Abstract
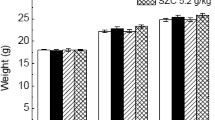
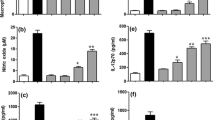
A polysaccharide, CrvpPS, was isolated from Caulerpa racemosa var peltata. It was reacted with nano-selenium in distilled water containing ascorbic acid (Vit C) to form a stable CrvpPS-nano-Se complex. The immunomodulatory effects of CrvpPS and CrvpPS-nano-Se on T lymphocytes subgroups and NK cells in mice were investigated. After intragastric administration for 10 days separately, both CrvpPS and CrvpPS-nano-Se showed significant stimulatory functions to thymus gland of mice. Moreover, the CrvpPS-nano-Se induced the percentage of CD3+, CD3+CD4+, NK cells and the CD4+/CD8+ value to increase significantly (P<0.05) when analyzed by flow cytometry, which is better than the CrvpPS, sucrose-nano-Se, and even the positive drug levamisole.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang A L, Hu J R. Advances in studies on biological activities of alga polysaccharide. Mar Sci, 2002, 26: 36–40
Tuo J J, Guo G Q, Shen W Z, et al. The immune modulatory effect of the Caulerpa racemosa var peltata polysaccharides on T lymphocyte subgroup and Natural killer cell in mice. J Jinan Univ (Med Ed), 2007, 28: 129–131, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2sXntFymurg%3D
Rayman M P. The importance of selenium to human health. Lancet, 2000, 356: 233–241, 10963212, 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02490-9, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXltVOgsL0%3D
Huang Z, Zheng W J, Li L N, et al. Research progress on biosynthesis and bioactivity of nano red elemental selenium. Chin Biotechnol, 2003, 23: 76–79, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXjtFeru7s%3D
Zhang J S, Wang H L, Yan X X, et al. Comparison of short-term toxicity between Nano-Se and selenite in mice. Life Sci, 2005, 76: 1099–1109, 15620574, 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.08.015, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhtFCqtLzN
Cui Q, Shang D J, Zou X. Research progress of polysaccharide containing selenium. Chin J Biochem Pharmaceut, 2003, 24: 155–157, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXivFert7Y%3D
Zhan L S, Zhang X S, Wu X H, et al. The immunomodulatory effect of polysaccharide from brown seaweed. Chin J Biochem Pharmaceut, 2001, 22: 116–118, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmt1Giu7Y%3D
Bai Y, Li W J, Wu Y Q, et al. Modulation effect of sucrose in the assembly nanometer Se0 particles and their stability in liquid phase. Chem J Chin Univ, 2007, 28: 153–155, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2sXhtlGmsro%3D
Zhang S Y, Zhang J, Wang H Y, et al. Synthesis of selenium nanoparticles of polysaccharides. Mater Lett, 2004, 58: 2590–2594, 10.1016/j.matlet.2004.03.031, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXlslyiuro%3D
Ramesh H P, Tharanathan R N. Carbohydrates the renewable raw materials of high biotech-nological value. Crit Rev Biotechnol, 2003, 23: 149–173, 12889744, 10.1080/713609312, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXlslyqsrs%3D
Huang B, Zhang J S, Hou J W, et al. Free radical scavenging efficiency of nano-se in vitro. Free Radical Biol Med, 2003, 35: 805–813, 10.1016/S0891-5849(03)00428-3, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXosVKnsLo%3D
Liang K Z. Selenium and immunity. Studies Trace Elements Health, 2004, 21: 60–70
Hu Q B, Guo B J. Analysis of spirulina-selenium polysaccharide improvement on mice immunological competence. Chin J Mar Drugs, 2001, 5: 18–20
Tang F, Zhou J, Gu L K, et al. In vivo and in vitro effects of selenium-enriched garlic on growth of human gastric carcinoma cells. Chin J Oncol, 2001, 23: 461–464, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XitVKitA%3D%3D
Li X K, Yan J C, Cui X Y, et al. Progress on study and utilization of Selenized polysaccharide. Chin Trad Herbal Drugs, 2006, 37: adnexal 6–8, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2sXksVajtrg%3D
Zhao M Y, Cai W D, Xiao Z J. The research on Se-lentinan’s intervention to SD rat’s immuno-deficiency. China Public Health, 2000, 16: 901–902, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXivVeit78%3D
Xu B H, Sun Y. Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled phase II clinical trial of K-selenocarrageenan in cancer chemotherapy patients. Chin J Clinic Oncol, 1999, 26: 678–680, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjt1Sjtg%3D%3D
Zhang J S, Wang H L, Bao Y P, et al. Nano red elemental selenium has no size effect in the induction of seleno-enzymes in both cultured cells and mice. Life Sci, 2004, 75: 237–244, 15120575, 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.02.004, 1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXjs1Wktbo%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Team Project of Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 039213)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, W., Wang, H., Guo, G. et al. Immunomodulatory effects of Caulerpa racemosa var peltata polysaccharide and its selenizing product on T lymphocytes and NK cells in mice. SCI CHINA SER C 51, 795–801 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-008-0106-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-008-0106-9