Abstract
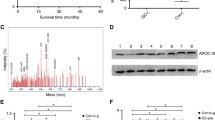
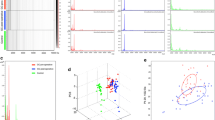
Two hundred and eighteen serum samples from 175 lung cancer patients and 43 healthy individuals were analyzed by using Surface Enhaced Laser Desorption/Ionization Time of Flight Mass Spectrome-try (SELDI-TOF-MS). The data analyzed by both Biomarker Wizard™ and Biomarker Patterns™ software showed that a protein peak with the molecular weight of 11.6 kDa significantly increased in lung cancer. Meanwhile, the level of this biomarker was progressively increased with the clinical stages of lung cancer. The candidate biomarker was then obtained from tricine one-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis by matching the molecular weight with peaks on WCX2 chips and was identified as Serum Amyloid A protein (SAA) by MALDI/MS-MS and database searching. It was further validated in the same serum samples by immunoprecipitation with commercial SAA antibody. To confirm the SAA differential expression in lung cancer patients, the same set of serum samples was measured by ELISA assay. The result showed that at the cutoff point 0.446 (OD value) on the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve, SAA could better discriminate lung cancer from healthy individuals with sensitivity of 84.1% and specificity of 80%. These findings demonstrated that SAA could be characterized as a biomarker related to pathological stages of lung cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SAA:
-
Serum Amyloid A protein
- ELISA:
-
enzyme linked immunosor-bent assay
- ROC:
-
receiver operating characteristic
- SELDI-TOF-MS:
-
Surface-Enhanced Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time of Flight-Mass Spectrometry
References
Xiao X Y, Wei X P, He D C. Proteomics approaches to biomarker discovery in lung cancers by SELDI Technology. Sci China Ser C-Life Sci, 2003, 46(5): 531–537
Xiao X Y, Liu D H, He D C, et al. Development of proteomic patterns for detecting lung cancer. Disease Marker, 2004, 19(1): 33–39
Pan Y Z, Xiao X Y, Zhao X J, et al. Application of surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight-based serum proteomic array technique for the early diagnosis of prostate cancer. Asian J Androl, 2006, 8(1): 45–51
Volker S, Matthias P A E, Thomas B. Advances in clinical cancer proteomics: SELDI-TOF-mass spectrometry and biomarker discovery. Brief Funct Genom Proteom, 2005, 4: 16–26
Kokubun M, Imafuku Y, Okada M, et al. Serum amyloid A (SAA) concentration varies among rheumatoid arthritis patients estimated by SAA/CRP ratio. Clin Chim Acta, 2005, 360: 97–102
Centre L B, Unite’d O M, et al. Protein chip array profiling analysis of sera from neuroblastoma patients. Cancer Lett, 2005, 228: 91–96
Cromer C J, Campa M, Patz E F. Clinical utility of serum amyloid A and macrophage migration inhibitory factor as serum biomarkers for the detection of 16 nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer, 2004, 101(2): 379–384
Petricoin E F, Ardekani A M, Hitt B A, et al. Use of proteomic patterns in serum to identify ovarian cancer. The Lancet, 2002, 359: 572–577
William E G, Semmes O J, et al. The early detection research network surface-enhanced laser desorption and ionization prostate cancer detection study. Urologic Oncol, 2004, 22: 337–343
Mueller J, Eggeling F V, Driesch D, et al. Protein chip technology reveals distinctive protein expression profiles in the urine of bladder cancer patients. Eur Urol, 2005, 47: 885–894
Xiao X Y, Zhao X, Liu J K, et al. Discovery of laryngeal carcinoma by serum proteomic pattern analysis. Sci China Ser C-Life Sci, 2004, 47(3): 219–223
Pia D, Magnus S, et al. Proteome studies of CSF in AD patients. Mech Ageing Devel, 2006, 127: 133–137
Malle E, De Beer F C. Human serum amyloid A (SAA) protein: A prominent acute-phase reactant for clinical practice. Eur J Clin Invest, 1996, 26(6): 427–435
Yip T, Chan J, Cho W, et al. Protein chip array profiling analysis in patients with severe acute respirator syndrome identified serum amyloid A protein as a biomarker potentially useful in monitoring the extent of pneumonia. Clin Chem, 2005, 51: 47–55
Kokubun M, Imafuku Y, Okada M, et al. Serum amyloid A (SAA) concentration varies among rheumatoid arthritis patients estimated by SAA/CRP ratio. Clin Chim Acta, 2005, 360(1–2): 97–102
Okoi K, Shih L C, Kobayashi R, et al. Serum amyloid A as a tumor marker in sera of nude mice with orthotopic human pancreatic cancer and in plasma of patients with pancreatic cancer. Int J Oncol, 2005, 27(5): 1361–1369
Le L L, Chi K, Tyldesley S, et al. Identification of serum amyloid A as a biomarker to distinguish prostate cancer patients with bone lesions. Clin Chem, 2005, 51: 695–707
Cho W, Yip T, Yip C, et al. Identification of serum amyloid A protein as a potential useful biomarkers to monitor relapse of nasopharyngeal cancer by serum proteomic profiling. Clin Cancer Res, 2004, 10: 43–52
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported in part by the Major State Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2006CB910100), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 30370712), Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (Grant No. 7051002), and Science Technology Committee of Beijing (Grant No.Y0204002040111
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, S., Wang, X., Liu, L. et al. Discovery and identification of Serum Amyloid A protein elevated in lung cancer serum. SCI CHINA SER C 50, 305–311 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-007-0053-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-007-0053-x