Abstract
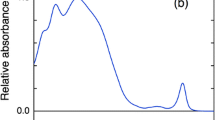
Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) is a new technique in studying the conformational state of a molecule in recent years. In this work, we reported the first use of THz-TDS to examine the denaturation of two photosynthesis membrane proteins: CP43 and CP47. THz-TDS was proven to be useful in discriminating the different conformational states of given proteins with similar structure and in monitoring the denaturation process of proteins. Upon treatment with guanidine hydrochloride (GuHCl), a 1.8 THz peak appeared for CP47 and free chlorophyll a (Chl a). This peak was deemed to originate from the interaction between Chl a and GuHCl molecules. The Chl a molecules in CP47 interacted with GuHCl more easily than those in CP43.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bricker T M. The structure and function of CP-1 and CP-2 in photo-system II. Photosynth Res, 1990, 24: 1–13
Bricker T M, Frankel L K. The structure and function of CP47 and CP43 in photosystem II. Photosynth Res, 2002, 72: 131–146
Barber J, Morris E, Büchel C. Revealing the structure of the photosystem II chlorophyll binding proteins, CP43 and CP47. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2000, 1459: 239–247
Walther M, Fischer B M, Jepsen P U. Noncovalent intermolecular forces in polycrystalline and amorphous saccharides in the far infrared. Chem Phys, 2003, 288: 261–268
Fischer B M, Walther M, Jepsen P U. Far-infrared vibrational modes of DNA components studied by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Phys Med Biol, 2002, 47: 3807–3814
Nishizawa J, Suto K, Sasaki T, et al. Spectral measurement of terahertz vibrations of biomolecules using a Gap terahertz-wave generator with automatic scanning control. J Phys, 2003, 36: 2958–2961
Shen Y C, Upadhya P C, Linfield E H, et al. Temperature-dependent low-frequency vibrational spectra of purine and adenine. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 82: 2350–2352
Markelz A G, Roitberg A, Heilweil E J. Pulsed terahertz spectroscopy of DNA, bovine serum albumin and collagen between 0.1 and 2.0 THz. Chem Phys Lett, 2000, 320: 42–48
Walther M, Fischer B, Schall M, et al. Far-infrared vibrational spectra of all-trans, 9-cis and 13-cis retinal measured by THz time-domain spectroscopy. Chem Phys Lett, 2000, 332: 389–395
Smye S W, Chamberlain J M, Fitzgerald A J, et al. The interaction between terahertz radiation and biological tissue. Phys Med Biol, 2001, 46: R101–R112
Markelz A, Whitmire S, Hillebrecht J, et al.. THz time domain spectroscopy of biomolecular conformational modes. Phys Med Biol, 2002, 47: 3797–3805
Wang W N, Yue W W, Yan H T, et al. THz time-domain spectroscopy of amino acids. Chin Sci Bull, 2005, 50(15): 1561–1565
Upadhyal P C, Shen Y C, Davies A G, et al. Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy of glucose and uric acid. J Biol Phys, 2003, 29: 117–121
Walther M, Plochocka P, Fischer B, et al. Collective vibrational modes in biological molecules investigated by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Biopolymers, 2002, 67: 310–313
Fischer B, Walther M, Jepsen P Uhd. Far-infrared spectroscopy of hydrogen bonding in nucleobases, nucleosides, and nucleotides. In: Chamberlain J M, ed. Proc. of 2002 IEEE 10th International Conference on Terahertz Electronics, Cambridge, 2002. Piscataway: IEEE, 2002. 74–76
Guo S K, Tang C Q, Yang Z L, et al. Effects of acid and alkali on the light absorption, energy transfer and protein secondary structures of core antenna subunits CP43 and CP47 of Photosystem II. Photochem Photobiol, 2004, 79: 291–296
Wang J S, Shan J X, Xu Q, et al. Light-and heat-induced denaturation of photosystem II core-antenna complexes CP43 and CP47. J Photochem Photobiol, 1999, 50: 189–196
Alfonson M, Montoya G, Cases R, et al. Core antenna complexes, CP43 and CP47, of higher plant photosystem II. Spectral properties, pigment stoichiometry, and amino acid composition. Biochemistry, 1994, 33: 10494–10500
Shan J X, Wang J S, Ruan X, et al. Changes of absorption spectra during heat-induced denaturation of photosystem II core antenna complexes CP43 and CP47: revealing the binding states of chlorophyll molecules in these two complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2001, 1504: 396–408
Groot M L, Peterman E J, van Stokkum I H, et al. Triplet and fluorescing states of the CP47 antenna complex of photosystem II studied as a function of temperature. Biophys J, 1995, 68: 281–290
Weerd F L De, van Stokkum I H M, van Amerongen H, et al. Pathways for energy transfer in the core light-harvesting complexes CP43 and CP47 of photosystem II. Biophys J, 2002, 82: 1586–1597
Shan J X, Yang K Y, Feng L J, et al. Resonance Raman spectra of purified PSII core antenna complexes CP43 and CP47. Acta Bot Sin, 1999, 41: 280–284
De Paula J C, Liefshitz A, Hinsley S, et al. Structure-function relationship in the 47-kDa antenna protein and its complex fluorescence decay kinetics and resonance Raman spectroscopy. Biochemistry, 1994, 33: 1455–1466
Nozaki Y. The preparation of guanidine hydrochloride. Methods Enzymol, 1972, 26: 43–51
Jankowiak R, Zazubovich V, Rätsep M, et al. The CP43 core antenna complex of photosystem II possesses two quasi-degenerate and weakly coupled Qy-trap states. J Phys Chem, 2000, 104: 11805–11815
Qu Y G, Gong Y D, Guo S K, et al. Structural characteristics of extra-membrane domains and guanidine hydrochloride-induced denaturation of photosystem 2 core antenna complexes CP43 and CP47. Photosynthetica, 2006, 44: 447–453
Dunbar J, Yennawar H P, Banerjee S, et al. The effect of denaturants on protein structure. Protein Sci, 1997, 6: 1727–1733
Korter T M, Balu R, Campbell M B, et al. Terahertz spectroscopy of solid serine and cysteine. Chem Phys Lett, 2006, 418: 65–70
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 39890390)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Y., Chen, H., Qin, X. et al. The guanidine hydrochloride-induced denaturation of CP43 and CP47 studied by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. SCI CHINA SER C 50, 350–355 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-007-0048-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-007-0048-7