Abstract
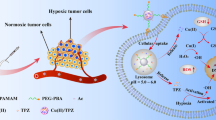
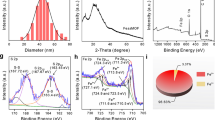
The development of promising strategies to improve the treatment efficacy of pancreatic carcinoma still remains to be a challenging task. We report here the development of a new dendrimer-based nanomedicine formulation to tackle pancreatic carcinoma through apoptosis-enhanced ferroptosis therapy. In this article, G5 dendrimers were partially modified with a Fe(III) chelator hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxylic acid (8-HQC) on their periphery, entrapped with gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) within their internal cavities, and chelated with Fe(III). The thus created dendrimer-entrapped Au NPs (Fe-Au DENP-HQC) with an Au core size of 1.9 nm and 20.0 Fe(III) ions complexed per dendrimer are stable, have a pH-dependent Fe(III) release profile, and can generate reactive oxygen species under the tumor microenvironment (TME) and effectively compact plasmid DNA encoding p53 protein to form polyplexes with a hydrodynamic size of 143.9 nm and a surface potential of 33.6 mV. We show that cancer cells treated with the created Fe-Au DENP-HQC/p53 polyplexes can be more significantly inhibited through vector-mediated chemodynamic therapy (CDT) effect via Fe(III)-induced Fenton reaction and the p53 gene delivery-boosted cell apoptosis and oxidative stress in the TME than single-mode CDT and gene therapy. Further investigations using a xenografted tumor model validated the effectiveness of apoptosis-enhanced ferropotosis therapy through the downregulation of GPX-4 and SLC7A11 proteins, upregulation of p53 and PTEN proteins, as well as histological examinations. Meanwhile, the dendrimer nanoplatform enabled tumor fluorescence imaging through gene delivery-mediated enhanced green fluorescent protein expression. The Fe(III)-complexed dendrimer vector system may be developed as a promising theranostic nanoplatform for ferroptosis or ferroptosis-based combination therapy of other cancer types.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Dyba T, Randi G, Bettio M, Gavin A, Visser O, Bray F. Eur J Cancer, 2018, 103: 356–387
Ryan DP, Hong TS, Bardeesy N. N Engl J Med, 2014, 371: 1039–1049
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71: 7–33
Hidalgo M. N Engl J Med, 2010, 362: 1605–1617
Zalatnai A, Molnar Z. In Vivo, 2007, 21: 339–347
Fink SL, Cookson BT. Infect Immun, 2005, 73: 1907–1916
Bialik S, Dasari SK, Kimchi A. J Cell Sci, 2018, 131: jcs215152
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS, Morrison III B, Stockwell BR. Cell, 2012, 149: 1060–1072
Tang D, Kroemer G. Curr Biol, 2020, 30: R1292–R1297
Lo M, Ling V, Wang YZ, Gout PW. Br J Cancer, 2008, 99: 464–472
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascón S, Hatzios SK, Kagan VE, Noel K, Jiang X, Linkermann A, Murphy ME, Overholtzer M, Oyagi A, Pagnussat GC, Park J, Ran Q, Rosenfeld CS, Salnikow K, Tang D, Torti FM, Torti SV, Toyokuni S, Woerpel KA, Zhang DD. Cell, 2017, 171: 273–285
Bogdan AR, Miyazawa M, Hashimoto K, Tsuji Y. Trends Biochem Sci, 2016, 41: 274–286
Zhang K, Xu H, Jia X, Chen Y, Ma M, Sun L, Chen H. ACS Nano, 2016, 10: 10816–10828
Aghevlian S, Cai Z, Lu Y, Hedley DW, Winnik MA, Reilly RM. Mol Pharmaceutics, 2019, 16: 768–778
Aghevlian S, Cai Z, Hedley D, Winnik MA, Reilly RM. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem, 2020, 5: 22
Lopez-Lazaro M. Cancer Lett, 2007, 252: 1–8
Levine AJ. Cell, 1997, 88: 323–331
Bieging KT, Mello SS, Attardi LD. Nat Rev Cancer, 2014, 14: 359–370
Jiang L, Kon N, Li T, Wang SJ, Su T, Hibshoosh H, Baer R, Gu W. Nature, 2015, 520: 57–62
Koppula P, Zhuang L, Gan B. Protein Cell, 2021, 12: 599–620
Chen X, Yu C, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D. Cell Death Differ, 2021, 28: 1135–1148
Li D, Lin L, Fan Y, Liu L, Shen M, Wu R, Du L, Shi X. Bioactive Mater, 2021, 6: 729–739
He H, Li Y, Jia XR, Du J, Ying X, Lu WL, Lou JN, Wei Y. Biomaterials, 2011, 32: 478–487
Xiao T, Li D, Shi X, Shen M. Macromol Biosci, 2020, 20: 1900282
Xiong Z, Shen M, Shi X. Sci China Mater, 2018, 61: 1387–1403
Zhu J, Zhao L, Yang J, Chen L, Shi J, Zhao J, Shi X. Langmuir, 2019, 35: 13405–13412
Shan Y, Luo T, Peng C, Sheng R, Cao A, Cao X, Shen M, Guo R, Tomás H, Shi X. Biomaterials, 2012, 33: 3025–3035
Navarro G, Tros de Ilarduya C. Nanomed-Nanotechnol Biol Med, 2009, 5: 287–297
Hou W, Wei P, Kong L, Guo R, Wang S, Shi X. J Mater Chem B, 2016, 4: 2933–2943
Gao Y, Ouyang Z, Yang C, Song C, Jiang C, Song S, Shen M, Shi X. Adv Healthcare Mater, 2021, 10: 2100833
Prachayasittikul V, Prachayasittikul S, Ruchirawat S, Prachayasittikul V. Drug Des, Dev Ther, 2013, 7: 1157–1178
Leanderson P, Tagesson C. Curr Alzheimer Rescinogenesis, 1996, 17: 545–550
Jonas SK, Riley PA. Free Radical Res Commun, 1992, 17: 407–418
Jonas SK, Riley PA. Cell Biochem Funct, 1991, 9: 245–253
Pesek J, Svoboda J, Sattler M, Bartram S, Boland W. Org Biomol Chem, 2015, 13: 178–184
Wang SH, Luo J, Zhang ZH, Dong D, Shen Y, Fang Y, Hu L, Liu M, Dai C, Peng S, Fang Z, Shang P. Am J Cancer Res, 2018, 8: 1933–1946
Kuang F, Liu J, Tang D, Kang R. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 586578
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun X, Kang R, Tang D. Cell Death Differ, 2016, 23: 369–379
Hosein AN, Brekken RA, Maitra A. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 17: 487–505
Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, Goeddel DV, Ferrara N. Science, 1989, 246: 1306–1309
Seo Y, Baba H, Fukuda T, Takashima M, Sugimachi K. Cancer, 2000, 88: 2239–2245
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81761148028, 21773026), the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (19XD1400100, 20520710300, 21490711500, 20DZ2254900) and the Shanghai Education Commission through the Shanghai Leading Talents Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supporting information The supporting information is available online at http://chem.scichina.com and http://link.springer.com/journal/11426. The supporting materials are published as submitted, without typesetting or editing. The responsibility for scientific accuracy and content remains entirely with the authors.
Supporting Information
11426_2021_1191_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Apoptosis-Enhanced Ferroptosis Therapy of Pancreatic Carcinoma through PAMAM Dendrimer-Iron(III) Complex-Based Plasmid Delivery
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, W., Gao, Y., Ouyang, Z. et al. Apoptosis-enhanced ferroptosis therapy of pancreatic carcinoma through PAMAM dendrimer-iron(III) complex-based plasmid delivery. Sci. China Chem. 65, 778–788 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-021-1191-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-021-1191-3