Abstract
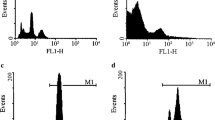
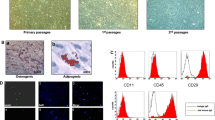
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) have the ability of self-renewal and multi-directional differentiation. Recent reports showed that BMSCs could differentiate into endocrine cells of pancreas. However, the differentiation is not efficient enough to produce insulin-producing cells for the future therapeutic use. Pdx-1 is a crucial regulator for pancreatic development. Therefore we constructed a eukaryotic expression vector containing Pdx-1 to determine the effect of Pdx-1 expression on differentiation of BMSCs in vitro. The results showed that BMSCs could self-assemble to form functional pancreatic islet-like structures after differentiation in vitro. The proportion of insulin-producing cells differentiated from Pdx-1+BMSCs was 28.23%±2.56%, higher than that from BMSCs transfected with vacant vector and Pdx-1 − BMSCs (7.23%±1.56% and 4.08%±2.69% respectively) by flow cytometry. Immunocytochemical examination also testified the expression of multiple β-cells-specific genes such as insulin, glucagons, somatostatin in differentiated BMSCs. The results also revealed that the expressions of genes mentioned above in Pdx-1+BMSCs were higher than that in Pdx-1−BMSCs, which was confirmed by Western blotting analysis and RT-PCR. Glucose-induced insulin secretion from Pdx-1+BMSCs in 5mmol/L and 25mmol/L glocuse was (56.61±4.82) µU/mL and (115.29±2.56) µU/mL respectively, which were much higher than those from Pdx-1−BMSCs((25.53±6.49) µU/mL and (53.26±7.56) µU/mL respectively). Grafted animals were able to maintain their body weight and survive for relatively longer periods of time than hyperglycemic sham-grafted controls, which demonstrated an overall beneficial effect of the grafted cells on the health of the animals. These findings thus suggested that exogenous expression of Pdx-1 should provide a promising approach for efficiently producing islet-like cells from BMSCs for the future therapeutic use in diabetic patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shapiro A M, Lakey J R, Ryan E A, Korbutt G S, Toth E, Warnock G L, et al. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med, 2000, 343(4): 230–238
Lumelsky N, Blondel O, Laeng P, Velasco I, Ravin R, McKay R. Differentiation of embryonic stem cells to insulin-secreting structures similar to pancreatic islets. Science, 2001, 292(5520): 1389–1394
Soria B, Roche E, Berna G, Leon-Quinto T, Reig J A, Martin F. Insulin-secreting cells derived from embryonic stem cells normalize glycaemia in streptozocin-induced diabetic mice. Diabetes, 2000, 49(2): 157–162
Assady S, Maor G, Amit M, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Skorecki K L, Tzukerman M. Insulin production by human embryonic stem cells. Diabetes, 2001, 50(8): 1691–1697
Segev H, Fishman B, Ziskind A, et al. Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into insulin-producing clusters. Stem Cells, 2004, 22(3): 265–274
Kopen G C, Prockop D J, Phinney D G. Marrow stromal cells migrate throughout forebrain and cerebellum, and they differentiate into astrocytes after injection into neonatal mouse brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1999, 96(19): 10711–10716
Asahara T, Masuda H, Takahashi T, Kalka C, Pastore C, Silver M, et al. Bone marrow origin of endothelial progenitor cells esponsible for postnatal vasculogenesis in physiological and pathological eovascularization. Circ Res, 1999, 85(3): 221–228
Gussoni E, Soneoka Y, Strickland C D, Buzney E A, Khan M K, Flint A F, et al. Dystrophin expression in the mdx mouse restored by stem cell transplantation. Nature, 1999, 401(6751): 390–394
Schwartz R E, Reyes M, Koodie L, Jiang Y, Blackstad M, Lund T, et al. Multipotent adult progenitor cells from bone marrow differentiate into functional hepatocyte-like cells. J Clin Invest, 2002, 109(10): 1291–1302
Zorina T D, Subbotin V M, Bertera S, Alexander A M, Haluszczak C, Gambrell B, et al. Recovery of the endogenous beta cell function in the NOD model of autoimmune diabetes. Stem Cells, 2003, 21(4): 377–388
Ianus A, Holz G G, Theise N D, Hussain M A. In vivo derivation of glucose-competent pancreatic endocrine cells from bone marrow without evidence of cell fusion. J Clin Invest, 2003, 111(6): 843–850
Oh S H, Muzzonigro T M, Bae S H, LaPlante J M, Hatch H M, Petersen B E. Adult bone marrow-derived cells trans-differentiating into insulin-producing cells for the treatment of type I diabetes. Lab Invest, 2004, 84(5): 607–617
Jahr H, Bretzel R G. Insulin-positive cells in vitro generated from rat bone marrow stromal cells. Transplant Proc, 2003, 35(6): 2140–2141
Jia Y J, Zhong L, Song J H, Luo F, Sun J P, Yang Y J. Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transdifferentiate into islet-secreting cells in vitro. Chin J Contemp Pediatr, 2003, 5(5): 393–397
Tang D Q, Cao L Z, Burkhardt B R, Xia C Q, Litherland S A, Atkinson M A, et al. In vivo and in vitro characterization of insulin-producing cells obtained from murine bone marrow. Diabetes, 2004, 53(7): 1721–1732
Jonsson J, Carlsson L, Edlund H. Insulin-promoter-factor 1 is required for pancreas development in mice. Nature, 1994, 371(6498): 606–609
Ahlgren U, Jonsson J, Jonsson L, Simu K, Edlund H. Beta-Cell-specific inactivation of the mouse Ipf1/Pdx1 gene results in loss of the beta-cell phenotype and maturity onset diabetes. Genes Dev, 1998, 12(12): 1763–1768
Yoshida S, Kajimoto Y, Yasuda T, Watada H, Fujitani Y, Kosaka H, et al. Pdx-1 induces differentiation of intestinal epithelioid IEC-6 into insulin-producing cells. Diabetes, 2002, 51(8): 2505–2513
Ferber S, Halkin A, Cohen H, Ber I, Einav Y, Goldberg I, et al. Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene 1 induces expression of insulin genes in liver and ameliorates streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia. Nat Med, 2000, 6(5): 568–572
Miyazaki S, Yamato E, Miyazaki J. Regulated expression of pdx-1 promoted in vitro differentiation of insulin-producing cells from embryonic stem cells. Diabetes, 2004, 53(4): 1030–1037
Moritoh Y, Yamato E, Yasui Y, Miyazaki S, Miyazaki J. Analysis of insulin-producing cells during in vitro differentiation from Feeder-free embryonic stem cells. Diabetes, 2003, 52(5): 1163–1168
Yang L, Li S, Hatch H, Ahrens K, Comelius J G, Petersen B E, et al. In vitro trans-differentiation of adult hepatic stem cells into pancreatic endocrine hormone-producing cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2002, 99(12): 8078–8083
Bonner-Weir S, Taneja M, Weir G C, Tatarkiewicz K, Song K H, Sharma A, et al. In vitro cultivation of human islets from expanded ductal tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2000, 97(14): 7999–8004
Ramiya V K, Maraist M, Arfors K E, Schatz D A, Peck A B, Cornelius J G Reversal of insulin-dependent diabetes using islets generated in vitro from pancreatic stem cells. Nat Med, 2000, 6(3): 278–282
Suzuki A, Nakauchi H, Taniguchi H. Glucagon-like peptide 1(1–37) converts intestinal epithelial cells into insulin-producing cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003, 100(9): 5034–5039
Otonkoski T, Beattie G M, Mally M I, Ricordi C, Hayek A. Nicotinamide is a potent inducer of endocrine differentiation in cultured human fetal pancreatic cells. J Clin Invest, 1993, 92(3): 1459–1466
Sjoholm A, Korsgren O, Andersson A. Polyamine requirements in nicotinamide-stimulated beta-cell differentiation in fetal porcine islet-like cell clusters. Endocrinology, 1994, 135(4): 1559–1565
Lechner A, Yang Y G, Blacken R A, Wang L, Nolan A L, Habener J F. No evidence for significant transdifferentiation of bone marrow into pancreatic β-cells in vivo. Diabetes, 2004, 53(3): 616–623
Rajagopal J, Anderson W J, Kume S, Martinez O I, Melton D A. Insulin staining of ES cell progeny from insulin uptake. Science, 2003, 299(5605): 363
Michele A, Domenick, M D, Suzanne T, et al. Impact of bone marrow transplantation on Type I diabetes. World Journal of Surgery, 2001, 25(4): 474–480
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Yang, Y., Wang, X. et al. Expression of Pdx-1 in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes differentiation of islet-like cells in vitro . SCI CHINA SER C 49, 480–489 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-006-2016-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-006-2016-z