Abstract
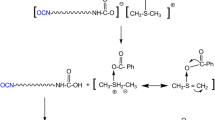
Polyurethanes (PUs) are well-known for their biocompatibility but their intrinsic inert property hampers cell-matrix interactions. Surface modifications are thus necessary to widen their use for biomedical applications. In this work, surface modifications of PU were achieved first by incorporating polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS), followed by alteration of the surface topography via the breath figures method. Subsequently, surface chemistry was also modified by immobilization of gelatin molecules through grafting, for the enhancement of the surface cytocompatibility. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to verify the formation of highly ordered microstructures while static contact angle, FTIR and XPS confirmed the successful grafting of gelatin molecules onto the surfaces. In vitro culture of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) revealed that endothelial cell adhesion and proliferation were significantly enhanced on the gelatin-modified surfaces, as shown by live/dead staining and WST-1 proliferation assay. The results indicated that the combination of the strategies yielded an interface that improves cell attachment and subsequent growth. This enhancement is important for the development of higher quality biomedical implants such as vascular grafts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roger VL. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2012 update: A report from the American heart association. Circulation, 2012, 125: e2–e220
Nieponice A, Soletti L, Guan J, Deasy BM, Huard J, Wagner WR, Vorp DA. Development of a tissue-engineered vascular graft combining a biodegradable scaffold, muscle-derived stem cells and a rotational vacuum seeding technique. Biomaterials, 2008, 29: 825–833
Saitow C, Kaplan DL, Castellot Jr JJ. Heparin stimulates elastogenesis: application to silk-based vascular grafts. Matrix biol, 2011, 30: 346–355
Wang DA, Ji J, Sun YH, Yu GH, Feng LX. Blends of stearyl poly(ethylene oxide) coupling-polymer in chitosan as coating materials for polyurethane intravascular catheters. J Biomed Mater Res, 2001, 58: 372–383
Wang DA, Ji J, Gao CY, Yu GH, Feng LX. Surface coating of stearyl poly(ethylene oxide) coupling-polymer on polyurethane guiding catheters with poly(ether urethane) film-building additive for biomedical applications. Biomaterials, 2001, 22: 1549–1562
Harris JR, Seikaly H. Evaluation of polytetrafluoroethylene micrografts in microvascular surgery. J Otolaryngol, 2002, 31: 89–92
Kannan RY, Salacinski HJ, Butler PE, Hamilton G, Seifalian AM. Current status of prosthetic bypass grafts: a review. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater, 2005, 74: 570–581
Santerre JP, Woodhouse K, Laroche G, Labow RS. Understanding the biodegradation of polyurethanes: from classical implants to tissue engineering materials. Biomaterials, 2005, 26: 7457–7470
Wang DA, Ji J, Feng LX. Surface analysis of poly(ether urethane) blending stearyl polycethylene oxide coupling polymer. Macromolecules, 2000, 33: 8472–8478
Wang DA, Ji J, Feng LX. Various-sized stearyl poly(ethylene oxide) coupling-polymer blending poly(ether urethane) material for surface study and biomedical applications. Macromol Chem Phys, 2000, 201: 1574–1584
Fields C, Cassano A, Allen C, Meyer A, Pawlowski KJ, Bowlin GL, Rittgers SE, Szycher M. Endothelial cell seeding of a 4-mm I.D. Polyurethane vascular graft. J Biomater Appl, 2002, 17: 45–70
Lin HB, Sun W, Mosher DF, García-Echeverría C, Schaufelberger K, Lelkes PI, Cooper SL. Synthesis, surface, and cell-adhesion properties of polyurethanes containing covalently grafted RGD-peptides. J Biomed Mater Res, 1994, 28: 329–342
Kannan RY, Salacinski HJ, Butler PE, Seifalian AM. Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanocomposites: the next generation material for biomedical applications. Acc Chem Res, 2005, 38: 879–884
Ghanbari H, de Mel A, Seifalian AM. Cardiovascular application of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanomaterials: a glimpse into prospective horizons. Int J Nanomedicine, 2011, 6: 775–786
Wang DA, Feng LX, Ji J, Sun YH, Zheng XX, Elisseeff JH. Novel human endothelial cell-engineered polyurethane biomaterials for cardiovascular biomedical applications. J Biomed Mater Res A, 2003, 65A: 498–510
Wang DA. Engineering blood-contact biomaterials by “H-bond grafting” surface modification. Adv Polym Sci, 2007, 179–227
Widawski G, Rawiso M, François B. Self-organized honeycomb morphology of star-polymer polystyrene films. Nature, 1994, 369: 387–389
François B, Pitois O, François J. Polymer films with a self-organized honeycomb morphology. Adv Mater, 1995, 7: 1041–1044
Schuler M, Owen GR, Hamilton DW, de Wild M, Textor M, Brunette DM, Tosatti SG. Biomimetic modification of titanium dental implant model surfaces using the RGDSP-peptide sequence: a cell morphology study. Biomaterials, 2006, 27: 4003–4015
Wang DA, Ji J, Sun YH, Shen JC, Feng LX, Elisseeff JH. In situ immobilization of proteins and RGD peptide on polyurethane surfaces via poly(ethylene oxide) coupling polymers for human endothelial cell growth. Biomacromolecules, 2002, 3: 1286–1295
Martins MC, Wang D, Ji J, Feng L, Barbosa MA. Albumin and fibrinogen adsorption on Cibacron blue F3G-A immobilised onto PU-PHEMA (polyurethane-poly (hydroxyethylmethacrylate)) surfaces. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed, 2003, 14: 439–455
Martins MC, Wang D, Ji J, Feng L, Barbosa MA. Albumin and fibrinogen adsorption on PU-PHEMA surfaces. Biomaterials, 2003, 24: 2067–2076
Wang DA, Chen BL, Ji J, Feng LX. Selective adsorption of serum albumin on biomedical polyurethanes modified by a poly(ethylene oxide) coupling-polymer with Cibacron Blue (F3G-A) endgroups. Bioconjug Chem, 2002, 13: 792–803
Wang DA, Ji J, Feng LX. Selective binding of albumin on stearyl poly(ethylene oxide) coupling polymer-modified poly(ether urethane) surfaces. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed, 2001, 12: 1123–1146
Lai Y, Xie C, Zhang Z, Lu W, Ding J. Design and synthesis of a potent peptide containing both specific and non-specific cell-adhesion motifs. Biomaterials, 2010, 31: 4809–4817
Zhu Y, Gao C, He T, Shen J. Endothelium regeneration on luminal surface of polyurethane vascular scaffold modified with diamine and covalently grafted with gelatin. Biomaterials, 2004, 25: 423–430
Liu W, Liu R, Li Y, Wang W, Ma L, Wu M, Huang Y. Self-organized ordered microporous thin films from grafting copolymers. Polymers, 2009, 50: 2716–2726
Xiong XP, Lin MF, Zou WW. Honeycomb structured porous films prepared by the method of breath figure: history and development. Curr Org Chem, 2011, 15: 3706–3718
Roohpour N, Wasikiewicz JM, Moshaverinia A, Paul D, Grahn MF, Rehman IU, Vadgama P. Polyurethane membranes modified with isopropyl myristate as a potential candidate for encapsulating electronic implants: a study of biocompatibility and water permeability. Polymers, 2010, 2: 102–119
Yabu H, Shimomura M. Single-step fabrication of transparent superhydrophobic porous polymer films. Chem Mater, 2005, 17: 5231–5234
Dong R, Ma H, Yan J, Fang Y, Hao J. Tunable morphology of 2D honeycomb-patterned films and the hydrophobicity of a ferrocenyl-based oligomer. Chem Eur J, 2011, 17: 7674–7684
Li L, Zhong YW, Chen CK, Li J. A novel path to patterning based on the static breath figure technique. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2010, 26: 1135–1142
Qin S, Li H, Yuan WZ, Zhang Y. Fabrication of polymeric honeycomb microporous films: breath figures strategy and stabilization of water droplets by fluorinated diblock copolymer micelles. J Mater Sci, 2012, 47: 6862–6871
Zhu Y, Sheng R, Luo T, Li H, Sun J, Chen S, Sun W, Cao A. Honeycomb-structured films by multifunctional amphiphilic biodegradable copolymers: surface morphology control and biomedical application as scaffolds for cell growth. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2011, 3: 2487–2495
François B, Pitois O, François J. Polymer films with a self-organized honeycomb morphology. Adv Mater, 1995, 7: 1041–1044
Sharma V, Song LL, Jones RL, Barrow MS, Williams R, Srinivasarao M. Effect of solvent choice on breath-figure-templated assembly of “holey” polymer films. EPL, 2010, 91: 38001
Ferrari E, Fabbri P, Pilati F. Solvent and substrate contributions to the formation of breath figure patterns in polystyrene films. Langmuir, 2011, 27: 1874–1881
Park MS, Joo W, Kim JK. Porous structures of polymer films prepared by spin coating with mixed solvents under humid condition. Langmuir, 2006, 22: 4594–4598
Peng J, Han YC, Yang YM, Li BY. The influencing factors on the macroporous formation in polymer films by water droplet templating. Polymer, 2004, 45: 447–452
Beysens D, Steyer A, Guenoun P, Fritter D, Knobler CM. How does dew form? Phase Transitions, 1991, 31: 219–246
Xu Y, Zhu B. A study on formation of regular honeycomb pattern in polysulfone film. Polymer, 2005, 46: 713–717
Lin DT, Young TH, Fang Y. Studies on the effect of surface properties on the biocompatibility of polyurethane membranes. Biomaterials, 2001, 22: 1521–1529
Freij-Larsson C, Jannasch P, Wesslen B. Polyurethane surfaces modified by amphiphilic polymers: Effects on protein adsorption. Biomaterials, 2000, 21: 307–315
De Wael K, Verstraete A, Van Vlierberghe S, Dejonghe W, Dubruel P, Adriaens A. The electrochemistry of a gelatin modified gold electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci, 2011, 6: 1810–1819
Ren ZY, Wu HP, Ma JM, Ma DZ. FTIR studies on the model polyurethane hard segments based on a new waterborne chain extender dimethylol butanoic acid (DMBA). Chin J Polym Sci, 2004, 22: 225–230
Lim HR, Baek HS, Lee MH, Woo YI, Han DW, Han MH, Baik HK, Choi WS, Park KD, Chung KH, Park JC. Surface modification for enhancing behaviors of vascular endothelial cells onto polyurethane films by microwave-induced argon plasma. Surf Coat Technol, 2008, 202: 5768–5772
Guan J, Gao C, Feng L, Sheng J. Surface photo-grafting of polyurethane with 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate for promotion of human endothelial cell adhesion and growth. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed, 2000, 11: 523–536
Guan J, Gao C, Feng L, Shen J. Preparation of functional poly(ether-urethane) for immobilization of human living cells. 1. Surface graft polymerization of poly(ether-urethane) with 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate and quaternization of grafted membrane. Eur Polym J, 2000, 36: 2707–2713
Guan J, Gao C, Feng L, Shen J. Surface modification of polyurethane for promotion of cell adhesion and growth 1: Surface photo-grafting with N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate and cytocompatibility of the modified surface. J Mater Sci Mater Med, 2001, 12: 447–452
Uttayarat P, Toworfe GK, Dietrich F, Lelkes PI, Composto RJ. Topographic guidance of endothelial cells on silicone surfaces with micro-to nanogrooves: orientation of actin filaments and focal adhesions. J Biomed Mater Res Part A, 2005, 75: 668–680
Narayan D, Venkatraman SS. Effect of pore size and interpore distance on endothelial cell growth on polymers. J Biomed Mater Res Part A, 2008, 87: 710–718
Lien SM, Ko LY, Huang TJ. Effect of pore size on ECM secretion and cell growth in gelatin scaffold for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater, 2009, 5: 670–679
Amirkhani M, Berger N, Abdelmohsen M, Zocholl F, Gonçalves MR, Marti O. The effect of different stabilizers on the formation of self-assembled porous film via the breath-figure technique. J Polym Sci Part B: Polym Phys, 2011, 49: 1430–1436
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, L., Peck, Y., Wang, X. et al. Surface patterning and modification of polyurethane biomaterials using silsesquioxane-gelatin additives for improved endothelial affinity. Sci. China Chem. 57, 596–604 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-013-4997-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-013-4997-3