, 2004, 2: e294
Schuler M, Ali F, Chambon C, Duteil D, Bornert JM, Tardivel A, Desvergne B, Wahli W, Chambon P, Metzger D. PGC1alpha expression is controlled in skeletal muscles by PPARbeta, whose ablation results in fiber-type switching, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab, 2006, 4: 407–414
Puigserver P, Wu Z, Park CW, Graves R, Wright M, Spiegelman BM. A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell, 1998, 92: 829–839
Wu Z, Puigserver P, Andersson U, Zhang C, Adelmant G, Mootha V, Troy A, Cinti S, Lowell B, Scarpulla RC, Spiegelman BM. Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell, 1999, 98: 115–124
Handschin C, Spiegelman BM. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 coactivators, energy homeostasis, and metabolism. Endocrine Rev, 2006, 27: 728–735
Puigserver P, Spiegelman BM. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1 alpha): transcriptional coactivator and metabolic regulator. Endocrine Rev, 2003, 24: 78–90
Kelly DP, Scarpulla RC. Transcriptional regulatory circuits controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Genes Dev, 2004, 18: 357–368
Finck BN, Kelly DP. PGC-1 coactivators: inducible regulators of energy metabolism in health and disease. J Clin Invest, 2006, 116: 615–622
Lelliott CJ, Medina-Gomez G, Petrovic N, Kis A, Feldmann HM, Bjursell M, Parker N, Curtis K, Campbell M, Hu P, Zhang D, Litwin SE, Zaha VG, Fountain KT, Boudina S, Jimenez-Linan M, Blount M, Lopez M, Meirhaeghe A, Bohlooly YM, Storlien L, Stromstedt M, Snaith M, Oresic M, Abel ED, Cannon B, Vidal-Puig A. Ablation of PGC-1beta results in defective mitochondrial activity, thermogenesis, hepatic function, and cardiac performance. PLoS Biol, 2006, 4: e369
Sonoda J, Mehl IR, Chong LW, Nofsinger RR, Evans RM. PGC-1beta controls mitochondrial metabolism to modulate circadian activity, adaptive thermogenesis, and hepatic steatosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2007, 104: 5223–5228
Vega RB, Huss JM, Kelly DP. The coactivator PGC-1 cooperates with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha in transcriptional control of nuclear genes encoding mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation enzymes. Mol Cell Biol, 2000, 20: 1868–1876
Pilegaard H, Saltin B, Neufer PD. Exercise induces transient transcriptional activation of the PGC-1alpha gene in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol, 2003, 546: 851–858
Vianna CR, Huntgeburth M, Coppari R, Choi CS, Lin J, Krauss S, Barbatelli G, Tzameli I, Kim YB, Cinti S, Shulman GI, Spiegelman BM, Lowell BB. Hypomorphic mutation of PGC-1beta causes mitochondrial dysfunction and liver insulin resistance. Cell Metab, 2006, 4: 453–464
Russell LK, Mansfield CM, Lehman JJ, Kovacs A, Courtois M, Saffitz JE, Medeiros DM, Valencik ML, McDonald JA, Kelly DP. Cardiac-specific induction of the transcriptional coactivator peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and reversible cardiomyopathy in a developmental stage-dependent manner. Circulat Res, 2004, 94: 525–533
Zechner C, Lai L, Zechner JF, Geng T, Yan Z, Rumsey JW, Collia D, Chen Z, Wozniak DF, Leone TC, Kelly DP. Total skeletal muscle PGC-1 deficiency uncouples mitochondrial derangements from fiber type determination and insulin sensitivity. Cell Metab, 2010, 12: 633–642
Goto M, Terada S, Kato M, Katoh M, Yokozeki T, Tabata I, Shimokawa T. cDNA cloning and mRNA analysis of PGC-1 in epitrochlearis muscle in swimming-exercised rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2000, 274: 350–354
Baar K, Wende AR, Jones TE, Marison M, Nolte LA, Chen M, Kelly DP, Holloszy JO. Adaptations of skeletal muscle to exercise: rapid increase in the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1. FASEB J, 2002, 16: 1879–1886
Lehman JJ, Barger PM, Kovacs A, Saffitz JE, Medeiros DM, Kelly DP. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 promotes cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis. J Clin Invest, 2000, 106: 847–856
Lin J, Wu H, Tarr PT, Zhang CY, Wu Z, Boss O, Michael LF, Puigserver P, Isotani E, Olson EN, Lowell BB, Bassel-Duby R, Spiegelman BM. Transcriptional co-activator PGC-1 alpha drives the formation of slow-twitch muscle fibres. Nature, 2002, 418: 797–801
Wende AR, Schaeffer PJ, Parker GJ, Zechner C, Han DH, Chen MM, Hancock CR, Lehman JJ, Huss JM, McClain DA, Holloszy JO, Kelly DP. A role for the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha in muscle refueling. J Biol Chem, 2007, 282: 36642–36651
Lin J, Wu PH, Tarr PT, Lindenberg KS, St-Pierre J, Zhang CY, Mootha VK, Jager S, Vianna CR, Reznick RM, Cui L, Manieri M, Donovan MX, Wu Z, Cooper MP, Fan MC, Rohas LM, Zavacki AM, Cinti S, Shulman GI, Lowell BB, Krainc D, Spiegelman BM. Defects in adaptive energy metabolism with CNS-linked hyperactivity in PGC-1alpha null mice. Cell, 2004, 119: 121–135
Arany Z, He H, Lin J, Hoyer K, Handschin C, Toka O, Ahmad F, Matsui T, Chin S, Wu PH, Rybkin, II, Shelton JM, Manieri M, Cinti S, Schoen FJ, Bassel-Duby R, Rosenzweig A, Ingwall JS, Spiegelman BM. Transcriptional coactivator PGC-1 alpha controls the energy state and contractile function of cardiac muscle. Cell Metab, 2005, 1: 259–271
Handschin C, Chin S, Li P, Liu F, Maratos-Flier E, Lebrasseur NK, Yan Z, Spiegelman BM. Skeletal muscle fiber-type switching, exercise intolerance, and myopathy in PGC-1alpha muscle-specific knock-out animals. J Biol Chem, 2007, 282: 30014–30021
Leone TC, Lehman JJ, Finck BN, Schaeffer PJ, Wende AR, Boudina S, Courtois M, Wozniak DF, Sambandam N, Bernal-Mizrachi C, Chen Z, Holloszy JO, Medeiros DM, Schmidt RE, Saffitz JE, Abel ED, Semenkovich CF, Kelly DP. PGC-1alpha deficiency causes multi-system energy metabolic derangements: muscle dysfunction, abnormal weight control and hepatic steatosis. PLoS Biol, 2005, 3: e101
Ruas JL, White JP, Rao RR, Kleiner S, Brannan KT, Harrison BC, Greene NP, Wu J, Estall JL, Irving BA, Lanza IR, Rasbach KA, Okutsu M, Nair KS, Yan Z, Leinwand LA, Spiegelman BM. A PGC-1α isoform induced by resistance training regulates skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Cell, 2012, 151: 1319–1331
Agudelo LZ, Femenia T, Orhan F, Porsmyr-Palmertz M, Goiny M, Martinez-Redondo V, Correia JC, Izadi M, Bhat M, Schuppe-Koistinen I, Pettersson AT, Ferreira DM, Krook A, Barres R, Zierath JR, Erhardt S, Lindskog M, Ruas JL. Skeletal muscle PGC-1alpha1 modulates kynurenine metabolism and mediates resilience to stress-induced depression. Cell, 2014, 159: 33–45
Lai L, Leone TC, Zechner C, Schaeffer PJ, Kelly SM, Flanagan DP, Medeiros DM, Kovacs A, Kelly DP. Transcriptional coactivators PGC-1alpha and PGC-lbeta control overlapping programs required for perinatal maturation of the heart. Genes Dev, 2008, 22: 1948–1961
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell, 2009, 136: 215–233
Mendell JT, Olson EN. MicroRNAs in stress signaling and human disease. Cell, 2012, 148: 1172–1187
Williams AH, Liu N, van Rooij E, Olson EN. MicroRNA control of muscle development and disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2009, 21: 461–469
Guttman M, Rinn JL. Modular regulatory principles of large non-coding RNAs. Nature, 2012, 482: 339–346
Small EM, Olson EN. Pervasive roles of microRNAs in cardiovascular biology. Nature, 2011, 469: 336–342
Song X, Shan D, Chen J, Jing Q. miRNAs and lncRNAs in vascular injury and remodeling. Sci China Life Sci, 2014, 57: 826–835
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell, 1993, 75: 843–854
Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell, 1993, 75: 855–862
Reinhart BJ, Weinstein EG, Rhoades MW, Bartel B, Bartel DP. MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev, 2002, 16: 1616–1626
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T. Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science, 2001, 294: 853–858
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP. An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science, 2001, 294: 858–862
Matkovich SJ, Hu Y, Eschenbacher WH, Dorn LE, Dorn GW, 2nd. Direct and indirect involvement of microRNA-499 in clinical and experimental cardiomyopathy. Circulat Res, 2012, 111: 521–531
Chen K, Rajewsky N. The evolution of gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet, 2007, 8: 93–103
van Rooij E, Quiat D, Johnson BA, Sutherland LB, Qi X, Richardson JA, Kelm RJ, Jr., Olson EN. A family of microRNAs encoded by myosin genes governs myosin expression and muscle performance. Dev Cell, 2009, 17: 662–673
Chen JF, Callis TE, Wang DZ. microRNAs and muscle disorders. J Cell Sci, 2009, 122: 13–20
van Rooij E, Liu N, Olson EN. MicroRNAs flex their muscles. Trends Genet, 2008, 24: 159–166
Bell ML, Buvoli M, Leinwand LA. Uncoupling of expression of an intronic microRNA and its myosin host gene by exon skipping. Mol Cell Biol, 2010, 30: 1937–1945
Ji J, Tsika GL, Rindt H, Schreiber KL, McCarthy JJ, Kelm RJ, Jr., Tsika R. Puralpha and Purbeta collaborate with Sp3 to negatively regulate beta-myosin heavy chain gene expression during skeletal muscle inactivity. Mol Cell Biol, 2007, 27: 1531–1543
Hagiwara N, Yeh M, Liu A. Sox6 is required for normal fiber type differentiation of fetal skeletal muscle in mice. Dev Dynam, 2007, 236: 2062–2076
von Hofsten J, Elworthy S, Gilchrist MJ, Smith JC, Wardle FC, Ingham PW. Prdm1- and Sox6-mediated transcriptional repression specifies muscle fibre type in the zebrafish embryo. EMBO Rep, 2008, 9: 683–689
Quiat D, Voelker KA, Pei J, Grishin NV, Grange RW, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN. Concerted regulation of myofiber-specific gene expression and muscle performance by the transcriptional repressor Sox6. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011, 108: 10196–10201
Narkar VA, Fan W, Downes M, Yu RT, Jonker JW, Alaynick WA, Banayo E, Karunasiri MS, Lorca S, Evans RM. Exercise and PGC-1alpha-independent synchronization of type I muscle metabolism and vasculature by ERRgamma. Cell Metab, 2011, 13: 283–293
Yan J, Zhao Y, Zhao B. Green tea catechins prevent obesity through modulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Sci China Life Sci, 2013, 56: 804–810
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is published with open access at link.springer.com
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Liang, X. & Gan, Z. Transcriptional regulatory circuits controlling muscle fiber type switching. Sci. China Life Sci. 58, 321–327 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-015-4833-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-015-4833-4