Abstract
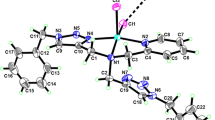
A series of crescent aromatic oligothioamides (4, 6, 8, 15, and 18) bearing different number of sulfur atoms were designed and synthesized via thionation of their corresponding aromatic oligoamides (3, 5, and 7) using Lawesson’s reagent. The X-ray structure of a trimeric analogue (13) revealed the presence of intramolecular three-center hydrogen bonds that are responsible for the rigidification of the molecular backbone. The extraction by these novel receptors toward some representative heavy metal cations (Zn2+, Cd2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Pb2+, and Cu2+) and alkali and alkaline earth metal cations (Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, Cs+, Ca2+, and Sr2+) demonstrated high efficiency (83.5%–96.4%) and superior selectivity for Cu2+ over other selected metal cations. Particularly, the extractability was correlated to both the number of sulfur atoms and orientation of thiocarbonyl groups as revealed in the order: 6 > 4 > 18 > 15. This is in stark contrast to the oligoamides that only gave much lower extractability (5.9%–16.4%), suggestive of the importance of replacement of carbonyl oxygen atoms with sulfur atoms in the extraction of Cu2+. The complexation behavior of 4, 6, and 8 with Cu2+ was also examined by UV-Vis and NMR techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Georgopoulos PG, Roy A, Yonone-Lioy MJ, Opiekun RE, Lioy PJ. Environmental copper: its dynamics and human exposure issues. J Toxicol Environ Health B, 2001, 4: 341–394
Jung HS, Kwon PS, Lee JW, Kim J, Hong CS, Kim JW, Yan S, Lee JY, Lee JH, Joo T, Kim JS. Coumarin-derived Cu2+-selective fluorescence sensor: synthesis, mechanisms and applications in living cells. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131: 2008–2012
Sutariya PG, Pandya A, Lodha A, Menon SK. Fluorescence switch on-off-on receptor constructed of quinoline allied calix[4]arene for selective recognition of Cu2+ from blood serum and F-from industrial waste water. Analyst, 2013, 138: 2531–2535
Xu YF, Lu F, Xu ZC, Cheng TY, Qian XH. Highly sensitive and selective ratiometric fluorescent copper sensors: different binding affinities modulated by three separate side chains of naphthalimide. Sci China Chem, 2009, 52: 771–779
Wang MQ, Li K, Hou JT, Wu MY, Huang Z, Yu XQ. BINOL-based fluorescent sensor for recognition of Cu(II) and sulfide anion in water. J Org Chem, 2012, 77: 8350–8354
Peng Y, Dong YM, Dong M, Wang YW. A selective, sensitive, colorimetric and fluorescence probe for relay recognition of fluoride and Cu(II) ions with “off-on-off” switching in ethanol-water solution. J Org Chem, 2012, 77: 9072–9080
Liu ZP, Zhang CL, Wang XQ, He WJ, Guo ZJ. Design and synthesis of a ratiometric fluorescent chemosensor for Cu(II) with a fluorophore hybridization approach. Org Lett, 2012, 14: 4378–4381
Zeng X, Wu C, Dong L, Mu L, Xue SF, Tao Z. A new tripodal rhodamine B derivative as a highly selective and sensitive fluorescence chemosensor for copper(II). Sci China Chem, 2009, 52: 523–528
Maity D, Govindaraju T. Highly selective visible and near-IR sensing of Cu2+ based on thiourea-salicylaldehyde coordination in aqueous media. Chem Eur J, 2011, 17: 1410–1414
Domaille DW, Que EL, Chang CJ. Synthetic fluorescent sensors for studying the cell biology of metals. Nat Chem Biol, 2008, 4: 168–175
Yu MX, Shi M, Chen ZG, Li FY, Li XX, Gao YH, Xu J, Yang H, Zhou ZG, Yi T, Huang CH. Highly sensitive and fast responsive fluorescence turn-on chemodosimeter for Cu2+ and its application in living cell imaging. Chem Eur J, 2008, 14: 6892–6900
Maity D, Manna AK, Karthigeyan D, Kundu TK, Pati SK, Govindaraju T. Visible-near-infrared and fluorescent copper sensors based on julolidine conjugates: selective detection and fluorescence imaging in living cells. Chem Eur J, 2011, 17: 11152–11161
Hill DJ, Mio MJ, Prince RB, Hughes TS, Moore JS. A field guide to foldamers. Chem Rev, 2001, 101: 3893–4011
Gong B. Crescent oligoamides: from acyclic “macromolecules” to folding nanotubes. Chem Eur J, 2001, 7: 4336–4342
Yang YA, Feng W, Hu JC, Zou SL, Gao RZ, Yamato K, Kline M, Cai ZH, Wang YB, Li YB, Yang YL, Yuan LH, Zeng XC, Gong B. Strong aggregation and directional assembly of aromatic oligoamide macrocycles. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133: 18590–18593
Zhang DW, Zhao X, Hou JL, Li ZT. Aromatic amide foldamers: structures, properties, and functions. Chem Rev, 2012, 112: 5271–5316
Gan Q, Li F, Li GP, Kauffmann B, Xiang JF, Huc I, Jiang H. Heteromeric double helix formation by cross-hybridization of chloro- and fluoro-substituted quinoline oligoamides. Chem Commun, 2010, 46: 297–299
Ong WQ, Zhao HQ, Du ZY, Yeh JZY, Ren CL, Tan LZW, Zhang K, Zeng HQ. Computational prediction and experimental verification of pyridine-based helical oligoamides containing four repeating units per helical turn. Chem Commun, 2011, 47: 6416–6418
Fu HL, Liu Y, Zeng HQ. Shape-persistent H-bonded macrocyclic aromatic pentamers. Chem Commun, 2013, 49: 4127–4144
Saraogi I, Hamilton AD. Recent advances in the development of aryl-based foldamers. Chem Soc Rev, 2009, 38: 1726–1743
Zou SL, He LT, Zhang J, He YZ, Yuan LH, Wu LX, Luo J, Wang YH, Feng W. Tunable mesogens based on shape-persistent aromatic oligoamides: from lamellar, columnar, to nematic liquid crystalline phase. Org Lett, 2012, 14: 3584–3587
Yang XS, Chen L. Yang YA, He YZ, Zou SL, Feng W, Yang YY, Liu N, Liao JL, Yuan LH. Synthesis of crescent aromatic oligoamides with preorganized chelating groups and their extraction towards transition metal ions. J Hazard Mater, 2012, 217-218: 171–176
Zhong LJ, Chen L, Feng W, Zou SL, Yang YY, Liu N, Yuan LH. Shape-persistent macrocycles: efficient extraction towards lanthanide and actinide elements. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem, 2012, 72: 367–373
Qin B, Ren CL, Ye RJ, Sun C, Chiad K, Chen XY, Li Z, Xue F, Su HB, Chass GA, Zeng HQ. Persistently folded circular aromatic amide pentamers containing modularly tunable cation-binding activities with high ion selectivity. J Am Chem Soc, 2010, 132: 9564–9566
Ren CL, Maurizot V, Zhao HQ, Shen J, Zhou F, Ong WQ, Du ZY, Zhang K, Su HB, Zeng HQ. Five-folded-symmetric macrocyclic aromatic pentamers: high-affinity cation recognition, ion-pair-induced columnar stacking and nanofibrillation. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133: 13930–13933
Gao RZ, Hu JC, Zhang K, He YZ, Liu P, Luo SZ, Yang YQ, Yang L, Feng W, Yuan LH. Highly selective fluorescent recognition towards Th4+ based on coumarin-derivatized crescent aromatic oligoamide. Chin J Chem, 2013, 31: 689–694
Jiang Q, He LT, Luo SZ, Yang YQ, Yang L, Feng W, Yuan LH. Synthesis of a crescent aromatic oligothioamide and its high selectivity in recognizing copper(II) ions. Chinese Chem Lett, 2013, 24: 881–884
Stylianides N, Danopoulos AA, Pugh D, Hancock F, Zanotti-Gerosa A. Cyclometalated and alkoxyphenyl-substituted palladium imidazolin-2-ylidene complexes. Synthetic, structural, and catalytic studies. Organometallics, 2007, 26: 5627–5635
Feng W, Yamato K, Yang LQ, Ferguson JS, Zhong LJ, Zou SL, Yuan LH, Zeng XC, Gong B. Efficient kinetic macrocyclization. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131: 2629–2637
Lewis FW, Harwood LM, Hudson MJ, Drew MGB, Sypula M, Modolo G, Whittaker D, Sharrad CA, Videva V, Hubscher-Bruder V, Arnaud-Neu F. Complexation of lanthanides, actinides and transition metal cations with a 6-(1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine ligand: implications for actinide(III)/lanthanide(III) partitioning. Dalton Trans, 2012, 41: 9209–9219
Pederson CJ. New macrocyclic polyethers. J Am Chem Soc, 1970, 92: 391–394
No K, Lee JH, Yang SH, Yu SH, Cho MH, Kim MJ, Kim JS. Syntheses and conformations of tetrahomodioxacalix[4]arene tetraamides and tetrathioamides. J Org Chem, 2002, 67: 3165–3168
Lee HJ, Choi YS, Lee KB, Park J, Yoon CJ. Hydrogen bonding abilities of thioamide. J Phys Chem A, 2002, 106: 7010–7017
Berstein J, Davis RE, Shimoni L, Chang NL. Patterns in hydrogen bonding: functionality and graph set analysis in crystals. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng, 1995, 34: 1555–1573
Zhu J, Parra RD, Zeng HQ, Skrzypczak-Jankun E, Zeng XC, Gong B. A new class of folding oligomers: crescent oligoamides. J Am Chem Soc, 2000, 122: 4219–4220
Tabakci B, Alici O, Karatas I. 4-tert-Butylcalix[4]arene having nitrile pendant groups as Hg2+ selective receptors. Talanta, 2013, 106: 92–96
Sheng RL, Wang PF, Gao YH, Wu Y, Liu WM, Ma JJ, Li HP, Wu SK. Colorimetric test kit for Cu2+ detection. Org Lett, 2008, 10: 5015–5018
Barba-Bon A, Costero AM, Gil S, Parra M, Soto J, Martínez-Máñez R, Sancenón F. A new selective fluorogenic probe for trivalent cations. Chem Commun, 2012, 48: 3000–3002
Zhu M, Yuan MJ, Liu XF, Xu JL, Lv J, Huang CS, Liu HB, Li YL, Wang S, Zhu DB. Visible near-infrared chemosensor for mercury ion. Org Lett, 2008, 10: 1481–1484
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, L., Jiang, Q., Gao, R. et al. Crescent aromatic oligothioamides as highly selective receptors for copper(II) ion. Sci. China Chem. 57, 1246–1256 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-014-5110-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-014-5110-2