Abstract
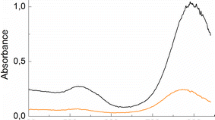
A novel and facile seed-mediated method for the preparation of monodispersed gold nanorods (GNRs) is presented by introducing pyrogallol as a reductant. Fast Fourier transformation of high-resolution transmission electron microscopy reveals that the synthesized GNRs are single crystalline. The longitudinal surface plasmon resonance of GNRs can be finely tuned by varying silver ion concentrations or seed amounts. Also, both thick (diameter >30 nm) and thin (diameter <10 nm) GNRs with exceptional monodispersity can be well prepared by this method. These findings indicate that this method has a greater performance in controlling the morphology of GNRs than that of traditional approach with ascorbic acid as a reductant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee A, Andrade GFS, Ahmed A, Souza ML, Coombs N, Tumarkin E, Liu K, Gordon R, Brolo AG, Kumacheva E. Probing dynamic generation of hot-spots in self-assembled chains of gold nanorods by surface-enhanced raman scattering. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133: 7563–7570
Wang LB, Zhu YY, Xu LG, Chen W, Kuang H, Liu LQ, Agarwal A, Xu CL, Kotov NA. Side-by-side and end-to-end gold nanorod assemblies for environmental toxin sensing. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2010, 49: 5472–5475
Huang XH, El-Sayed IH, Qian W, El-Sayed MA. Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-infrared region by using gold nanorods. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128: 2115–2120
Huang YF, Sefah K, Bamrungsap S, Chang HT, Tan W. Selective photothermal therapy for mixed cancer cells using aptamer-conjugated nanorods. Langmuir, 2008, 24: 11860–11865
Zhou WB, Shao JY, Qiao J, Wei QS, Tang JG, Jian J. Zwitterionic phosphorylcholine as a better ligand for gold nanorods cell uptake and selective photothermal ablation of cancer cells. Chem Commun, 2010, 46: 1479–1481
Choi WI, Kim JY, Kang C, Byeon CC, Kim YH, Tee G. Tumor regression in vivo by photothermal therapy based on gold-nanorod-loaded, functional nanocarriers. ACS Nano, 2011, 5: 1995–2003
Pandey S, Thakur M, Mewada A, Anjarlekar D, Mishra N, Sharon M. Carbon dots functionalized gold nanorod mediated delivery of doxorubicin: tri-functional nano-worms for drug delivery, photothermal therapy and bioimaging. J Mater Chem B, 2013, 1: 4972–4982
Takahashi H, Niidome Y, Yamada S. Controlled release of plasmid DNA from gold nanorods induced by pulsed near-infrared light. Chem Commun, 2005, 17: 2247–2449
Guo R, Zhang LY, Qian HQ, Li RT, Jiang XQ, Liu BR. Multifunctional nanocarriers for cell imaging, drug delivery, and near-IR photothermal therapy. Langmuir, 2010, 26: 5428–5434
Kang HZ, Trondoli AC, Zhu GZ, Chen Y, Chang YJ, Liu HP, Huang YF, Zhang XL, Tan WH. Near-infrared light-responsive core-shell nanogels for targeted drug delivery. ACS Nano, 2011, 5: 5094–5099
Zijlstra P, Chon JWM, Gu M. Five-dimensional optical recording mediated by surface plasmons in gold nanorods. Nature, 2009, 459: 410–413
Martin CR. Membrane-based synthesis of nanomaterials. Chem Mater, 1996, 8: 1739–1746
Yu YY, Chang SS, Lee CL, Wang CRC. Gold nanorods: electrochemical synthesis and optical properties. J Phys Chem B, 1997, 101: 6661–6664
Kim F, Song JH, Yang PD. Photochemical synthesis of gold nanorods. J Am Chem Soc, 2002, 124: 14316–14317
Jana NR, Gearheart L, Murphy CJ. Wet chemical synthesis of high aspect ratio cylindrical gold nanorods. J Phys Chem B, 2001, 105: 4065–4067
Nikoobakht B, El-Sayed MA. Preparation and growth mechanism of gold nanorods (NRs) using seed-mediated growth method. Chem Mater, 2003, 15: 1957–1962
Sau TK, Murphy CJ. Seeded high yield synthesis of short Au nanorods in aqueous solution. Langmuir, 2004, 20: 6414–6420
Jana NR. Gram-scale synthesis of soluble, near-monodisperse gold nanorods and other anisotropic nanoparticles. Small, 2005, 1: 875–882
Wang CG, Wang TT, Ma ZF, Su ZM. pH-tuned synthesis of gold nanostructures from gold nanorods with different aspect ratios. Nanotechnology, 2005, 16: 2555–2560
Park HJ, Ah CS, Kim WJ, Choi IS, Lee KP, Yun WS. Temperature-induced control of aspect ratio of gold nanorods. J Vac Sci Technol A, 2006, 24: 1323–1326
Garg N, Scholl C, Mohanty A, Jin RC. The role of bromide ions in seeding growth of Au nanorods. Langmuir, 2010, 26: 10271–10276
Smith DK, Korgel BA. The importance of the CTAB surfactant on the colloidal seed-mediated synthesis of gold nanorods. Langmuir, 2008, 24: 644–649
Ahmed W, Kooij ES, van Silfhout A, Poelsema B. Quantitative analysis of gold nanorod alignment after electric field-assisted deposition. Nano Lett, 2009, 9: 3786–3794
Ye XC, Jin LH, Caglayan H, Chen J, Xing GZ, Zheng C, Doan-Nguyen V, Kang YJ, Engheta N, Kagan CR, Murray CB. Improved size-tunable synthesis of monodisperse gold nanorods through the use of aromatic additives. ACS Nano, 2012, 6: 2804–2817
Ye XC, Gao YZ, Chen J, Reifsnyder DC, Zheng C, Murray CB. Seeded growth of monodisperse gold nanorods using bromide-free surfactant mixtures. Nano Lett, 2013, 13: 2163–2171
Ye XC, Zheng C, Chen J, Gao YZ, Murray CB. Using binary surfactant mixtures to simultaneously improve the dimensional tunability and monodispersity in the seeded growth of gold nanorods. Nano Lett, 2013, 13: 765–771
Khlebtsov BN, Ithanadeev VA, Ye J, Sukhorukov GB, Khlebtsov NG. Overgrowth of gold nanorods by using a binary surfactant mixture. Langmuir, 2014, 30: 1696–1703
Xu XD, Cortie MB. Shape change and color gamut in gold nanorods, dumbbells, and dog bones. Adv Funct Mater, 2006, 16: 2170–2176
Lohse SE, Murphy CJ. The quest for shape control: a history of gold nanorod synthesis. Chem Mater, 2013, 25: 1250–1261
Jain PK, Lee KS, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA. Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J Phys Chem B, 2006, 110: 7238–7248
Prescott SW, Mulvaney P. Gold nanorod extinction spectra. J Appl Phys, 2006, 99: 123504–123507
Lin Z, Cai JJ, Scriven LE, Davis HT. Spherical-to-wormlike micelle transition in ctab solutions. J Phys Chem, 1994, 98: 5984–5993
Hassan PA, Yakhmi JV. Growth of cationic micelles in the presence of organic additives. Langmuir, 2000, 16: 7187–7191
Scarabelli L, Grzelczak M, Liz-Marzan LM. Tuning gold nanorod synthesis through prereduction with salicylic acid. Chem Mater, 2013, 25: 4232–4238
Johson CJ, Dujardin E, Davis SA, Murphy CJ, Mann S. Growth and form of gold nanorods prepared by seed-mediated, surfactant-directed synthesis. J Mater Chem, 2002, 12: 1765–1770
Sun HM, Yuan QH, Zhang BH, Ai KL, Zhang PG, Lu LH. Gd-III functionalized gold nanorods for multimodal imaging applications. Nanoscale, 2011, 3: 1990–1996
Wang SF, Zhang CF, Sun GA, Chen B, Xiang X, Ding QP, Zu XT. Chelating agents role on phase formation and surface morphology of single orthorhombic YMn2O5 nanorods via modified polyacrylamide gel route. Sci China Chem, 2014, 57: 402–408
Wang C, Bao CC, Liang SJ, Fu HL, Wang K, Deng M, Liao QD, Cui DX. RGD-conjugated silica-coated gold nanorods on the surface of carbon nanotubes for targeted photoacoustic imaging of gastric cancer. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2014, 9: 264
Zhen SJ, Guo FL, Li YF, Huang CZ. A facile one-pot method to fabricate gold nanoparticle chains with dextran. Sci China Chem, 2013, 56: 387–392
Wang W, Liu C, Ling J, Huang CZ. Mercuric ions induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles as investigated by localized surface plasmon resonance light scattering and dynamic light scattering techniques. Sci China Chem, 2013, 56: 806–812
Ye XS, Shi H, He XX, Wang KM, Li D, Qiu PC. Gold nanorod-seeded synthesis of Au@Ag/Au nanospheres with broad and intense near-infrared absorption for photothermal cancer therapy. J Mater Chem B, 2014, 2: 3667–3673
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Xia, K., He, N. et al. Size-tunable synthesis of gold nanorods using pyrogallol as a reducing agent. Sci. China Chem. 58, 1759–1765 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-015-5437-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-015-5437-3