Abstract
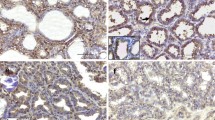
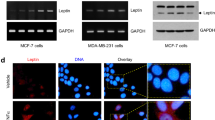
Leptin is an autocrine and paracrine factor which affects the development of duct, formation of gland alveolus, expression of milk protein gene and onset involution of mammary gland. In order to know the function and mechanism of leptin in mammary gland, the protein expression and localization of leptin and its long form receptor (OB-Rb) were detected by a confocal laser scanning microscope. To study the impacts of leptin on mammary gland and leptin signal transduction pathway in pregnancy-, lactation-and involution-stage mammary gland, explants were cultured and Western blotting was used. The results showed that in the whole development cycle of mammary gland, the expression of leptin and OB-Rb was in positive correlation. In virgin the leptin expression was the highest and then decreased in pregnancy. In lactation the expression of leptin was low and upgraded in involution, and recovered to the original level about virgin on involution 13 d. The localization of leptin and OB-Rb revealed that leptin induced the expression of OB-Rb specifically and controlled the development and physiological function of the mammary gland by binding to OB-Rb. In pregnancy stage, leptin stimulated proliferation and differentiation of ductal epithelial cells by JAK-MAPK signal pathway. In lactation, leptin induced gene expression of β-casein by JAK-STAT5 signal pathway, and in involution leptin induced mammary epithelial cell apoptosis and mammary gland restitution by JAK-STAT3 signal pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, et al. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature, 1994, 372: 425–432
Houseknecht K L, Baile C A, Matteri R L, et al. The biology of leptin: A review. J Anim Sci, 1998, 76: 1405–1420
Wauters M, Considine R V, van Gaal L F. Human leptin: From an adipocyte hormone to an endocrine mediator. Eur J Endocrinol, 2000, 143: 293–311
Hu X, Juneja S C, Maihle N J, et al. Leptin—A growth factor in normal and malignant breast cells and for normal mammary gland development. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2002, 94: 1704–1711
Aoki N, Kawamura M, Matsuda T. Lactation-dependent down regulation of leptin production in mouse mammary gland. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1999, 1427: 298–306
Baratta M, Grolli S, Tamanini C. Effect of leptin in proliferating and differentiated HC11 mouse mammary cells. Regul Pept, 2003, 113(1-3): 101–107
Bonnet M, Gourdou I, Leroux C, et al. Leptin expression in the ovine mammary gland: Putative sequential involvement of adipose, epithelial, and myoepithelial cells during pregnancy and lactation. J Anim Sci, 2002, 80: 723–728
Elias J J, Pitelka D R, Armstrong R C. Changes in fat cell morphology during lactation in the mouse. Anat Rec, 1973, 177: 533–547
Feuermann Y, Mabjeesh S J, Shamay A. Leptin affects prolactin action on milk protein and fat synthesis in the bovine mammary gland. J Dairy Sci, 2004, 87(9): 2941–2946
Tartaglia L A, Dembski M, Weng X, et al. Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor OB-R. Cell, 1995, 83(7): 1263–1271
Baumann H, Morella K K, White D W, et al. The full-length leptin receptor has signaling capabilities of interleukin 6-type cytokine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996, 93(16): 8374–8378
Tartaglia L A. The leptin receptor. J Biol Chem, 1997, 272: 6093–6096
Laud K, Gourdon I, Belair L, et al. Detection and regulation of leptin receptor mRNA in ovine mammary epithelial cells during pregnancy and lactation. FEBS Lett, 1999, 463: 194–198
Fantuzzi G, Faggioni R. Leptin in the regulation of immunity, inflammation and hematopoiesis. J Leukoc Biol, 2000, 68: 437–446
Bjorbaek C, Uotani S, da Silva B, et al. Divergent signaling capacities of the long and short isoforms of the leptin receptor. J Biol Chem, 1997, 272(51): 32686–32695
Carpenter L R, Farruggella T J, Symes A, et al. Enhancing leptin response by preventing SH2-containing phosphatase 2 interaction with Ob receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1998, 95(11): 6061–6066
Banks A S, Davis S M, Bates S H, et al. Activation of downstream signals by the long form of the leptin receptor. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275(19): 14563–14572
Takahashi Y, Okimura Y, Mizuno I, et al. Leptin induces mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent proliferation of C3H10T1/2 cells. J Biol Chem, 1997, 272: 12897–12900
Li C, Friedman J M. Leptin receptor activation of SH2 domain containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 2 modulates Ob receptor signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,1999, 96: 9677–9682
Bjorbaek C, El-Haschimi K, Frantz J D, et al. The role of SOCS-3 in leptin signaling and leptin resistance. J Biol Chem, 1999, 274: 30059–30065
Miyoshi K, Shillingford J M, Smith G H, et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription (Stat) 5 controls the proliferation and differentiation of mammary alveolar epithelium. J Cell Biol, 2001, 155: 531–542
Liu X, Robinson G W, Wagner K U, et al. Stat5a is mandatory for adult mammary gland development and lactogenesis. Genes Dev, 1997, 11: 179–186
Teglund S, McKay C, Schuetz E, et al. Stat5a and Stat5b proteins have essential and nonessential, or redundant, roles in cytokine responses. Cell, 1998, 93: 841–850
Chehab F F, Lim M E, Lu R. Correction of the sterility defect in homozygous obese female mice by treatment with the human recombinant leptin. Nat Genet, 1996, 12: 318–320
Bjorbæk C, Lavery H J, Bates S H, et al. SOCS3 mediates feedback inhibition of the leptin receptor via Tyr985. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275: 40649–40657
Hutt J A, O’Rourke J P, DeWille J. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activates CCAAT enhancer-binding protein δ gene transcription in G0 growth-arrested mouse mammary epithelial cells and in involuting mouse mammary gland. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275: 29123–29131
Humphrey R C, Bierie B, Zhao L, et al. Deletion of Stat3 blocks mammary gland involution and extends functional competence of the secretory epithelium in the absence of lactogenic stimuli. Endocrinology, 2002, 143(9): 3641–3650
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30671538)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Y., Li, Q. Expression and function of leptin and its receptor in mouse mammary gland. SCI CHINA SER C 50, 669–675 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-007-0077-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-007-0077-2